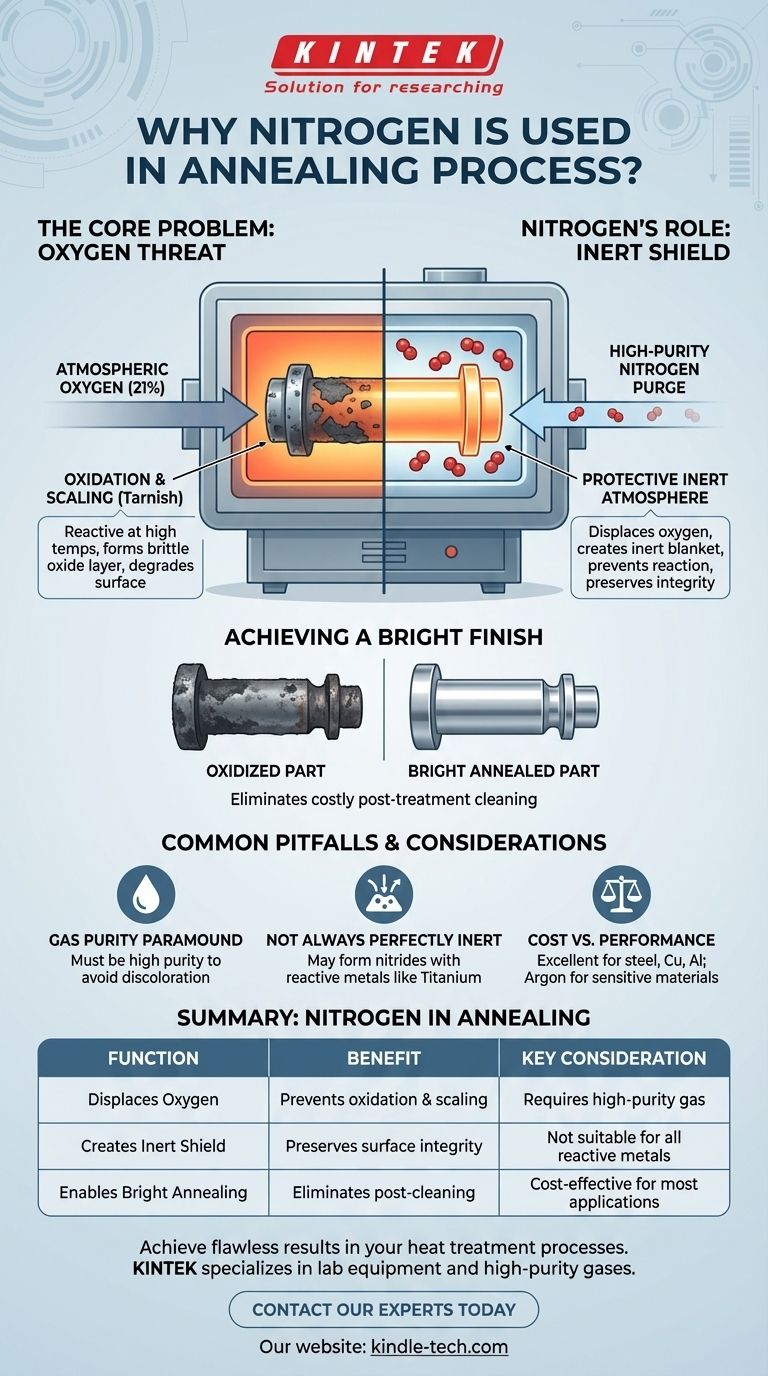
The primary reason nitrogen is used in annealing is to create a controlled, protective atmosphere inside the furnace. This inert environment displaces atmospheric oxygen, which would otherwise react with the hot metal and cause undesirable oxidation, scaling, and discoloration on the component's surface.
At its core, the challenge of annealing isn't just about heat; it's about controlling the chemical environment at that heat. Nitrogen acts as a stable, cost-effective shield, preventing the damaging effects of oxygen and ensuring the metal's surface integrity is preserved throughout the process.

The Core Problem: Why Annealing Needs a Protective Atmosphere
Annealing involves heating a metal to a specific temperature and holding it there to alter its internal microstructure, typically to increase ductility and reduce hardness. This high-temperature environment, however, creates a significant chemical vulnerability.
The Threat of Oxygen
When metals are heated, their atoms become more energetic and reactive. If exposed to the ambient air (which is ~21% oxygen), the metal's surface will rapidly react with oxygen molecules.
The Consequences of Oxidation
This reaction, known as oxidation, forms a brittle layer of metallic oxide on the surface, commonly called scale or tarnish. This oxide layer is almost always undesirable as it degrades the component's surface finish, alters its precise dimensions, and can negatively impact its mechanical properties.
Nitrogen's Role as the Ideal Solution
Introducing nitrogen into the furnace is a direct and effective strategy to counteract the threat of oxidation. It serves as a protective or "shielding" gas that fundamentally changes the furnace's internal environment.
Displacing Reactive Gases
The first step is to purge the furnace chamber with nitrogen gas. This process physically pushes out the oxygen-rich ambient air, replacing it with a stable, nitrogen-rich atmosphere.
Creating an Inert Shield
Nitrogen is a relatively inert gas, meaning it does not readily react with other elements, even at the high temperatures used in annealing. It effectively blankets the metal components, creating a barrier that prevents oxygen molecules from reaching and reacting with the hot metal surfaces.
Achieving a "Bright Finish"
By preventing oxidation, a nitrogen atmosphere ensures that parts exit the furnace with a clean, scale-free, and bright surface. This process, known as bright annealing, is critical for components where a pristine surface finish is required, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming post-treatment cleaning operations.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While highly effective, using nitrogen is not without its nuances. Success depends on understanding its limitations and ensuring the process is correctly controlled.
Gas Purity is Paramount
The effectiveness of the nitrogen shield is directly tied to its purity. Even small amounts of oxygen or moisture contamination within the nitrogen supply can be enough to cause surface discoloration or light oxidation on sensitive materials.
Not Always Perfectly Inert
For certain highly reactive metals like titanium, or at extremely high temperatures with some stainless steels, nitrogen can cease to be inert. It may react with the metal to form nitrides on the surface, which can be undesirable unless intentionally part of a case-hardening process (nitriding).
Cost vs. Performance
Nitrogen offers an exceptional balance of cost and performance, making it the go-to choice for most applications involving steel, copper, aluminum, and brass. However, for the most sensitive or reactive materials, more expensive inert gases like argon may be required for absolute protection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct protective atmosphere is crucial for achieving the desired outcome in any heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective oxidation prevention for common steels and non-ferrous metals: Nitrogen is the industry-standard solution, providing excellent results for bright annealing, tempering, and sintering.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or certain stainless steels: You must consider a truly inert gas like argon to avoid the potential for unwanted nitride formation.
- If your primary focus is achieving the brightest possible finish on sensitive alloys: A specialized mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen (known as a forming gas) may be necessary to actively reduce any trace oxides present on the surface.
Ultimately, using nitrogen is a foundational strategy in metallurgy for controlling the furnace environment to produce clean, reliable, and high-quality components.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Displaces Oxygen | Prevents oxidation & scaling | Requires high-purity gas |
| Creates Inert Shield | Preserves surface integrity | Not suitable for all reactive metals |
| Enables Bright Annealing | Eliminates post-cleaning | Cost-effective for most applications |
Achieve flawless results in your heat treatment processes. The right protective atmosphere is critical for preventing oxidation and ensuring part quality. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables, including furnace systems and high-purity gases, to create the perfect annealing environment for your specific metals and alloys.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's annealing and heat treatment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab



















