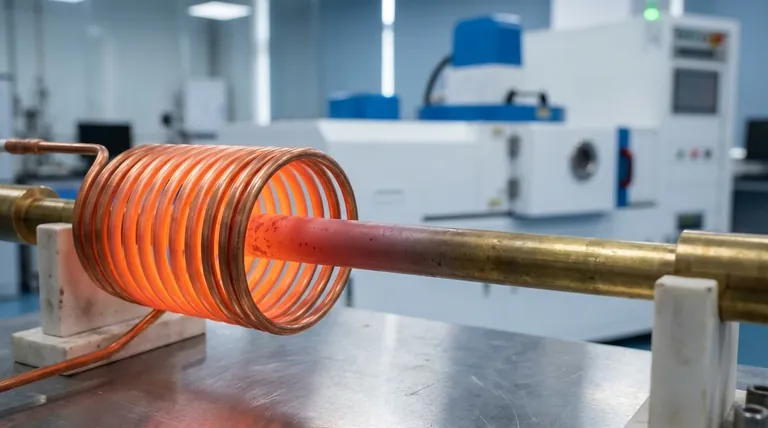
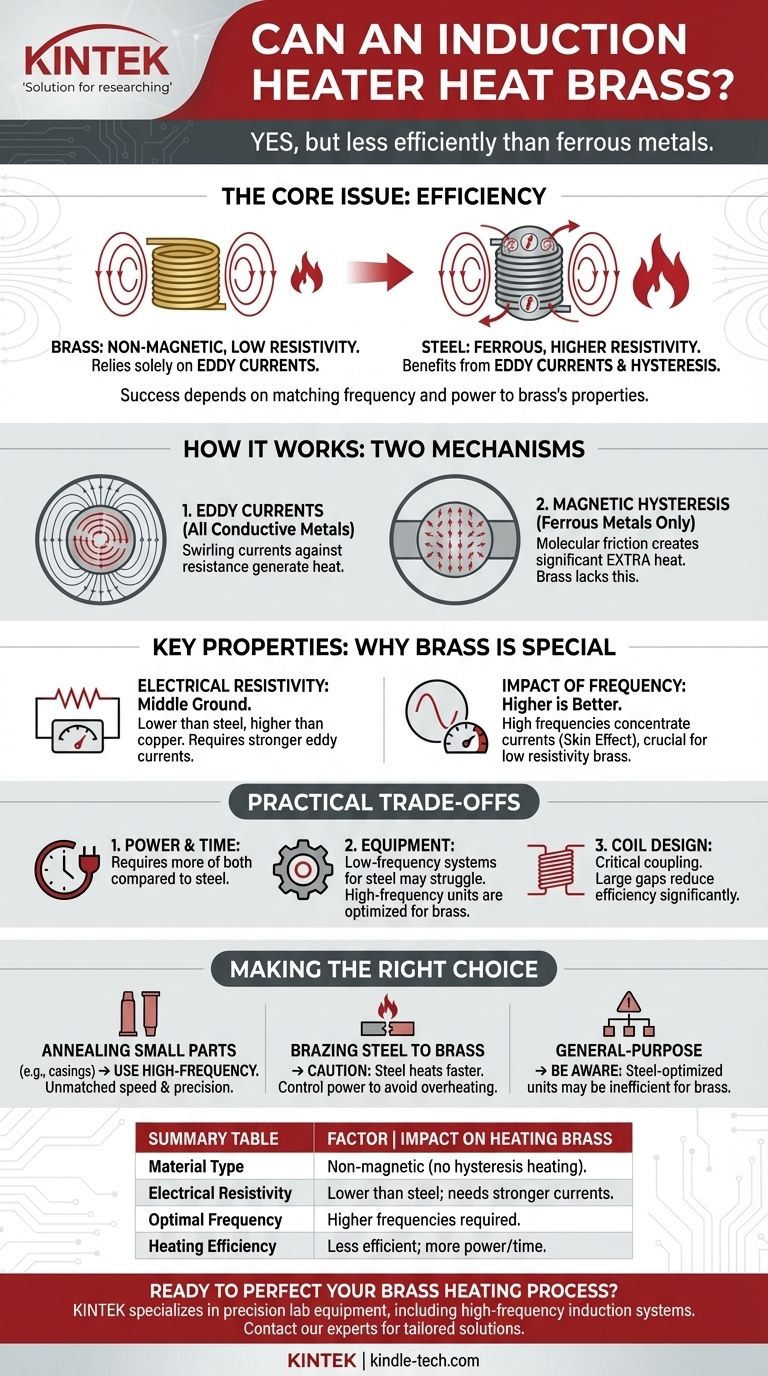
Yes, an induction heater will heat brass, but it does so less efficiently than it heats ferrous metals like steel. Because brass is non-magnetic and has relatively low electrical resistivity, successful heating depends heavily on the frequency and power of the induction system.
The core issue isn't if you can heat brass with induction, but how effectively you can do it. Success requires matching the induction heater's frequency and power to brass's specific material properties, which differ significantly from those of steel.

How Induction Heating Actually Works
To understand why brass behaves differently, we first need to grasp the two fundamental principles of induction heating: eddy currents and hysteresis.
The Role of Eddy Currents
An induction heater creates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When a conductive material like brass is placed inside this field, it induces electrical currents within the metal.
These swirling currents, known as eddy currents, flow against the material's natural electrical resistance. This friction generates precise and instantaneous heat directly within the part. This is the primary way all conductive metals, including brass, are heated by induction.
Why Steel Heats Differently
Ferrous metals like steel have an additional, highly effective heating mechanism: magnetic hysteresis. The magnetic domains within the steel rapidly flip back and forth, trying to align with the alternating magnetic field.
This internal molecular friction generates a significant amount of extra heat. This effect, combined with steel's higher electrical resistivity, is why it heats so quickly and efficiently. Brass, being non-magnetic, does not benefit from hysteresis heating at all.
Key Properties: Why Brass is a Special Case
The efficiency of induction heating for any given material is governed by its physical properties. For brass, two factors are paramount.
Electrical Resistivity
Resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. Paradoxically, a higher resistivity is often better for induction heating.
Brass has a much lower resistivity than steel but a higher resistivity than copper. This places it in a middle ground where it can be heated effectively, but it requires stronger eddy currents to generate the same amount of heat as steel.
The Impact of Frequency
The frequency of the alternating magnetic field is a critical variable. Higher frequencies cause the eddy currents to concentrate near the surface of the material, a phenomenon known as the skin effect.
Because brass is a very good conductor (low resistivity), a higher frequency is often required to generate heat efficiently. A low-frequency system designed for large steel parts may struggle to induce enough current in a piece of brass to heat it effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While induction is a viable method for heating brass, you must be aware of the practical implications and potential challenges.
Power and Time Requirements
Heating brass to a target temperature will almost always require more power or more time compared to heating an identically sized piece of steel. The system has to work harder to generate the strong eddy currents needed to overcome brass's lower resistivity.
Equipment Considerations
A general-purpose, low-frequency induction heater optimized for steel may perform poorly with brass and other non-ferrous metals. Systems designed for applications like brazing or annealing brass are typically higher-frequency units to ensure efficient energy transfer.
Coil Design is Critical
The induction coil (the copper tube surrounding the part) must be coupled closely to the brass workpiece. A larger gap between the coil and the part will result in a weaker magnetic field and significantly less efficient heating, a problem that is more pronounced with brass than with steel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the suitability of induction heating depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is annealing small brass parts (e.g., ammunition casings): A properly tuned, high-frequency induction heater is an ideal tool, offering unmatched speed and precision.
- If your primary focus is brazing or soldering steel to brass: Be aware that the steel will heat much faster. Careful coil design and power control are critical to avoid overheating the steel while the brass comes to temperature.
- If you are choosing a general-purpose shop heater: A unit optimized for steel may be inefficient for brass. To handle both effectively, you will likely need a machine with higher power or a broader frequency range.
By understanding these principles, you can select the right equipment and process to apply the clean, rapid heat of induction to your brass workpiece successfully.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Heating Brass |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Non-magnetic (no hysteresis heating); relies solely on eddy currents. |
| Electrical Resistivity | Lower than steel; requires stronger eddy currents for efficient heating. |
| Optimal Frequency | Higher frequencies are typically required for efficient energy transfer. |
| Heating Efficiency | Less efficient than steel; may require more power or time. |
Ready to perfect your brass heating process?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for non-ferrous metals like brass. Whether you're annealing, brazing, or conducting research, our experts can help you select the right high-frequency system for efficient and controlled results.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your application and discover the KINTEK solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the power consumption for melting light aluminum scrap? Optimize Your Energy Efficiency and Costs
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What are induction coils used for? Precision Heating for Metal Hardening, Brazing & Forging
- What is the role of a Vacuum Induction Furnace in RAFM steel? Ensure High Purity for Reactive Elements Y & Ti
- What frequency is required for induction heating? Match Frequency to Your Heating Depth
- What is the power rating capacity for a medium frequency furnace? Find the Perfect kW for Your Melting Needs
- What metals can be melted with induction? From Steel to Gold, Discover the Versatility
- How does magnetic field heat metal? Achieve Precise Thermal Control with Induction Heating



















