Yes, producing high-quality carbon nanotubes at industrial scale is a significant technical challenge. While it is possible to synthesize them in a lab, the difficulty lies in controlling their structure, ensuring purity, and scaling production in a cost-effective manner. These factors create a major bottleneck between their remarkable properties and widespread commercial adoption.
The core challenge is not simply making carbon nanotubes, but consistently and affordably making the right type of nanotubes—with the specific diameter, length, and electronic properties required for a given application.
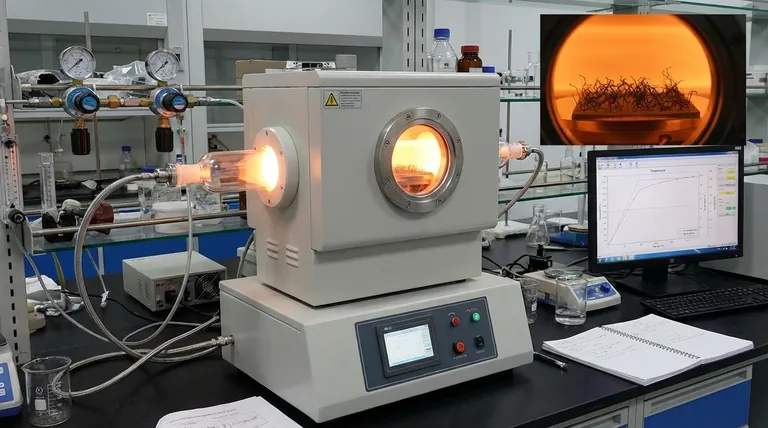

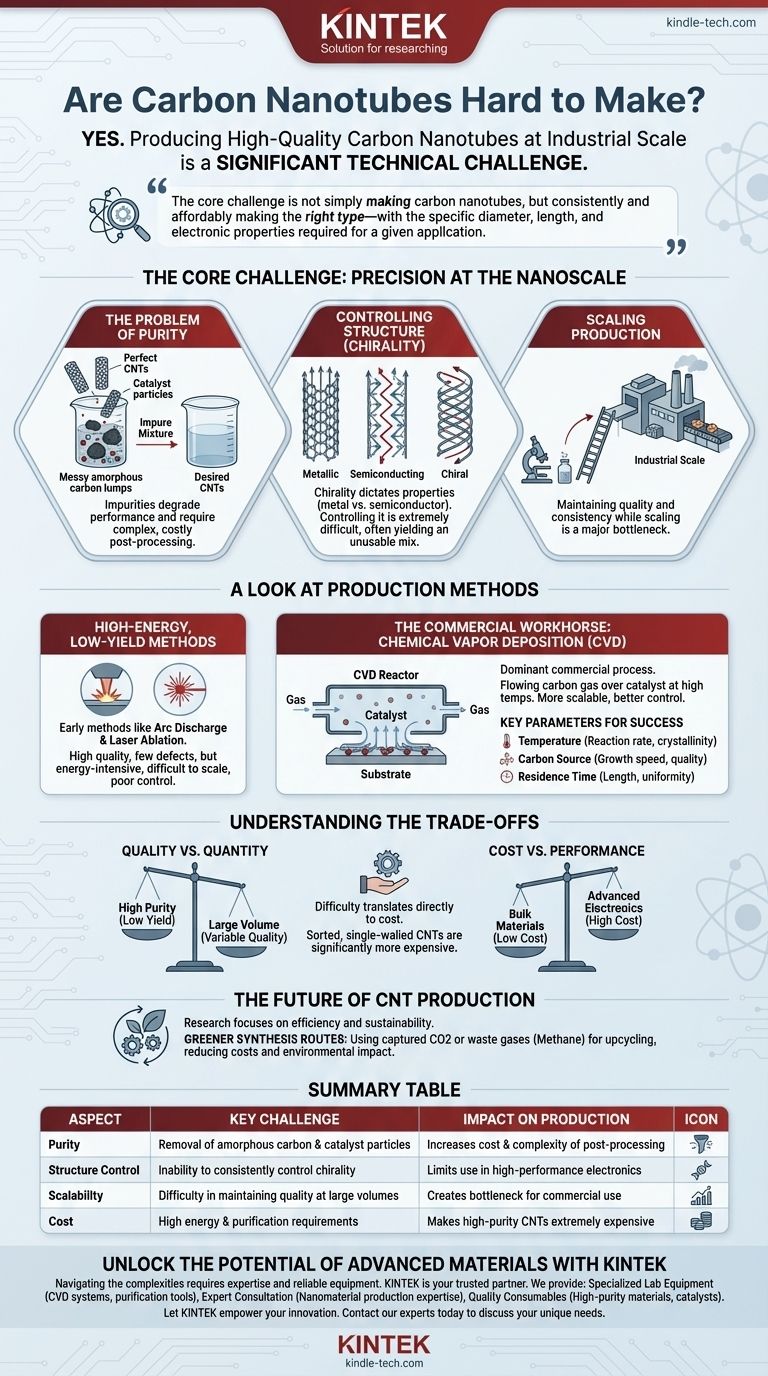
The Core Challenge: Precision at the Nanoscale
Synthesizing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is fundamentally a process of controlled, atomic-level self-assembly. Unlike macro-scale manufacturing, you cannot simply machine a part. You must create the perfect conditions for carbon atoms to arrange themselves into a flawless cylindrical structure.
The Problem of Purity
Most synthesis methods produce a mixture of materials. This includes the desired CNTs, but also unwanted byproducts like amorphous carbon and leftover catalyst particles.
These impurities degrade performance and must be removed through complex post-processing steps, which adds significant cost and complexity.
Controlling Structure (Chirality)
The properties of a CNT are dictated by its chirality—the angle at which the graphene sheet is "rolled up" to form the tube. This determines if the CNT behaves as a metal or a semiconductor.
Controlling chirality during synthesis is one of the most difficult challenges in the field. Most processes yield a mix of different types, which is unusable for high-performance electronics that require purely semiconducting CNTs.
A Look at Production Methods
Different methods have been developed, each with a distinct profile of quality, yield, and scalability.
High-Energy, Low-Yield Methods
Early methods like arc discharge and laser ablation use intense energy to vaporize a carbon source (like graphite). These techniques can produce high-quality CNTs with few structural defects.
However, they are energy-intensive, difficult to scale, and offer poor control over the final product mix, making them unsuitable for bulk commercial production.
The Commercial Workhorse: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the dominant commercial process today. It involves flowing a carbon-containing gas over a substrate coated with catalyst nanoparticles at high temperatures.
The catalyst particles crack the gas molecules, and carbon atoms assemble into tubes on their surface. CVD is more scalable and offers better control than older methods.
Key Parameters for Success
Success with CVD depends on meticulously controlling the operating parameters.
- Temperature: Influences the reaction rate and the crystallinity of the CNTs.
- Carbon Source: The type and concentration of the gas affect the growth speed and quality.
- Residence Time: The duration the gas spends in the reactor impacts the length and uniformity of the nanotubes.
Even minor deviations in these conditions can dramatically alter the productivity of the process and the quality of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a production method involves a critical balancing act between quality, quantity, and cost.
Quality vs. Quantity
High-energy methods like arc discharge excel at producing high-purity CNTs but in very small amounts.
Conversely, CVD can produce tons of CNTs, but achieving consistent high quality and purity across those large volumes remains the primary engineering hurdle.
Cost vs. Performance
The difficulty of production directly translates to cost. Bulk, multi-walled CNTs used for strengthening composites can be relatively inexpensive.
In contrast, sorted, single-walled CNTs for advanced electronics can be thousands of times more expensive due to the complex synthesis and purification required.
The Future of CNT Production
Research is heavily focused on making CNT synthesis more efficient, controllable, and sustainable.
Greener Synthesis Routes
Emerging methods aim to use more sustainable feedstocks. This includes innovative processes that convert captured carbon dioxide (CO2) or waste gases like methane into valuable CNTs.
These "upcycling" approaches could simultaneously reduce production costs and provide a positive environmental impact, potentially revolutionizing the industry if they can be scaled effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "difficulty" of making CNTs is relative to your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or research: Be prepared to source expensive, high-purity CNTs from specialized suppliers, as achieving this quality is the most difficult challenge.
- If your primary focus is bulk material enhancement (e.g., composites, coatings): Commercially available CNTs made via CVD are a viable and cost-effective option, but you must account for variability in your design.
- If your primary focus is future-proofing and sustainability: Closely monitor emerging methods using waste feedstocks, as these could dramatically change the cost-benefit analysis for future projects.
Understanding these production realities is the first step to successfully leveraging the remarkable properties of carbon nanotubes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Challenge | Impact on Production |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Removal of amorphous carbon & catalyst particles | Increases cost & complexity of post-processing |
| Structure Control | Inability to consistently control chirality | Limits use in high-performance electronics |
| Scalability | Difficulty in maintaining quality at large volumes | Creates a bottleneck for widespread commercial use |
| Cost | High energy & purification requirements | Makes high-purity CNTs extremely expensive |
Unlock the Potential of Advanced Materials with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of carbon nanotube production requires expertise and reliable equipment. Whether you are scaling up your research or integrating CNTs into commercial applications, KINTEK is your trusted partner.
We provide:
- Specialized Lab Equipment: From precise CVD systems to purification tools, we supply the technology needed for advanced material synthesis.
- Expert Consultation: Our team understands the nuances of nanomaterial production and can help you select the right solutions for your specific quality and scalability goals.
- Quality Consumables: Ensure consistent results with our high-purity materials and catalysts.
Let KINTEK empower your innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique needs in advanced material science and help you overcome the challenges of next-generation manufacturing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision



















