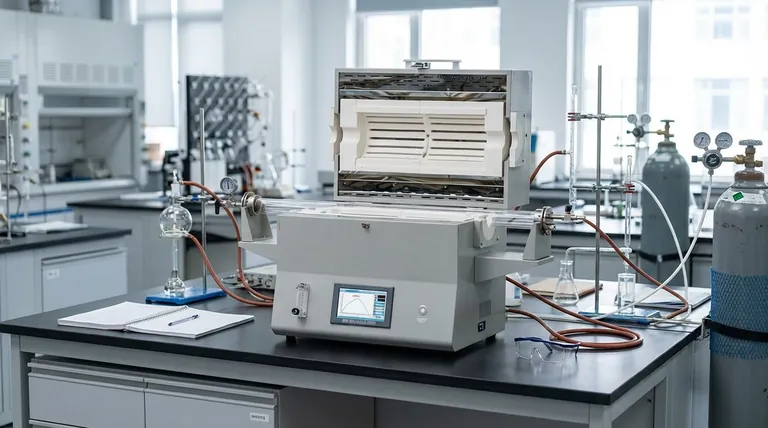
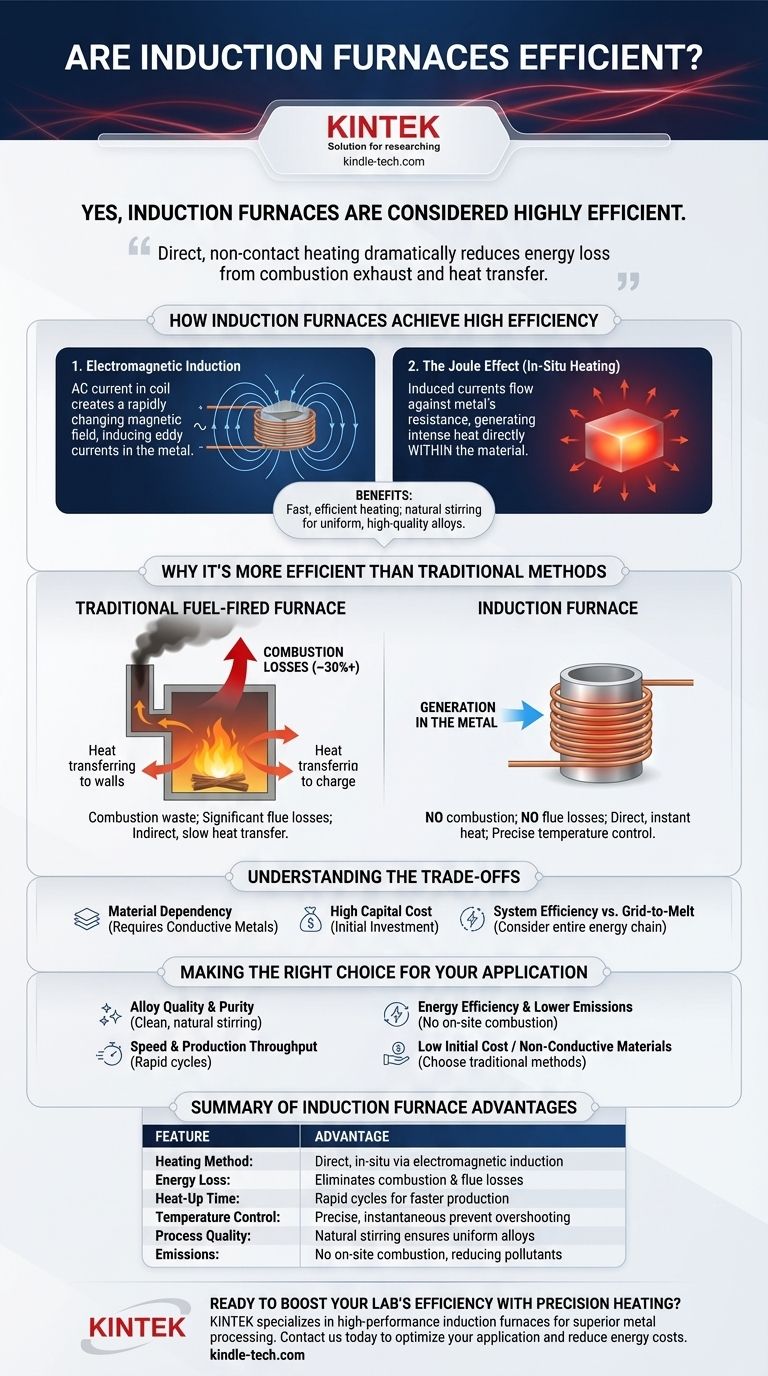
Yes, induction furnaces are considered highly efficient. Their design fundamentally changes how heat is generated, allowing them to convert electrical energy into useful heat within the target material far more effectively than traditional fuel-based furnaces. This efficiency stems from heating the material directly, rather than heating a chamber and waiting for that heat to transfer.
The core reason for an induction furnace's high efficiency is its principle of direct, non-contact heating. It uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat inside the conductive material itself, which dramatically reduces the primary sources of energy loss—combustion exhaust and heat transfer—that plague conventional furnaces.

How Induction Furnaces Achieve High Efficiency
The efficiency of induction technology is not magic; it is the direct result of two fundamental physical principles working in tandem.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a coil with a powerful alternating current (AC). This current creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
When a conductive material, such as metal, is placed within this field, the magnetic field induces electrical currents (known as eddy currents) to flow within the metal.
The Joule Effect
These induced eddy currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance. This resistance to the current flow generates intense heat directly within the material.
This process, known as the Joule effect, is the same principle that causes any electrical wire to heat up, but it is magnified to melt industrial-grade metals.
The Benefits of In-Situ Heating
Because the heat is generated in-situ (within the material itself), the process is incredibly fast and efficient. There is no need to first heat an external element or burn fuel to heat the furnace chamber.
The magnetic fields also create a natural stirring effect in molten metal. This ensures a uniform temperature and homogenous mixture, which is a form of process efficiency that leads to higher-quality alloys.
Why This is More Efficient Than Traditional Methods
To understand the efficiency of induction, it's best to compare it to conventional fuel-fired furnaces that burn natural gas, oil, or coal.
No Combustion Losses
Fuel-burning furnaces generate heat through combustion. A significant portion of this heat energy—often 30% or more—is immediately lost up the exhaust flue along with the waste gases.
Induction furnaces have no flue because there is no combustion. This single factor represents a massive gain in energy efficiency.
Minimized Heat Transfer Losses
Traditional furnaces must first heat their own structure (the refractory walls) and the air inside the chamber. Only then does that heat begin to transfer to the target material via radiation and convection. This is a slow, indirect process with significant energy waste.
Induction bypasses this entirely. The furnace walls remain cool relative to the charge, as only the metal itself is being heated. This leads to faster startup times and less wasted energy on heating the surrounding equipment.
Precise and Instantaneous Control
The power applied to the induction coil can be controlled instantly and precisely. This allows for exact temperature management, preventing the energy waste that comes from overshooting temperature targets.
Fuel-based systems have much slower response times, making such precise control difficult and often leading to inefficient heating cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, induction technology is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is subject to specific limitations and considerations.
Material Dependency
The core principle of induction heating relies on the material being electrically conductive. It is an exceptionally effective method for metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum but is completely ineffective for non-conductive materials like ceramics or glass.
High Capital Cost
The initial investment for an induction furnace system, including the power supply, water-cooling circuits, and coil, is typically higher than for a simple fuel-fired furnace. The long-term energy savings must be weighed against this upfront cost.
System Efficiency vs. "Grid-to-Melt" Efficiency
While the process of converting electricity into heat in the metal is highly efficient, one must consider the entire energy chain. The overall "grid-to-melt" efficiency depends on how the electricity was generated and transmitted, which involves its own set of losses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing an induction furnace depends entirely on your operational goals, material, and budget.
- If your primary focus is alloy quality and purity: Induction is superior due to its clean, non-contact heating and natural stirring, which prevents contamination and ensures uniformity.
- If your primary focus is speed and production throughput: The rapid heating cycles of induction furnaces offer a significant advantage for processes like annealing or shrink-fitting.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and reducing local emissions: Induction is an excellent choice, as it eliminates on-site combustion, flue losses, and associated pollutants.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost or heating non-conductive materials: A traditional fuel-fired furnace or a different type of electric resistance furnace would be a more appropriate solution.
Ultimately, the exceptional energy efficiency of induction furnaces makes them a cornerstone of modern, precise, and clean metallurgical processes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct, in-situ heating via electromagnetic induction |
| Energy Loss | Eliminates combustion and flue losses (~30%+ savings) |
| Heat-Up Time | Rapid heating cycles for faster production |
| Temperature Control | Precise, instantaneous control prevents overshooting |
| Process Quality | Natural stirring ensures uniform, high-quality alloys |
| Emissions | No on-site combustion, reducing local pollutants |
Ready to Boost Your Lab's Efficiency with Precision Heating?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for superior metal processing. Our solutions deliver the speed, control, and energy savings your operations need.
Contact us today to discuss how an induction furnace can optimize your specific application and reduce your energy costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















