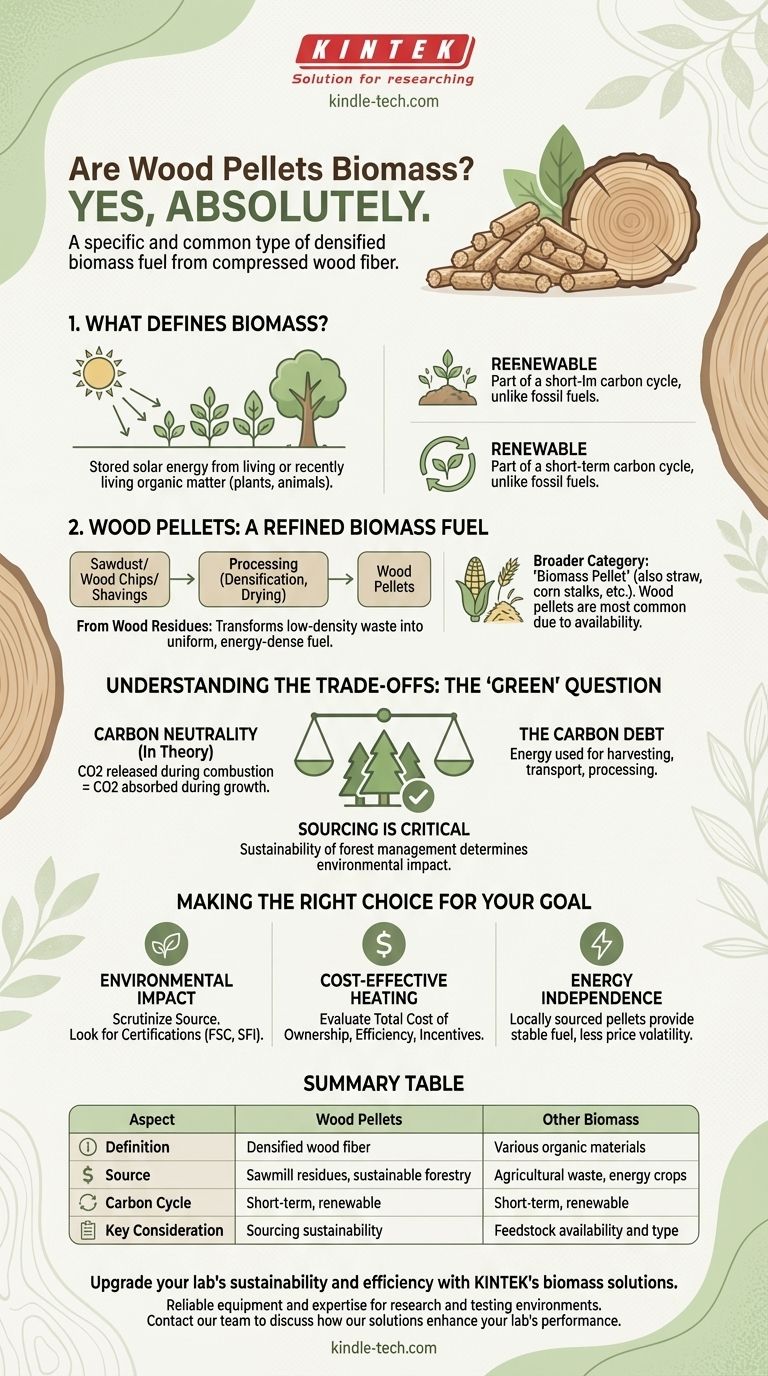
Yes, absolutely. Wood pellets are a specific and very common type of biomass. Since biomass is defined as any organic material derived from plants or animals, and wood pellets are made from compressed wood fiber (a plant material), they fit squarely within this category.
Wood pellets are not just a form of biomass; they are the most prevalent example of a densified biomass fuel. The key distinction is that while all wood pellets are biomass, not all biomass comes in the form of a wood pellet.

What Defines Biomass?
To understand why wood pellets qualify, we must first establish a clear definition of biomass itself.
The Foundation in Organic Matter
At its core, biomass is stored solar energy. It refers to any material that originates from living or recently living organisms, primarily plants and animals.
This includes a vast range of materials, from wood and agricultural crops to animal manure and food waste.
The Principle of Renewal
The defining characteristic of biomass as an energy source is its renewability. Because plants can be regrown and waste is continually produced, biomass is considered part of a relatively short-term carbon cycle, unlike fossil fuels which take millions of years to form.
Wood Pellets: A Refined Biomass Fuel
Wood pellets are simply a processed and densified form of raw biomass, specifically woody biomass.
From Waste to Energy
Most wood pellets are manufactured from wood residues. This includes sawdust, wood chips, and shavings that are byproducts of sawmills and other wood processing industries.
This process transforms low-density waste material into a uniform, dry, and energy-dense fuel that is easy to transport, store, and use in automated heating systems.
Wood Pellets vs. Other Biomass Pellets
While "wood pellet" is a common term, the broader category is "biomass pellet." These can be made from other organic materials like straw, corn stalks (stover), switchgrass, or even dried distillers grains.
However, wood pellets are by far the most common type due to the large-scale availability of raw material from the forestry and wood products industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The "Green" Question
The classification of biomass as "environmentally friendly" is not absolute and comes with important considerations. True objectivity requires looking at the entire lifecycle.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
In theory, burning biomass is carbon neutral. The carbon dioxide (CO2) released during combustion is equivalent to the amount the plant absorbed from the atmosphere during its growth.
However, this neutrality depends on the source of the biomass and the timescale. If forests are harvested faster than they can regrow, the system releases more carbon than it absorbs.
Sourcing Is Everything
The environmental impact of a wood pellet is determined almost entirely by its origin. Pellets made from sustainably managed forests or sawmill residues have a much lower carbon footprint than those derived from clear-cutting old-growth forests.
Responsible sourcing is the single most critical factor in the sustainability equation.
The Energy Cost of Production
We must also account for the energy used to harvest, transport, dry, and compress the raw material into pellets. This "carbon debt" means that no biomass fuel is perfectly carbon-free, but it is typically a fraction of the footprint of fossil fuels like coal or heating oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding that wood pellets are biomass allows you to ask more specific and important questions about your energy choices.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: Scrutinize the source of the pellets. Look for certifications from third-party organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI).
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including the price of pellets in your region, the efficiency of the pellet stove or boiler, and available incentives.
- If your primary focus is energy independence: Locally sourced biomass pellets can provide a stable and reliable fuel source that is less susceptible to global energy price volatility.
Ultimately, knowing that wood pellets are biomass is the first step toward making a more informed and responsible energy decision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Wood Pellets | Other Biomass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Densified wood fiber | Various organic materials (straw, grass, etc.) |
| Source | Sawmill residues, sustainable forestry | Agricultural waste, energy crops |
| Carbon Cycle | Short-term, renewable | Short-term, renewable |
| Key Consideration | Sourcing sustainability | Feedstock availability and type |
Upgrade your lab's sustainability and efficiency with KINTEK's biomass solutions. As a specialist in lab equipment and consumables, we understand the critical role of reliable, clean energy sources in research and testing environments. Whether you're exploring biomass properties or need consistent heating for your processes, KINTEK provides the equipment and expertise to support your goals. Contact our team today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's performance and contribute to your sustainability initiatives.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why are zirconia grinding balls preferred for NiCrAlY-Mo-Ag powders? Ensure Maximum Purity and Durability
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- Why are high-purity zirconia grinding balls recommended for LATP ceramic powders? Ensure Purity and High Conductivity.
- Why are 3mm zirconia grinding balls selected for Na3FePO4CO3 synthesis? Optimize Energy and Purity







