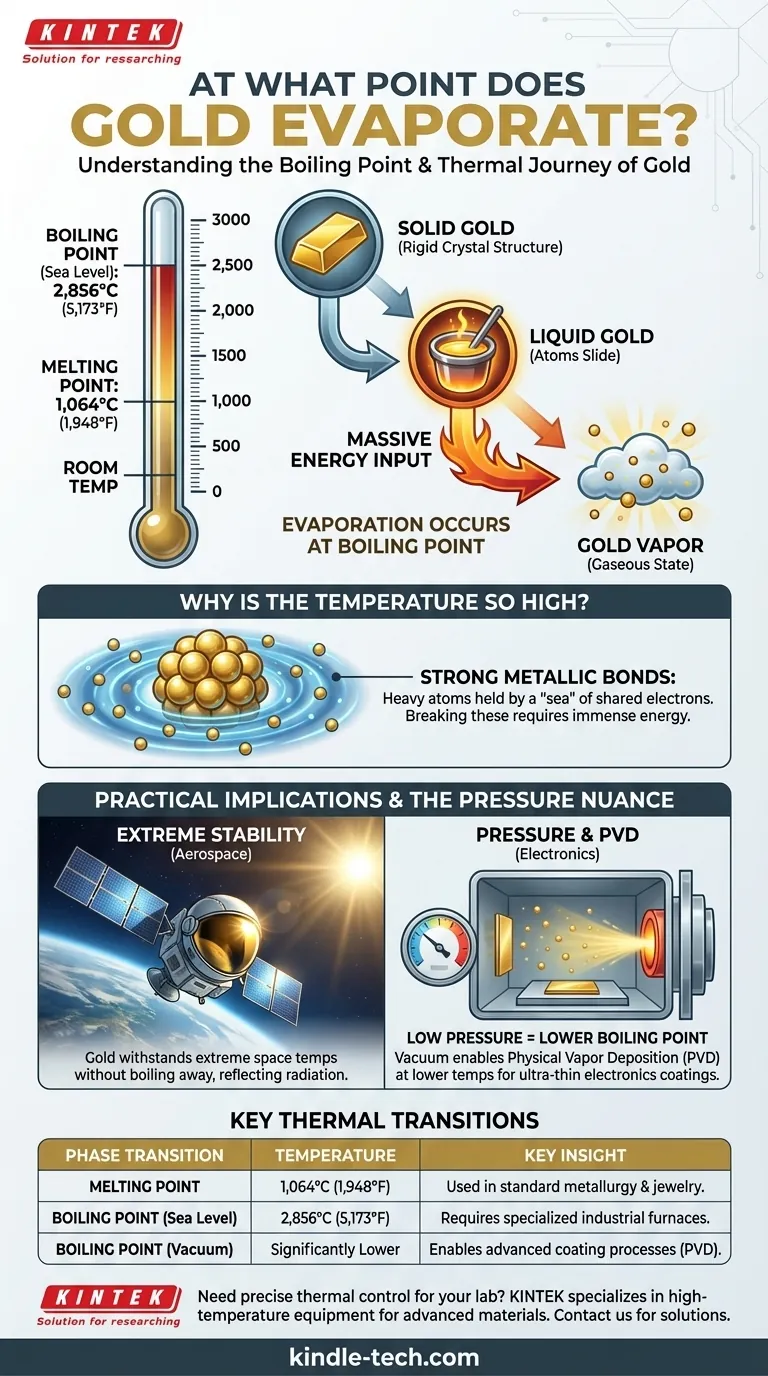
In short, gold evaporates at its boiling point. This occurs at a staggering temperature of approximately 2,856° Celsius (5,173° Fahrenheit). At this point, the liquid gold has absorbed enough thermal energy to transform into a gaseous state, or a vapor.
The key to understanding gold's behavior isn't just memorizing a number, but recognizing that its extremely high boiling point is a direct consequence of its atomic structure and a primary reason for its durability and value in specialized applications.

From Solid to Gas: Gold's Thermal Journey
To fully grasp what evaporation means for gold, we must look at its entire thermal process, from a solid bar to a hot gas. Each phase transition requires a massive input of energy.
The First Hurdle: The Melting Point
Before gold can boil, it must first melt. The melting point of gold is 1,064° C (1,948° F). This is the temperature where the rigid crystal structure of solid gold breaks down, allowing the atoms to slide past one another as a liquid. While this is a high temperature, it's routinely achieved in metallurgy and jewelry making.
The Boiling Point: Becoming a Vapor
The leap from liquid to gas requires significantly more energy. Reaching the boiling point of 2,856° C (5,173° F) means the gold atoms have absorbed enough energy to completely overcome the metallic bonds holding them together, allowing them to escape as a vapor. This temperature is far beyond the capabilities of standard furnaces.
Why Is This Temperature So High?
Gold's resistance to boiling stems from its atomic properties. Gold atoms are heavy and form strong metallic bonds, where a "sea" of shared electrons holds the atomic nuclei tightly together. Vaporizing gold requires injecting enough energy to break these powerful bonds and launch those heavy atoms into the air, a much more demanding task than simply melting them.
The Practical Implications of Gold's Boiling Point
This extreme temperature is not just an academic fact; it has significant real-world consequences that make gold invaluable for specific, high-stakes applications.
Stability in Extreme Environments
Gold's high boiling point is a key reason it is used in aerospace. Satellites and astronaut visors are often coated with a thin layer of gold to reflect intense solar radiation. The gold can withstand the extreme temperatures of space without degrading or boiling away.
Purity and Refining
In advanced metallurgy, the different boiling points of metals are used to separate them. Processes like vacuum distillation can purify gold by heating a mixture in a low-pressure environment, causing impurities with lower boiling points (like zinc or mercury) to vaporize and leave the pure, liquid gold behind.
Understanding the Key Nuance: Pressure
The boiling point of any substance, including gold, is not an absolute constant. It is fundamentally tied to the atmospheric pressure around it.
How Pressure Changes the Game
The standard boiling point of 2,856° C is measured at sea-level atmospheric pressure. If you decrease the pressure, such as in a vacuum chamber, the boiling point of gold drops significantly. This is because there is less external force pushing down on the liquid, making it easier for the atoms to escape into a gaseous state.
The Foundation of Modern Electronics
This principle is the cornerstone of a manufacturing process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). In a vacuum, gold is heated until it evaporates at a much lower temperature. This gold vapor then travels and condenses as an ultra-thin, highly pure film on target surfaces like computer chips and electrical connectors.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Your takeaway from gold's boiling point depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is academic or general knowledge: Understand that gold's high boiling point is a direct result of its strong metallic bonds, making it one of the most thermally stable elements.
- If your primary focus is industrial technology: Recognize that gold's boiling point is not fixed and can be manipulated with pressure, a key principle for creating advanced coatings and electronics.
- If your primary focus is jewelry or hobbyist metallurgy: Know that you will work with molten gold, but reaching its boiling point requires specialized industrial vacuum equipment and is not a factor in standard casting or shaping.
Ultimately, appreciating gold's immense resistance to vaporization is key to understanding why it has been a symbol of permanence and value for centuries.
Summary Table:
| Phase Transition | Temperature (°C) | Temperature (°F) | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1,064°C | 1,948°F | Gold becomes liquid, used in standard metallurgy. |
| Boiling Point (at sea level) | 2,856°C | 5,173°F | Gold turns to vapor; requires immense energy. |
| Boiling Point (in vacuum) | Significantly Lower | Significantly Lower | Enables processes like PVD for electronics coating. |
Need precise thermal control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces capable of handling advanced materials like gold. Whether you're refining metals, developing electronics coatings, or conducting high-stakes research, our solutions ensure accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's unique challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering



















