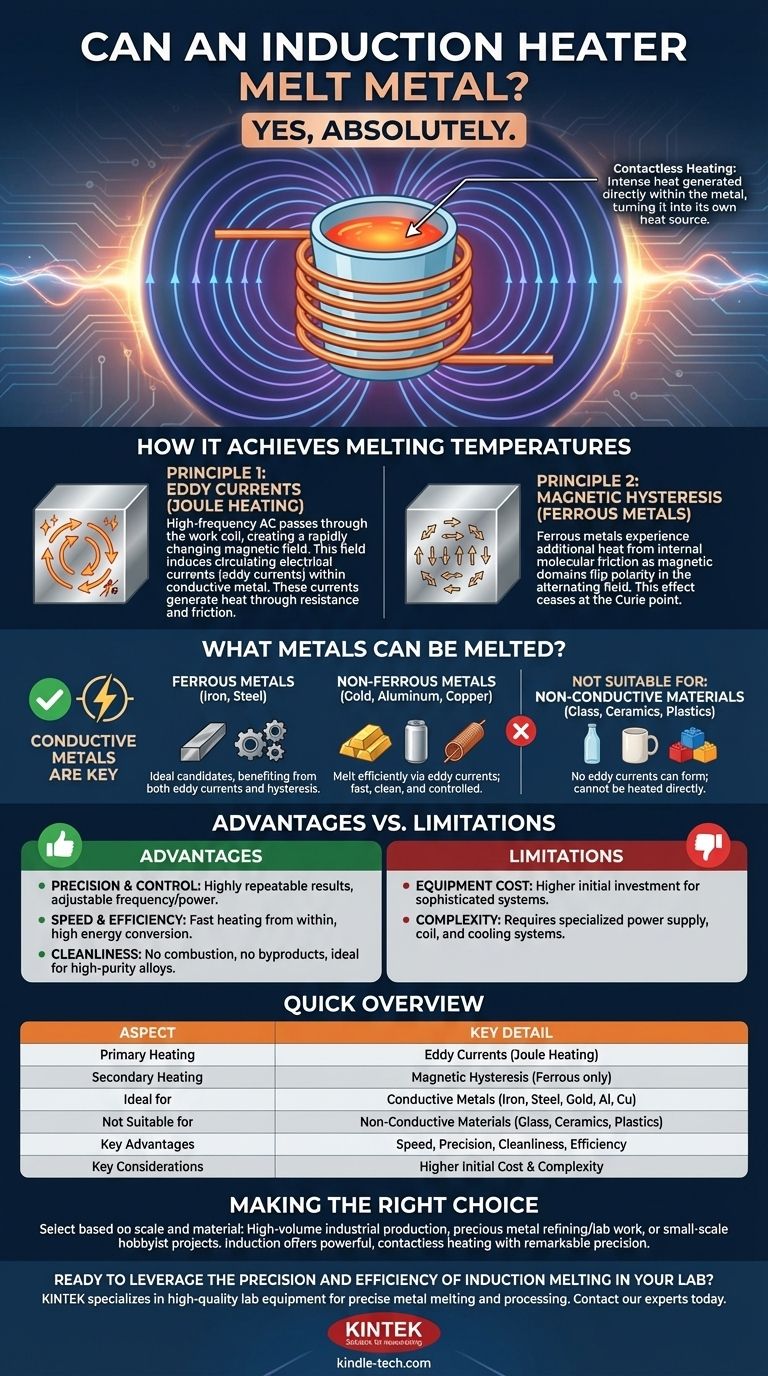
Yes, absolutely. An induction heater is not only capable of melting metal, it is a highly controlled and efficient industrial method for doing so. This contactless heating process uses electromagnetic principles to generate intense heat directly within the metal itself, allowing it to reach its melting point with remarkable speed and precision.
The core principle to understand is that induction heating turns the metal object into its own heat source. Unlike a traditional furnace that heats from the outside in, an induction system uses a magnetic field to generate heat from the inside out, resulting in a faster, cleaner, and more efficient melting process.

How Induction Heating Achieves Melting Temperatures
The "magic" of induction heating lies in two fundamental principles of physics that work together to rapidly increase a metal's temperature. It all starts with a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil.
The Role of the Alternating Magnetic Field
An induction heater's primary component is a work coil, typically made of copper.
When a powerful, high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, it generates a rapidly changing and intense magnetic field in the space within and around it.
Principle 1: Eddy Currents (Joule Heating)
When a conductive material, like a piece of metal, is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
These currents swirl inside the metal against its natural electrical resistance, generating immense friction and, consequently, intense heat. This phenomenon, known as Joule heating, is the primary source of heat in induction melting.
Principle 2: Magnetic Hysteresis (For Ferrous Metals)
For magnetic metals like iron and certain types of steel, a secondary heating effect occurs. This is called magnetic hysteresis.
The rapidly alternating magnetic field forces the magnetic domains within the metal to rapidly flip their polarity back and forth. This internal molecular friction generates additional heat. This effect, however, ceases once the metal reaches its Curie point and loses its magnetic properties.
What Metals Can Be Melted?
The effectiveness of induction melting is directly tied to a material's physical properties.
Conductive Metals are Key
The absolute requirement for induction heating is that the material must be electrically conductive. If eddy currents cannot be induced, the primary heating mechanism will not work.
Ferrous Metals (Iron, Steel)
These are the ideal candidates for induction heating. They benefit from both powerful eddy current heating and the secondary hysteresis effect, allowing them to melt very quickly and efficiently.
Non-Ferrous Metals (Gold, Aluminum, Copper)
Precious metals and other non-ferrous conductive metals also melt extremely well with induction. Their heating relies solely on eddy currents, but the process is still exceptionally fast, clean, and controlled, making it ideal for high-purity applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While powerful, induction melting is not a universal solution. It has a distinct set of characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications.
Advantage: Precision and Control
The heating process can be controlled with surgical precision by adjusting the current's frequency and power. This allows for highly repeatable results and prevents overheating or contamination of the melt.
Advantage: Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the material, the process is incredibly fast. Energy conversion is highly efficient, with less waste heat escaping into the surrounding environment compared to traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
Advantage: Cleanliness
Induction is a clean process. There is no combustion, which means no byproducts like smoke or carbon are introduced into the metal. This is critical for creating high-purity alloys for aerospace, medical, or other demanding industries.
Limitation: Equipment Cost and Complexity
Induction melting systems are sophisticated pieces of equipment. The initial investment in the power supply, work coil, and cooling systems can be substantial compared to simpler heating methods.
Limitation: Material Suitability
This method is ineffective for non-conductive materials (insulators) like glass, ceramics, or plastics. These materials do not allow for the formation of eddy currents and therefore cannot be heated directly by induction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting induction technology depends entirely on your scale, material, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: Induction furnaces offer unmatched speed and capacity, with industrial melters capable of processing anywhere from one to over fifty tons per hour.
- If your primary focus is precious metal refining or laboratory work: The precision, speed, and contamination-free nature of induction heating make it the superior choice for ensuring the purity and quality of valuable or sensitive alloys.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or hobbyist projects: Smaller benchtop induction units are available, providing a much faster and cleaner alternative to traditional torches for melting small quantities of metal for casting or craftwork.
Ultimately, induction heating offers a powerful, contactless method for melting metal, transforming electrical energy into thermal energy with remarkable precision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Heating Mechanism | Eddy currents (Joule heating) generated within the metal |
| Secondary Heating (Ferrous Metals) | Magnetic hysteresis (stops at Curie point) |
| Ideal for Melting | Electrically conductive metals (e.g., Iron, Steel, Gold, Aluminum, Copper) |
| Not Suitable For | Non-conductive materials (e.g., glass, ceramics, plastics) |
| Key Advantages | Speed, precision, cleanliness, and high efficiency |
| Key Considerations | Higher initial equipment cost and complexity |
Ready to leverage the precision and efficiency of induction melting in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including induction heating systems designed for precise metal melting and processing. Whether you are refining precious metals, developing new alloys, or require controlled heating for research, our solutions ensure clean, fast, and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how our induction heating technology can meet your specific laboratory needs and enhance your operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















