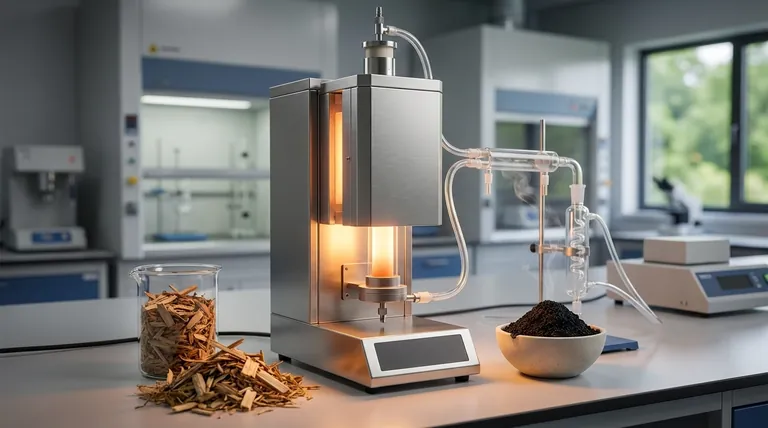
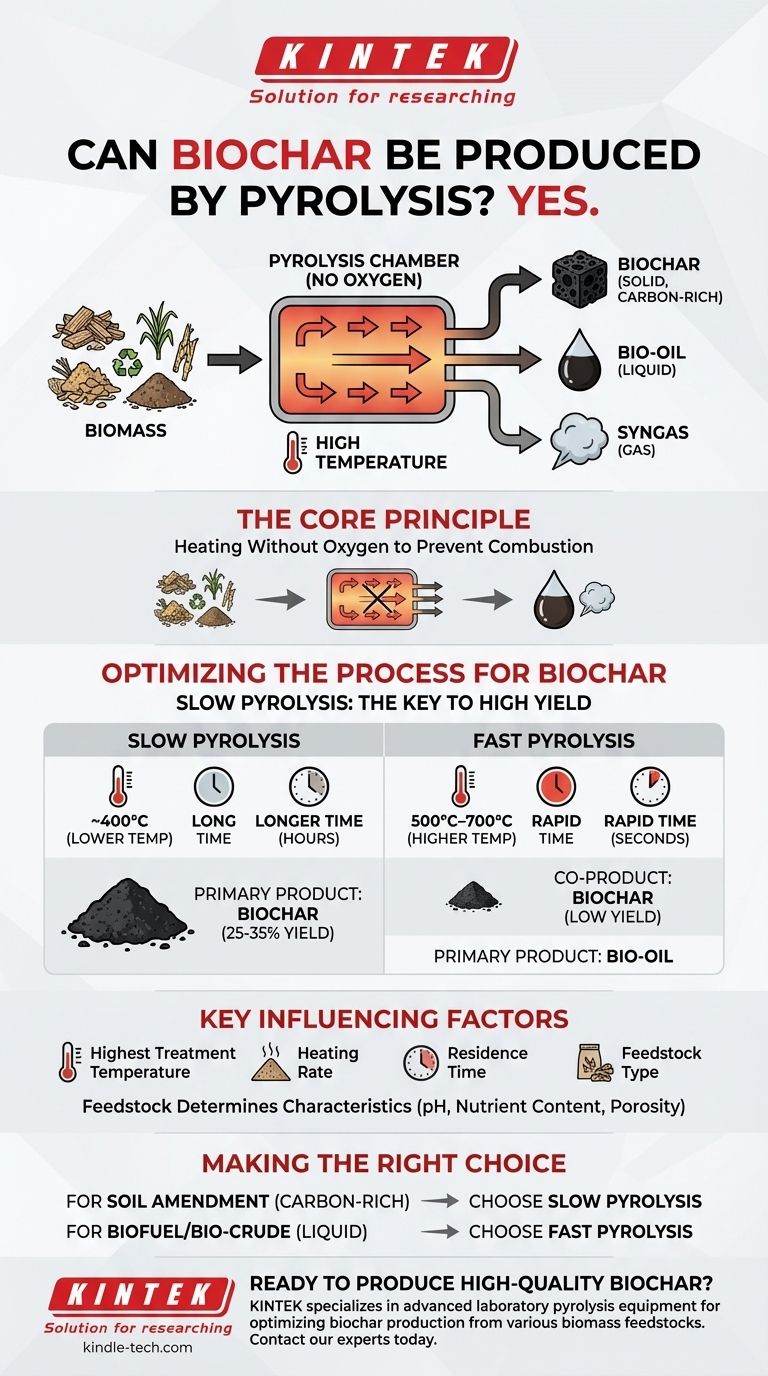
Yes, pyrolysis is the fundamental process used to create biochar. It is a method of thermochemical decomposition where biomass, such as wood or agricultural waste, is heated to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen. This lack of oxygen prevents combustion and instead breaks the material down into a solid carbon-rich product (biochar), a liquid (bio-oil), and a gas (syngas).
The critical distinction is that while all pyrolysis produces some char, slow pyrolysis is the specific method intentionally optimized with lower temperatures and longer processing times to maximize the yield and quality of biochar.

The Core Principle of Pyrolysis
Heating Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is defined by heating organic material in an oxygen-free or oxygen-limited chamber. Preventing oxygen from entering the system is crucial because it stops the biomass from burning (combustion).
Instead of burning, the intense heat breaks down the complex chemical structures within the biomass, driving off volatile compounds and leaving behind a stable, carbon-dense solid.
The Three Primary Products
The process separates the initial biomass into three distinct outputs:
- Biochar: A solid, charcoal-like material rich in carbon.
- Bio-oil: A liquid formed by cooling and condensing the pyrolysis vapors.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable gases.
The specific conditions of the pyrolysis process determine the proportion of each product.
Optimizing the Process for Biochar
Slow Pyrolysis: The Key to High Yield
To maximize the amount of biochar, slow pyrolysis is the preferred method. This technique uses relatively lower temperatures, typically around 400°C, and a much longer duration, often lasting several hours.
These slow and steady conditions favor the formation of the solid char, resulting in biochar yields that can make up 25-35% of the original biomass weight.
Fast Pyrolysis: A Different Goal
In contrast, fast pyrolysis is optimized to produce liquid bio-oil. This process uses much higher temperatures (500°C–700°C) and heats the biomass very rapidly.
The goal is to quickly break down the biomass and immediately cool the resulting vapors to condense them into bio-oil. In this scenario, biochar is merely a co-product, not the primary output.
Key Factors Influencing the Final Product
Several variables can be controlled to fine-tune the output, but the highest treatment temperature has the most significant impact on the final properties of the biochar. Other critical factors include the heating rate, how long the vapors remain in the reactor, and the type of biomass used as feedstock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Yield vs. Product Type
The central trade-off is between the different outputs. A process designed for a high yield of biochar (slow pyrolysis) will inherently produce less bio-oil. Conversely, a system designed to maximize bio-oil (fast pyrolysis) will produce a lower yield of char.
Feedstock Determines Characteristics
The initial biomass feedstock is not interchangeable. The type of wood, crop residue, or manure used directly influences the final biochar's characteristics, such as its pH, nutrient content, and porous structure (surface area).
This is why biochar is often characterized by its elemental composition and physical properties to determine its suitability for specific applications, like soil amendment or filtration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the different pyrolysis methods allows you to select the right process for your intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing a stable, carbon-rich soil amendment: You must use slow pyrolysis to maximize the yield and quality of the solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is creating a liquid biofuel or bio-crude: You must use fast pyrolysis to maximize the yield of condensed bio-oil.
Ultimately, controlling the parameters of pyrolysis empowers you to transform raw biomass into precisely the valuable bioproduct you need.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature Range | Heating Rate | Residence Time | Primary Product | Biochar Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | ~400°C | Slow | Hours | Biochar | 25-35% |
| Fast Pyrolysis | 500°C–700°C | Rapid | Seconds | Bio-oil | Low (Co-product) |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory pyrolysis equipment designed to help you optimize biochar production from various biomass feedstocks. Whether your goal is soil enhancement, carbon sequestration, or research, our reactors provide precise temperature control and process parameters to achieve the exact biochar characteristics you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your biochar production efficiency and quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer



















