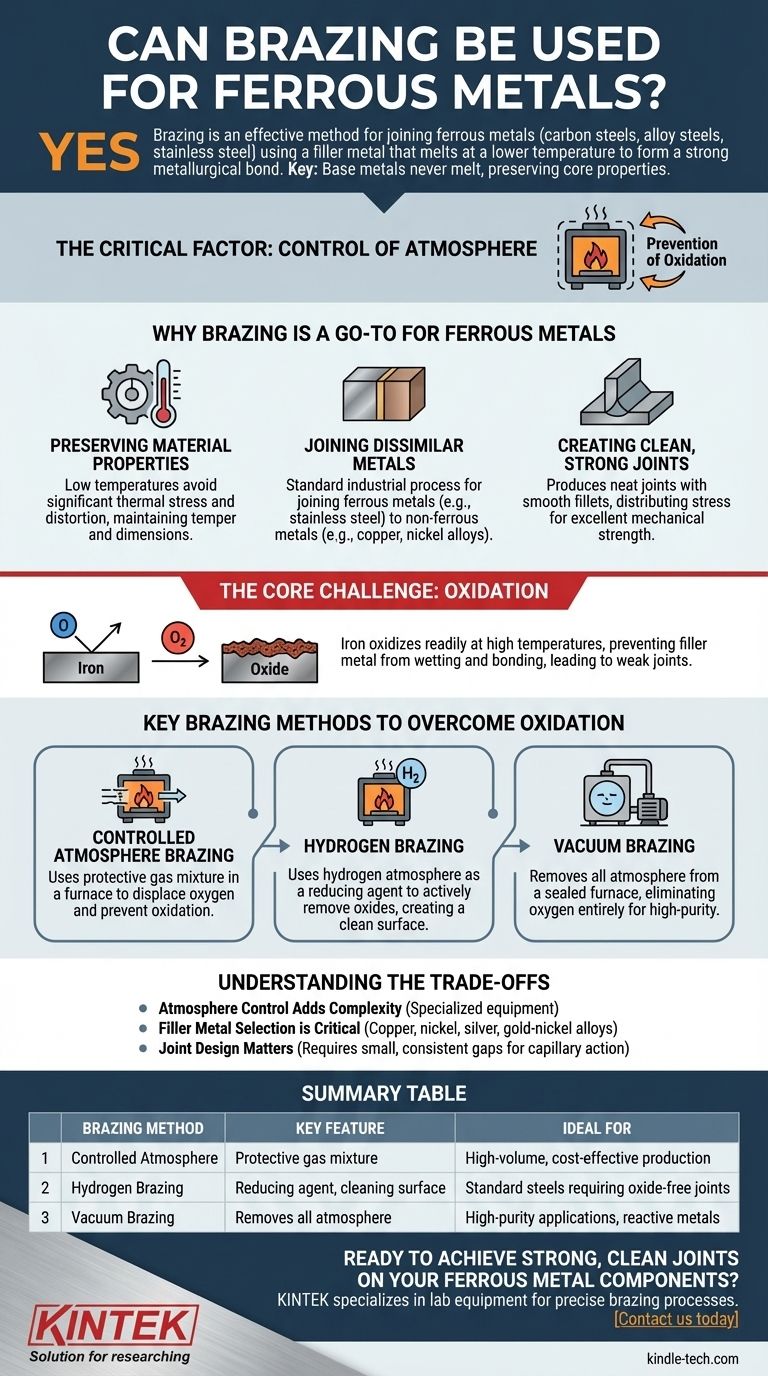
Yes, brazing is an exceptionally common and effective method for joining ferrous metals, including carbon steels, alloy steels, and stainless steel. The process works by heating the base metals and using a filler metal, such as a copper or nickel alloy, that melts at a lower temperature to form a strong metallurgical bond. The key is that the steel parts themselves never melt, preserving their core properties.
The critical factor when brazing ferrous metals is not the process itself, but the control of the atmosphere. Because iron oxidizes readily at brazing temperatures, success hinges on using a protective environment like a vacuum or hydrogen to prevent weak, oxide-contaminated joints.

Why Brazing is a Go-To for Ferrous Metals
Brazing offers distinct advantages over other joining methods like welding when working with steel and other iron-based alloys.
Preserving Material Properties
Because brazing occurs at temperatures below the melting point of steel, it avoids the significant thermal stress and distortion common in welding. This is crucial for maintaining the precise temper, hardness, and dimensions of heat-treated components.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
Brazing excels at creating strong bonds between different types of metals. It is a standard industrial process for joining ferrous metals like stainless steel to non-ferrous metals like copper or nickel alloys.
Creating Clean, Strong Joints
A properly brazed joint is neat, with a smooth fillet that often requires no further finishing. The bond occurs across the entire surface area of the joint, distributing stress evenly and resulting in excellent mechanical strength.
The Core Challenge: Oxidation
The primary technical hurdle when brazing any ferrous metal is the rapid formation of iron oxides at high temperatures.
The Problem with Iron and Oxygen
As steel is heated, the iron in the alloy reacts aggressively with any oxygen present in the air. This creates a layer of oxide scale on the surface.
The Impact on the Joint
This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten filler metal from "wetting" and bonding with the base metal. This results in a weak, incomplete, or failed joint.
Key Brazing Methods for Steel
To overcome oxidation, specialized furnaces are used to control the environment during the heating and cooling cycle.
Controlled Atmosphere Brazing
This is a broad category where the parts are heated in a furnace filled with a specific gas mixture. This protective atmosphere displaces the oxygen and prevents oxidation.
Hydrogen Brazing
A common method for ferrous metals, hydrogen brazing uses a pure hydrogen or hydrogen-nitrogen atmosphere. Hydrogen is a "reducing" agent, meaning it actively removes oxides from the metal surface, creating an exceptionally clean surface for the filler metal to bond to.
Vacuum Brazing
In this process, all the air and gases are pumped out of a sealed furnace chamber, creating a near-perfect vacuum. By removing the atmosphere entirely, there is no oxygen available to form oxides. This is often used for high-purity applications or when joining steel to highly reactive metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing ferrous metals requires careful consideration of the process and materials.
Atmosphere Control Adds Complexity
The need for a controlled atmosphere means brazing steel is not as simple as using a torch in open air. It requires specialized, and often expensive, furnace equipment.
Filler Metal Selection is Critical
The choice of filler metal is crucial. Common fillers for steel include alloys of copper, nickel, silver, and gold-nickel. The selection depends on the required strength, operating temperature of the final part, and compatibility with the base metals.
Joint Design Matters
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into a tight-fitting joint. Proper joint design with consistent, small gaps is essential for creating a strong bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Controlled atmosphere brazing in a continuous belt furnace is often the most efficient method.
- If your primary focus is joining highly reactive metals or achieving the cleanest possible joint: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice as it removes contaminants entirely.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, oxide-free joints on standard steels: Hydrogen brazing provides an active "cleaning" effect that ensures excellent filler metal flow.
Ultimately, successfully brazing ferrous metals is a matter of mastering the environment, not just the heat.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Uses a protective gas mixture | High-volume, cost-effective production |
| Hydrogen Brazing | Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, cleaning the surface | Standard steels requiring oxide-free joints |
| Vacuum Brazing | Removes all atmosphere to prevent oxidation | High-purity applications and reactive metals |
Ready to achieve strong, clean joints on your ferrous metal components?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise brazing processes. Our expertise in controlled atmosphere and vacuum furnace technology ensures your steel, stainless steel, and alloy parts are joined with maximum strength and minimal distortion.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's brazing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining



















