Yes, an induction furnace is a highly effective and widely used tool for melting copper. These furnaces are not only capable of reaching the necessary temperatures but are often the preferred method for copper and its alloys, like brass and bronze. Their design offers significant advantages in control, efficiency, and the quality of the final melted product.
The core issue isn't whether an induction furnace can melt copper, but why it is one of the best tools for the job. The technology's ability to provide precise temperature control and minimize metal loss through oxidation makes it superior for applications demanding high-quality results.
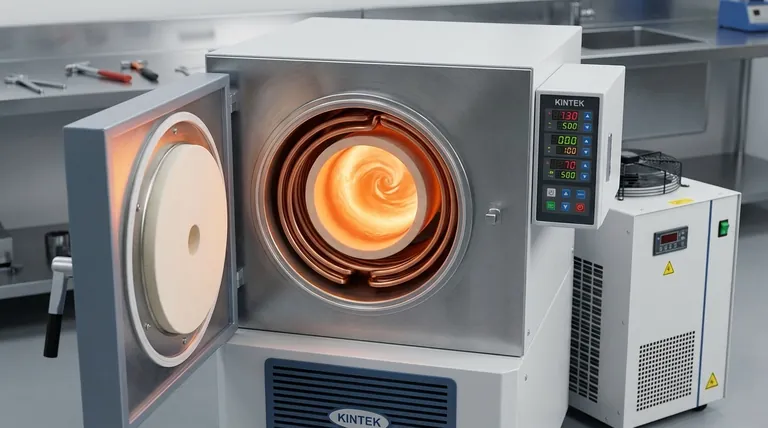

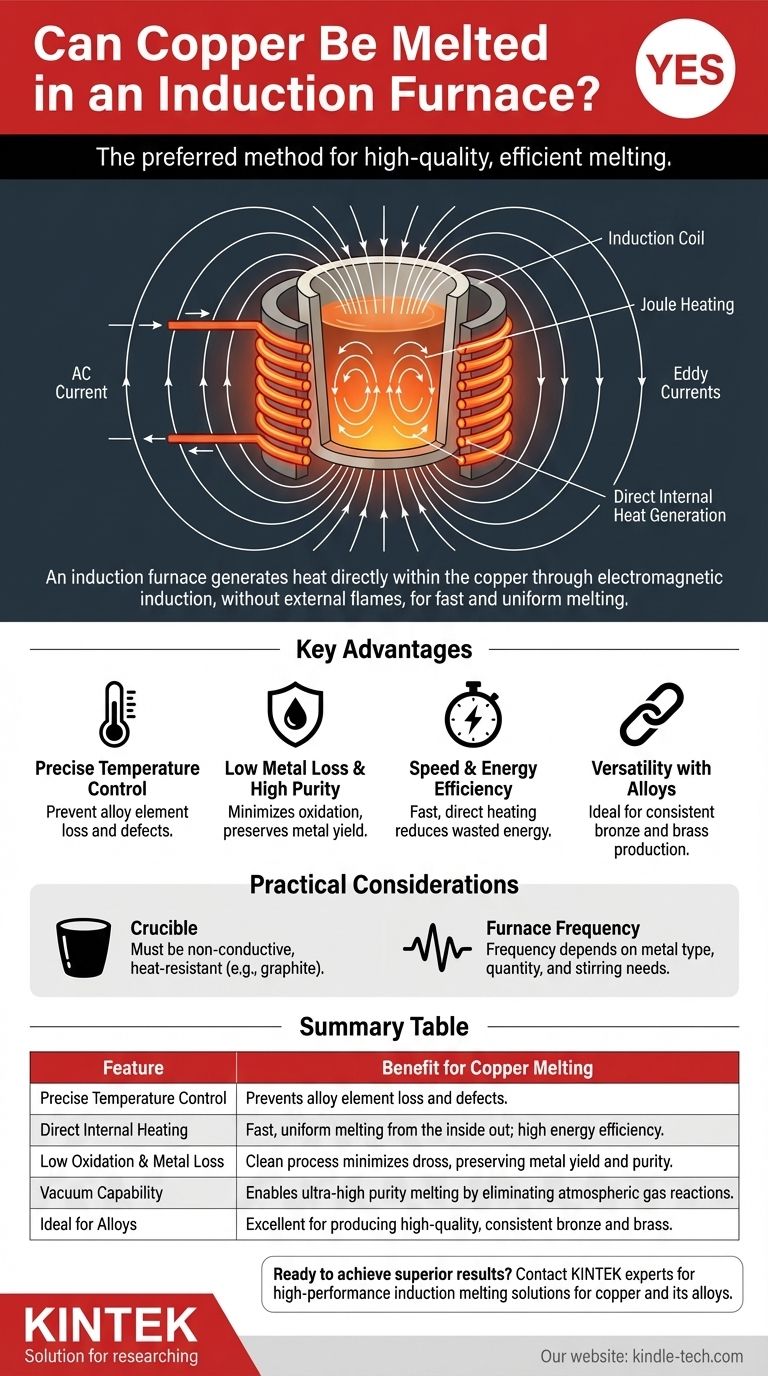
How Induction Furnaces Melt Copper
An induction furnace does not use an external flame or heating element. Instead, it uses the principles of electromagnetism to generate heat directly within the copper itself.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace operates using a coil, typically made of copper tubing, that has a high-frequency alternating current (AC) passed through it. This current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil. When conductive metal like copper is placed within this field, the magnetic field induces strong electrical currents (known as eddy currents) within the metal.
These eddy currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance, generating immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This heat is created inside the copper, allowing it to melt quickly and uniformly from the inside out.
Why This Method Excels for Copper
Copper is an excellent electrical conductor, which makes it highly responsive to the induced currents generated by the furnace. The ability to control the frequency and power of the electrical current in the coil gives the operator precise control over the heating rate and final temperature of the molten copper.
This level of control is critical for preventing overheating, which can lead to gas porosity and other defects in the final cast product.
Key Advantages for Copper Applications
Using an induction furnace for copper goes beyond simple melting. It provides tangible benefits that impact cost, quality, and process efficiency.
Precise Temperature Control
Induction furnaces allow for exact temperature management. This is vital when working with copper alloys like brass, as it prevents the more volatile elements (like zinc) from boiling off and being lost. This ensures the final alloy composition is correct.
Low Metal Loss and High Purity
Traditional fuel-fired furnaces expose molten metal to the byproducts of combustion and open air, leading to significant oxidation and metal loss (dross). Because induction heating is clean and contained, oxidation is drastically reduced.
For applications demanding the highest purity, a vacuum induction furnace can be used. This variation operates in a vacuum, preventing the molten copper from reacting with any atmospheric gases like oxygen or nitrogen.
Speed and Energy Efficiency
Since heat is generated directly within the copper, the melting process is extremely fast and energy-efficient. There is very little wasted energy, as you are not heating the furnace chamber or the air around the metal first.
Versatility with Copper Alloys
The controlled and uniform heating of an induction furnace makes it ideal for producing high-quality copper alloys. It can effectively melt steel, aluminum, gold, and silver, but it is particularly well-suited for creating specific grades of bronze and brass for custom castings or large structures.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While highly effective, induction melting is a sophisticated process with specific requirements that differ from simpler methods.
The Importance of the Crucible
The copper must be held in a container called a crucible. This crucible must be made from a non-conductive, heat-resistant (refractory) material like graphite or ceramic. If the crucible were conductive, it would heat up alongside—or instead of—the metal charge, defeating the purpose of direct induction heating.
Matching Furnace Frequency
Induction furnaces operate at different frequencies (low, medium, high). The optimal frequency depends on the type of metal, the quantity being melted, and the desired stirring effect in the molten bath. Medium-frequency furnaces are very common for melting copper and its alloys.
Initial Investment
The technology involved in an induction furnace, including the power supply and control systems, typically requires a higher initial capital investment compared to a simple gas or coke-fired furnace. However, this cost is often justified by lower operational costs, higher metal yield, and superior product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an induction furnace depends entirely on your specific objectives for quality, scale, and purity.
- If your primary focus is high-quality custom casting or alloying: An induction furnace is the ideal choice due to its precise temperature control and ability to preserve the integrity of alloys.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: A properly sized medium-frequency induction furnace will provide the speed, efficiency, and consistency required for high-throughput operations.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for specialty applications: A vacuum induction furnace is the only method that can reliably prevent reactions with atmospheric gases to produce ultra-clean metal.
Ultimately, leveraging an induction furnace for copper is not just about melting the metal; it's about precisely controlling the entire process to achieve superior and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Copper Melting |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Prevents alloy element loss (e.g., zinc in brass) and defects. |
| Direct Internal Heating | Fast, uniform melting from the inside out; high energy efficiency. |
| Low Oxidation & Metal Loss | Clean process minimizes dross, preserving metal yield and purity. |
| Vacuum Capability | Enables ultra-high purity melting by eliminating atmospheric gas reactions. |
| Ideal for Alloys | Excellent for producing high-quality, consistent bronze and brass. |
Ready to achieve superior results in your copper melting process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction melting solutions tailored for copper and its alloys. Our expertise ensures you get the precise control and efficiency needed for high-quality casting and alloy production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver the purity and consistency your work demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















