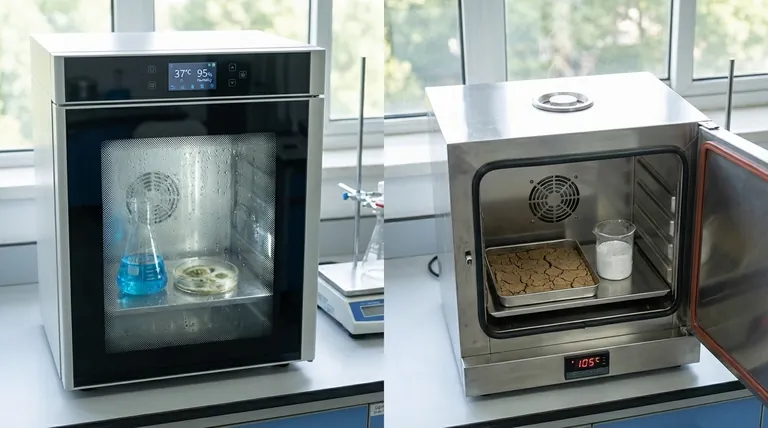
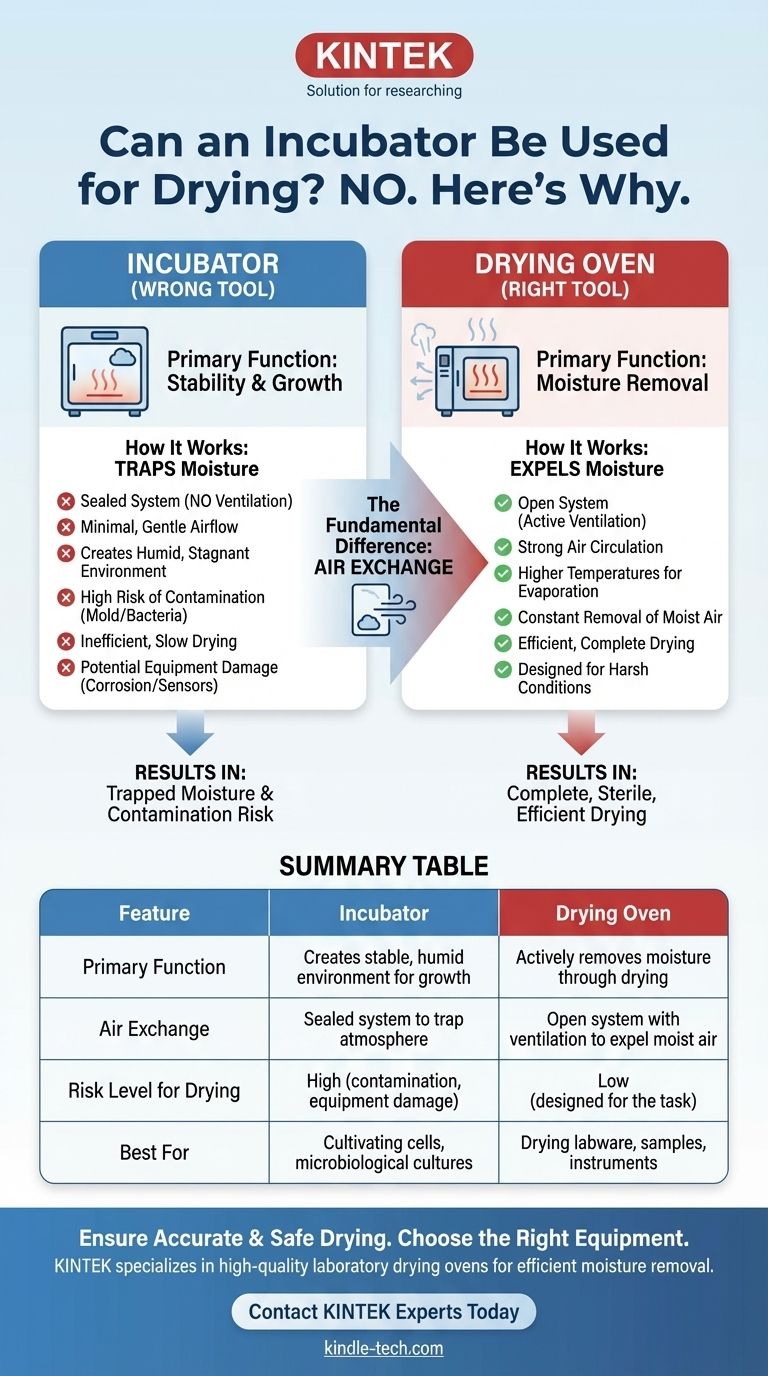
Yes, an incubator can technically be used for very light drying, but it is fundamentally the wrong tool for the task. An incubator is engineered to create a stable, often humid, and controlled environment ideal for growth. In contrast, a drying oven is designed specifically to remove moisture through higher heat and, most critically, active ventilation. Using an incubator for drying is highly inefficient and poses significant risks to your sample and the equipment itself.
The core distinction comes down to a single principle: air exchange. An incubator is a sealed system designed to trap a controlled atmosphere, while a drying oven is an open system designed to expel moist air. This makes an incubator a poor choice for any serious drying application.

The Fundamental Difference: Environment Control vs. Moisture Removal
To understand why using an incubator for drying is problematic, it's essential to recognize the core purpose behind each piece of equipment. They are designed with opposing goals in mind.
How an Incubator Works
An incubator's primary function is stability. It provides precise, gentle heating within a sealed chamber to maintain a consistent temperature for biological growth.
Many models also control humidity and gas levels (like CO2) to mimic physiological conditions. Air circulation is minimal and gentle to prevent samples from drying out or being disturbed.
How a Drying Oven Works
A drying oven's primary function is moisture removal. It uses higher temperatures to accelerate evaporation and incorporates a ventilation system—often an adjustable port or a fan—to exhaust the resulting water vapor.
This constant removal of moist air is what allows the contents to become completely dry. Without it, the air inside would quickly become saturated, and the drying process would stop.
The Inherent Risks of Using an Incubator for Drying
Attempting to use an incubator as a makeshift oven introduces several problems that can compromise your work and damage your equipment.
The Problem of Trapped Moisture
When you place a wet item in a heated, sealed incubator, the water will evaporate. However, that water vapor has nowhere to go.
The air inside the chamber quickly becomes saturated with moisture. This leads to extreme inefficiency, condensation on the chamber walls and your samples, and an environment that prevents complete drying.
The High Risk of Contamination
A warm, humid, and stagnant environment is the perfect breeding ground for fungi, mold, and bacteria.
By introducing excess moisture, you risk contaminating not only the item you are trying to dry but the entire incubator. This can compromise all future experiments performed in that unit.
Potential Damage to the Incubator
Incubators, especially those with sensitive electronics for CO2 or humidity control, are not designed to handle high levels of condensation.
Persistent moisture can lead to corrosion of internal components or damage to delicate sensors, resulting in costly repairs and invalidating the incubator's primary function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision must be driven by the requirements of your process and a respect for the function of your lab equipment. Using the wrong tool for the job is not a shortcut; it's a liability.
- If your primary focus is cultivating cells or microbiological cultures: Never use your incubator for drying. The risk of widespread, persistent contamination is far too high.
- If your primary focus is drying lab samples, glassware, or instruments: You must use a dedicated laboratory or drying oven. It is the only way to ensure efficient, complete, and sterile results.
- If you are in an emergency with a non-critical, slightly damp item: You could theoretically use an incubator at a low temperature, but you must accept the risks of slow performance, condensation, and potential contamination.
Ultimately, choosing the right instrument is fundamental to ensuring your results are repeatable and your equipment remains reliable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Incubator | Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates stable, humid environment for growth | Actively removes moisture through drying |
| Air Exchange | Sealed system to trap atmosphere | Open system with ventilation to expel moist air |
| Risk Level for Drying | High (contamination, equipment damage) | Low (designed for the task) |
| Best For | Cultivating cells, microbiological cultures | Drying labware, samples, instruments |
Ensure accurate and safe drying in your lab. Using the right equipment is critical for reliable results and protecting your investment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory drying ovens designed for efficient moisture removal without the risks of contamination or equipment damage.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect drying solution for your specific application and safeguard your laboratory processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a laboratory freeze dryer? A Guide to the 5 Essential Systems
- What is the difference between crystalline and amorphous materials in freeze drying? Master the Critical Temperature for Success
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a freeze dryer? Match Your Needs for Optimal Performance & Value
- What are the key factors that influence the price of a lab freeze dryer? A Guide to Capacity, Performance & Features
- How do you evaporate DMSO solvent? Master Gentle, High-Vacuum Techniques for Sensitive Samples



















