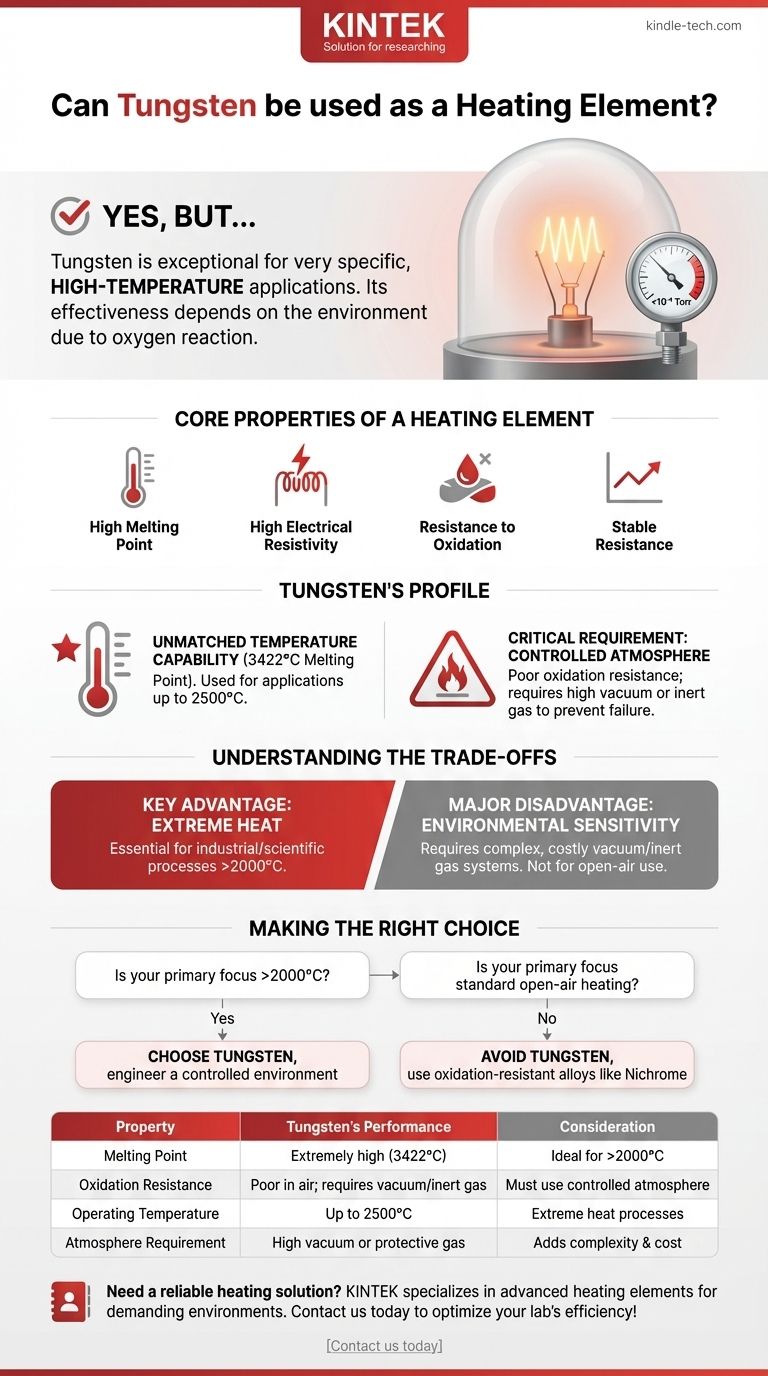
Yes, tungsten is an exceptional heating element, but its use is reserved for very specific, high-temperature applications. Its effectiveness is entirely dependent on the operating environment due to its reaction with oxygen at high temperatures.
Tungsten's primary advantage is its incredibly high melting point, making it one of the few materials capable of generating heat up to 2500°C. However, this benefit comes with a critical requirement: it must be operated in a high-vacuum or protective atmosphere to prevent rapid failure from oxidation.

The Core Properties of a Heating Element
To understand where tungsten fits, we must first define what makes any material suitable for generating heat. The choice of material directly impacts the longevity, reliability, and efficiency of the entire heating process.
High Melting Point
A heating element works by getting extremely hot. The material's melting point must be significantly higher than its operating temperature to ensure it remains structurally sound.
High Electrical Resistivity
Heat is generated when electrical current encounters resistance (Joule heating). A material with high resistivity can generate substantial heat efficiently without requiring excessive current.
Resistance to Oxidation
High temperatures dramatically accelerate chemical reactions, especially with oxygen in the air. A good heating element must resist this degradation to have a reasonable service life.
Stable Resistance
As a material heats up, its electrical resistance can change. A low temperature coefficient of resistance ensures that the heat output remains stable and predictable as the element reaches its target temperature.
Tungsten's Profile as a Heating Element
Tungsten excels in one of these categories more than almost any other metal, but it has a significant weakness in another.
Unmatched Temperature Capability
Tungsten has the highest melting point of all metals (3422°C). This unique property allows it to be used in applications requiring extreme heat, such as those reaching 2500°C.
The Critical Requirement: A Controlled Atmosphere
Tungsten's primary drawback is its poor resistance to oxidation at high temperatures. When heated in the presence of air, it burns up and fails very quickly.
To prevent this, it must be shielded. This is why tungsten filaments are used inside vacuum-sealed incandescent bulbs or in specialized high-temperature vacuum furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing tungsten is a decision based on balancing its unique strength against its demanding operational needs.
Key Advantage: Extreme Heat
For industrial or scientific processes that demand temperatures above what common alloys like nichrome or kanthal can handle, tungsten is often the only viable choice.
Major Disadvantage: Environmental Sensitivity
The need for a high vacuum (less than 10⁻⁴ Torr) or an inert gas atmosphere adds significant complexity and cost to the equipment design. It is not a material you can use for simple, open-air heating coils.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will determine if tungsten is the correct material.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (above 2000°C): Tungsten is an ideal choice, but you must engineer a system that provides a vacuum or protective atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is a standard heating application in open air: Tungsten is entirely unsuitable, and you should use a material designed for oxidation resistance, such as a nickel-chromium or iron-chromium-aluminum alloy.
Ultimately, selecting tungsten is a decision driven by the absolute need for extreme heat, which justifies the cost and complexity of a controlled environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Tungsten's Performance | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Extremely high (3422°C) | Ideal for applications above 2000°C |
| Oxidation Resistance | Poor in air; requires vacuum/inert gas | Must be used in a controlled atmosphere |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 2500°C | Suited for extreme heat processes |
| Atmosphere Requirement | High vacuum or protective gas | Adds complexity and cost to system design |
Need a reliable heating solution for your high-temperature processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced heating elements tailored for demanding environments. Whether you're working with extreme heat requirements or need guidance on material selection, our experts are here to help. Contact us today to optimize your lab's heating efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- What is the function of high-temperature metal filaments in HFCVD? Catalyzing Diamond Growth Success
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- Is tungsten a good heating element? Unlock Extreme Temperatures in Vacuum Environments















