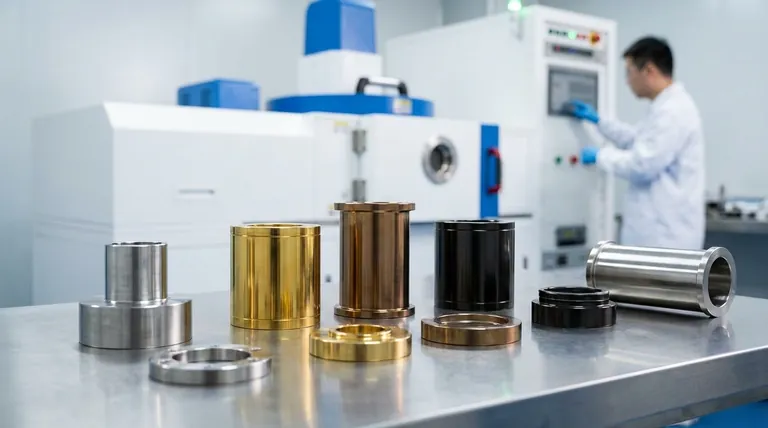
Yes, you can absolutely apply a PVD coating to stainless steel. In fact, it is a highly effective and common practice used to enhance both the aesthetic and functional properties of the material. The process provides excellent adhesion to stainless steel, creating a durable, thin film that protects the underlying metal while offering a wide range of decorative finishes.
PVD coating is not just a simple layer on top of stainless steel; it's a molecularly bonded finish that enhances its durability and aesthetic possibilities without compromising the steel's inherent strength. This makes it a preferred finishing method for high-performance and high-design applications.

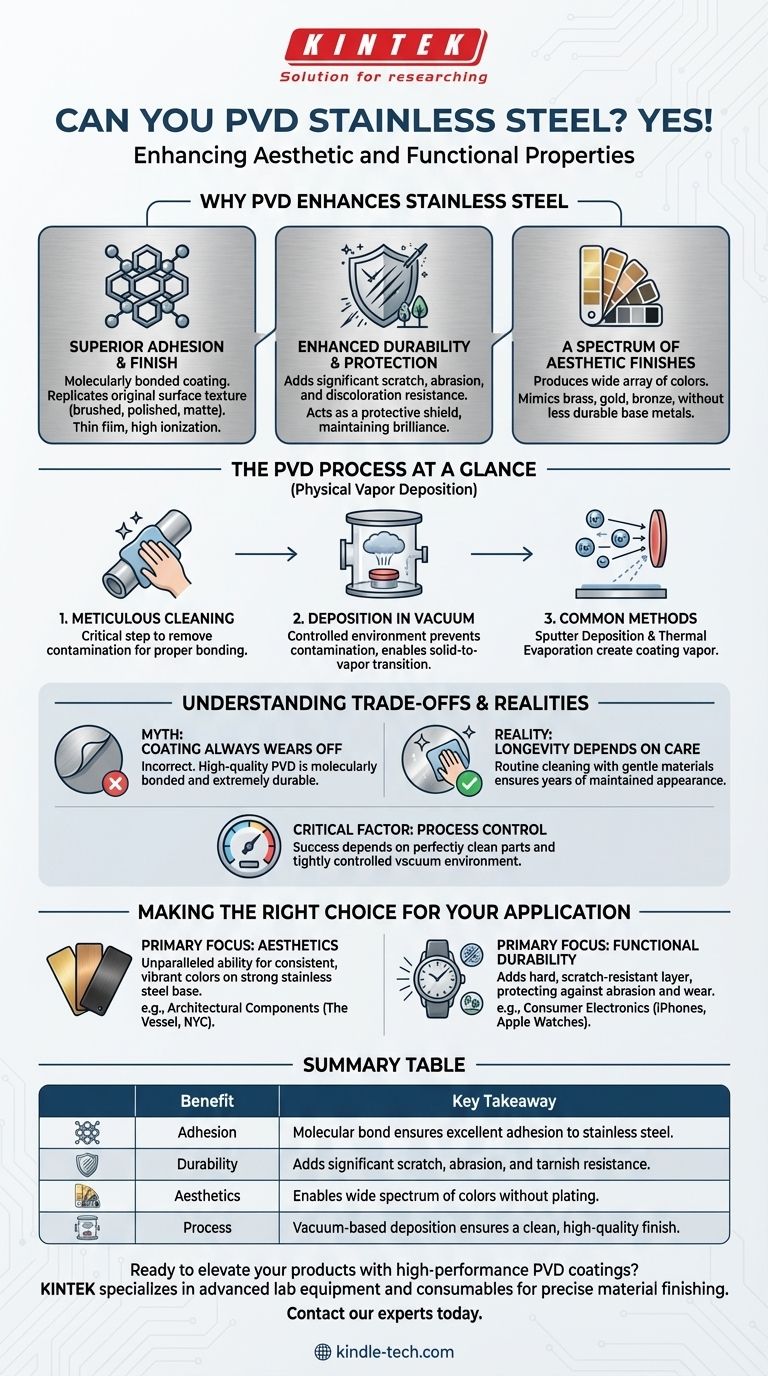
Why PVD Enhances Stainless Steel
The combination of stainless steel's strength with a PVD finish creates a superior material for demanding applications. The benefits are both functional and visual.
Superior Adhesion and Finish
The PVD process creates a high level of metal ionization within a vacuum chamber, resulting in a coating that bonds exceptionally well to the stainless steel substrate.
Because the coating is extremely thin, it precisely replicates the original surface texture, whether it's a brushed, polished, or matte finish.
Enhanced Durability and Protection
The PVD layer adds significant resistance to scratches, abrasions, and discoloration. This acts as a protective shield for the stainless steel.
This added protection helps maintain the material's brilliance and luster, especially when exposed to environmental conditions.
A Spectrum of Aesthetic Finishes
By precisely controlling the vaporized materials and process duration, PVD can produce a wide array of colors.
This allows stainless steel to convincingly mimic the appearance of brass, gold, bronze, and even darker tones like "space gray" without using different, less durable base metals.
The PVD Process at a Glance
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a group of advanced vacuum deposition methods. The core principle involves turning a solid material into a vapor, which then condenses onto the target object as a thin film.
The Importance of Surface Preparation
The first and most critical step is meticulous cleaning of the stainless steel part. Any surface contamination will prevent the coating from bonding correctly and can ruin the final quality.
Deposition in a Vacuum
The entire process takes place in a vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is essential for preventing contamination and allowing the material to transition from solid to vapor.
Common Deposition Methods
The most common PVD processes are sputter deposition and thermal evaporation. These methods involve bombarding a solid target with ions or heating it until it evaporates, creating the vapor that will form the coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
While highly effective, the success of a PVD coating depends on understanding its characteristics and proper handling.
Myth: The Coating Always Wears Off
A common misconception is that the PVD finish will inevitably wear away like traditional plating. This is incorrect.
A high-quality PVD coating is molecularly bonded to the steel and is extremely durable.
Reality: Longevity Depends on Care
With proper maintenance, PVD-coated stainless steel can maintain its appearance for many years. This involves routine cleaning with gentle materials and avoiding harsh, abrasive chemicals.
Critical Factor: Process Control
PVD has a larger operating window than some other coating processes, which aids in consistent quality. However, the success of the coating is still heavily dependent on maintaining a perfectly clean part and a tightly controlled vacuum environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
PVD-coated stainless steel is used across industries, from architectural marvels like The Vessel in NYC to consumer electronics like iPhones and Apple Watches. Your primary goal will determine your focus.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics: PVD offers an unparalleled ability to achieve consistent, vibrant colors like gold, bronze, or black on a strong and corrosion-resistant stainless steel base.
- If your primary focus is functional durability: The PVD coating adds a hard, scratch-resistant layer that protects the stainless steel from abrasion and environmental wear, extending its service life and pristine appearance.
By choosing PVD, you are selecting a sophisticated finishing process that elevates the performance and design potential of stainless steel.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Adhesion | Molecular bond ensures excellent adhesion to the stainless steel substrate. |
| Durability | Adds significant scratch, abrasion, and tarnish resistance. |
| Aesthetics | Enables a wide spectrum of colors (e.g., gold, bronze, black) without plating. |
| Process | Vacuum-based deposition (sputtering/evaporation) ensures a clean, high-quality finish. |
Ready to elevate your products with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise material finishing. Whether you're developing consumer electronics, architectural components, or medical devices, our solutions ensure superior adhesion and durability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's coating and material enhancement needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















