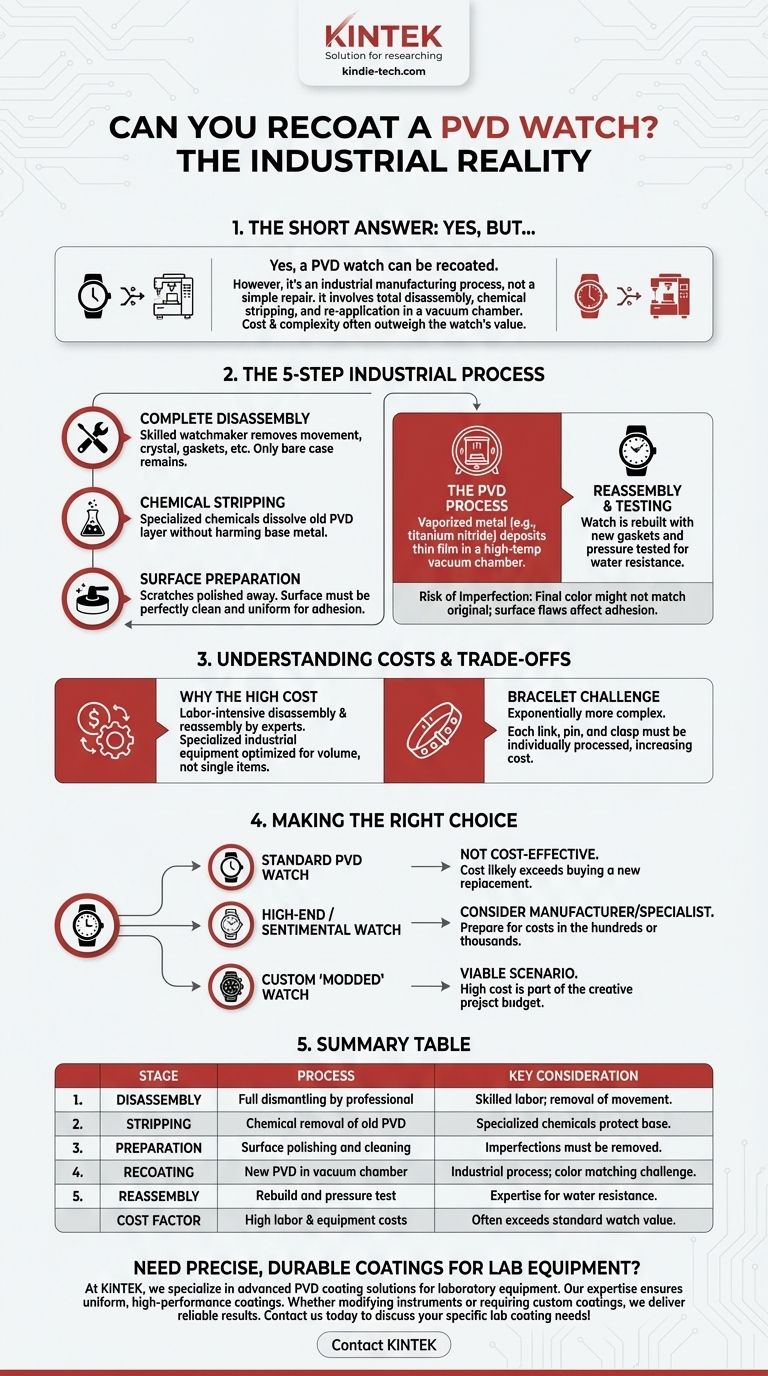
Yes, a PVD watch can be recoated, but the process is not a simple touch-up. It requires completely disassembling the watch, chemically stripping the old coating down to the base metal, preparing the surface, and then re-applying the new layer in a specialized industrial vacuum chamber. For most timepieces, the cost and complexity involved can significantly outweigh the watch's original value.
While the technology exists to strip and reapply a PVD coating, the procedure is an industrial manufacturing process, not a simple repair. The critical question isn't "can it be done," but rather "is it financially practical for your specific watch?"

What Recoating a PVD Watch Actually Involves
To understand the cost and complexity, it's essential to understand that PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is not a paint. It is a thin film of metal or ceramic bonded to the watch case at a molecular level within a high-temperature vacuum. Replicating this is a multi-stage technical process.
Step 1: Complete Disassembly
Before anything else, the watch must be fully dismantled by a professional watchmaker. The movement, crystal, gaskets, crown, and any other non-metal components must be removed. Only the bare metal case parts can enter the PVD chamber.
Step 2: Chemical Stripping
The old, damaged PVD coating must be entirely removed. This is done using specialized de-coating chemical processes that dissolve the PVD layer without harming the underlying substrate, such as stainless steel or titanium.
Step 3: Surface Preparation
Once stripped, the base metal is exposed. Any scratches or dings on the case itself must be polished or bead-blasted away. The surface must be perfectly clean and uniform for the new coating to adhere properly.
Step 4: The PVD Process
The prepared watch parts are placed in a vacuum chamber. A target material (like titanium nitride for a gold color, or titanium carbonitride for black) is vaporized. This vapor then deposits onto the watch parts, creating a new, durable coating a few microns thick.
Step 5: Reassembly and Testing
Finally, a skilled watchmaker must reassemble the entire watch, installing new gaskets and pressure testing it to ensure its original water resistance is restored. This step alone requires significant expertise.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Costs
The decision to recoat a PVD watch almost always comes down to a cost-benefit analysis. The technical possibility is clear, but the financial reality is often a major barrier.
Why the Cost Is So High
The entire process—from disassembly by a watchmaker to chemical stripping and application in an industrial PVD chamber—is both labor-intensive and requires highly specialized equipment. These services are optimized for producing thousands of new parts at once, making a one-off job for a single watch disproportionately expensive.
The Challenge with Bracelets
Recoating a bracelet is even more complex and costly than the watch case. Each individual link, pin, and clasp component must be disassembled, individually coated, and then painstakingly reassembled. This exponential increase in labor often makes recoating a PVD bracelet prohibitively expensive.
The Risk of Imperfection
While a professional job should yield excellent results, there is always a risk. The final color or finish might not be a perfect match to the original, and any oversight during surface prep can lead to flaws in the final coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Consider the primary reason you want to recoat your watch to determine the most logical path forward.
- If your primary focus is restoring a standard, affordable PVD watch: It is almost never cost-effective. The total cost of recoating will likely exceed the price of simply buying a new replacement watch.
- If your primary focus is repairing a high-end or sentimentally priceless PVD watch: Contact the original manufacturer or a specialist watch restoration service for a quote, but be prepared for a bill that can run into many hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
- If your primary focus is creating a unique, custom "modded" watch: This is the most viable scenario. Here, the high cost is factored into the budget for a personalized piece, making the expense a part of the creative project.
Ultimately, understanding the industrial nature of PVD empowers you to see it not as a simple paint job, but as a complex manufacturing process with specific economic realities.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Disassembly | Watch is fully dismantled by a professional. | Requires skilled labor; movement and gaskets are removed. |
| 2. Stripping | Old PVD coating is chemically removed. | Specialized chemicals are needed to protect the base metal. |
| 3. Preparation | Surface is polished and cleaned. | Imperfections must be removed for proper adhesion. |
| 4. Recoating | New PVD layer is applied in a vacuum chamber. | Industrial process; color matching can be a challenge. |
| 5. Reassembly | Watch is rebuilt and pressure tested. | Requires expertise to restore water resistance. |
| Cost Factor | High labor and equipment costs. | Often exceeds the value of a standard watch. |
Need precise, durable coatings for your lab equipment? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced PVD coating solutions for laboratory equipment and consumables. Our expertise ensures uniform, high-performance coatings that enhance durability and functionality. Whether you're modifying instruments or require custom coatings for specialized applications, our team delivers reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can meet your specific lab coating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Why is CVD better than PVD? Achieve Superior, Uniform Coatings on Complex Geometries
- Are CVD diamonds worth it? Unlock Brilliant Value & Ethical Clarity
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- What is the apparatus of chemical vapor deposition? The Essential Components for Thin Film Deposition
- How long does it take to process a CVD diamond? A Guide to the 2-4 Week Growth Cycle



















