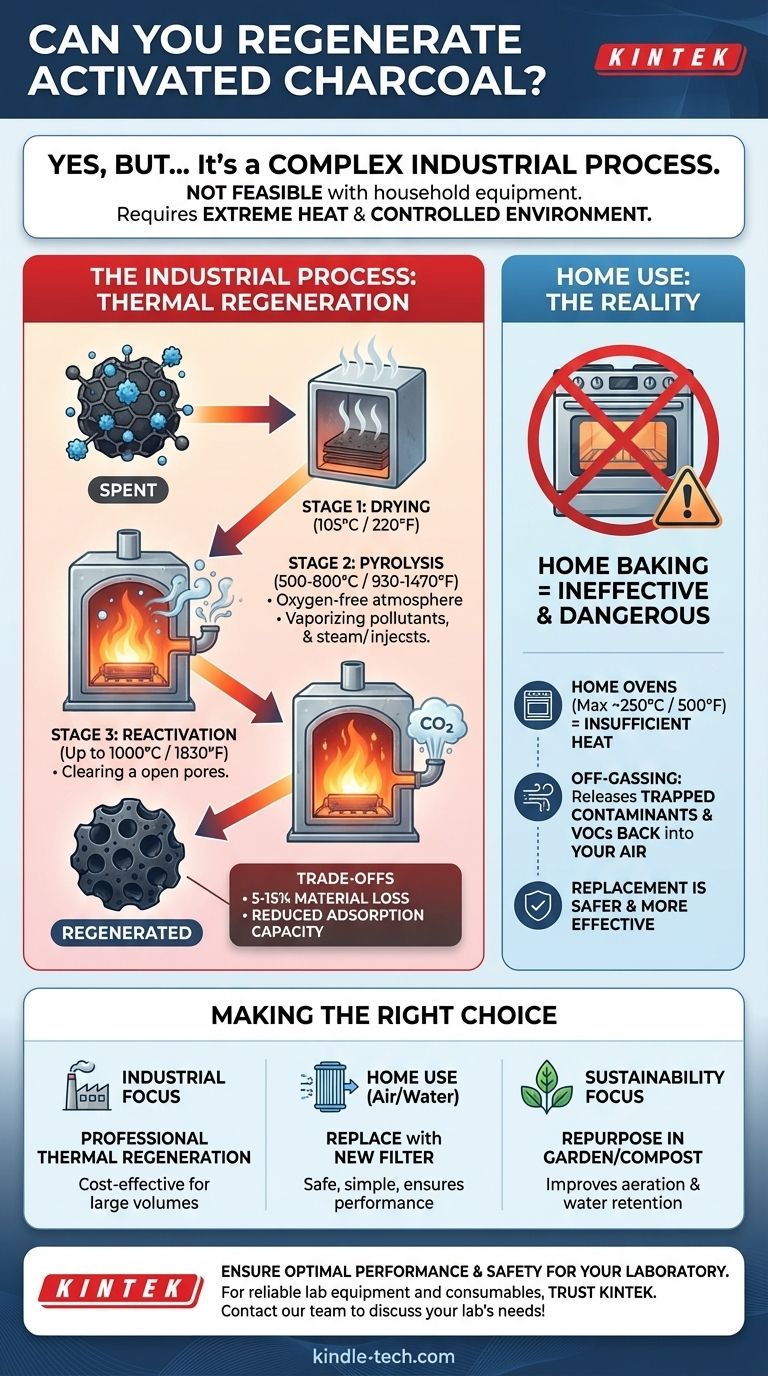
Yes, activated charcoal can be regenerated, but it is a complex industrial process that is not feasible with household equipment. True regeneration involves heating the spent carbon to extremely high temperatures in a controlled environment to incinerate the trapped contaminants, effectively cleaning its porous structure for reuse.
While many hope to "recharge" their filters at home to save money, true regeneration is an industrial process. For home users, attempting to bake or wash activated charcoal is largely ineffective and can be hazardous, making replacement the only safe and reliable option.

What "Spent" Activated Charcoal Means
The Principle of Adsorption
Activated charcoal works through a process called adsorption, where pollutant molecules physically stick to the immense internal surface area of the carbon. Think of it as a microscopic sponge with millions of pores that trap and hold contaminants.
Reaching Saturation
This "sponge" has a finite capacity. When all of its active sites and pores are filled with adsorbed pollutants, it is considered "spent" or saturated. At this point, it can no longer effectively remove contaminants from air or water.
The Industrial Process: Thermal Regeneration
How It's Done
The most common method is thermal regeneration, which occurs in multi-stage, high-temperature rotary kilns or furnaces.
- Drying: The spent carbon is first heated to around 105°C (220°F) to boil off all water.
- Pyrolysis: The temperature is then raised to 500-800°C (930-1470°F) in an oxygen-free environment (usually with steam). This vaporizes and carbonizes the adsorbed pollutants without burning the charcoal itself.
- Reactivation: Finally, the temperature is increased again, often up to 1000°C (1830°F), and a controlled gas (like steam or CO2) is introduced. This gasifies and burns away the carbonized residue, clearing the pores and reactivating the carbon.
Why This Isn't a DIY Project
This process requires specialized equipment to achieve and control extreme temperatures and manage the injection of inert gases. A standard home oven, which typically maxes out around 250°C (500°F), cannot come close to the temperatures needed to break down and remove the majority of trapped pollutants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Inevitable Material Loss
Each regeneration cycle is aggressive. It inevitably burns off a small amount of the activated carbon itself, typically resulting in a 5-15% loss of material by weight. The carbon granules can also become more brittle over time.
Reduced Adsorption Capacity
The process is not perfect. Some pores may become permanently blocked or damaged. As a result, regenerated activated carbon usually has a slightly lower adsorption capacity than virgin (new) material.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
For large-scale industrial or municipal applications, regenerating tons of carbon is significantly cheaper than purchasing new material and paying for the disposal of the spent carbon. For a home user, the economics are reversed; simple replacement is far more cost-effective.
The Dangers of "Home Baking"
Attempting to "reactivate" spent charcoal in a home oven is not only ineffective but potentially dangerous. Heating the carbon will cause it to release the trapped contaminants (off-gassing) back into your home's air, which can include volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful pollutants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Based on the realities of regeneration, your best course of action depends entirely on your use case.
- If your primary focus is industrial efficiency: Regeneration is a standard, cost-effective, and environmentally sound practice for managing large volumes of spent carbon.
- If your primary focus is home air or water quality: It is safer, simpler, and more effective to dispose of the spent charcoal and replace it with a new filter cartridge.
- If your primary focus is sustainability at home: Repurpose your spent activated charcoal by mixing it into your garden soil or compost pile, where it can help improve aeration and water retention.
Ultimately, knowing the difference between industrial regeneration and ineffective home methods is crucial for using activated charcoal safely and getting the performance you expect.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Recommended Action | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Use | Professional Thermal Regeneration | Cost-effective for large volumes |
| Home Use (Air/Water Filters) | Replace with new filter | Safe, simple, and ensures performance |
| Sustainability Focus | Repurpose in garden/compost | Provides aeration and water retention |
Ensure optimal performance and safety for your laboratory.
Trying to regenerate activated charcoal in-house can compromise your results and safety. For reliable, high-performance lab equipment and consumables, trust KINTEK.
We specialize in supplying laboratories with the precise tools they need to operate efficiently and safely. Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific applications.
Contact our team today to discuss your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results



















