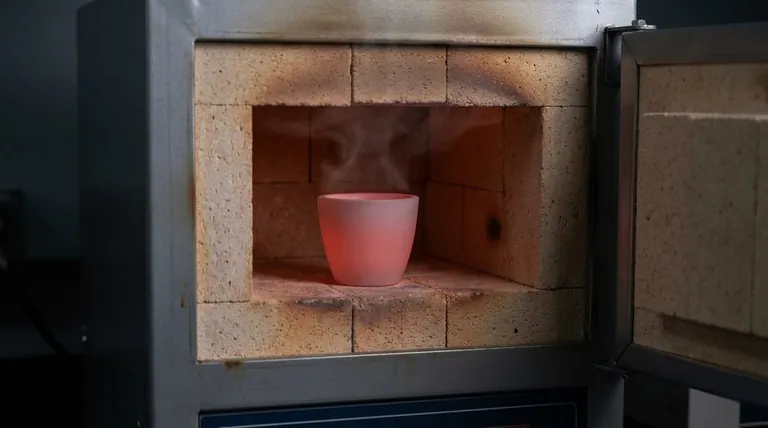
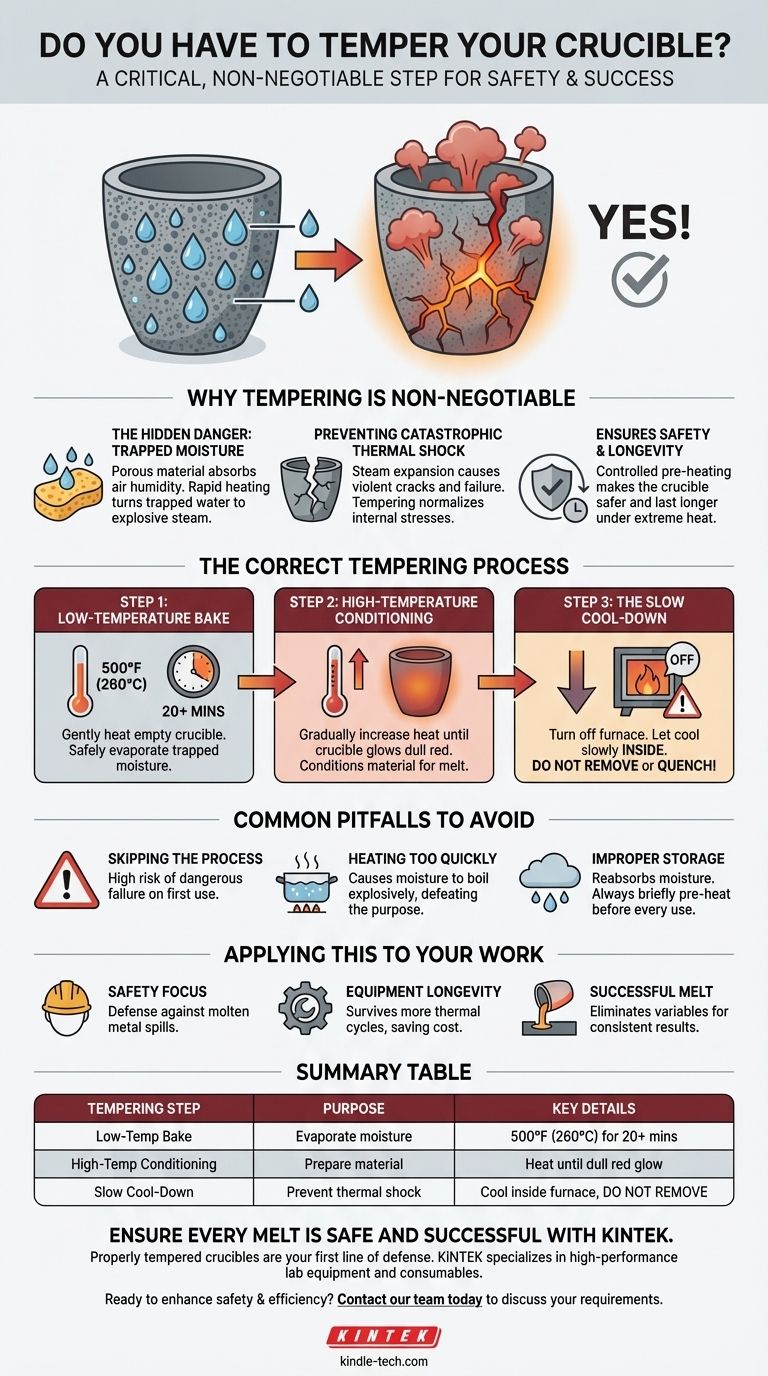
Yes, tempering your crucible is a critical, non-negotiable step before its first use. This process involves a slow, controlled heating cycle that drives out any trapped moisture from the porous material. Skipping this step can lead to the moisture turning into steam, expanding violently, and causing the crucible to crack or even shatter under thermal stress.
Tempering is not about making the crucible stronger; it's about making it safer. The process eliminates hidden moisture that can cause catastrophic failure when exposed to the extreme temperatures of a forge or furnace.

Why Tempering is Non-Negotiable
A new crucible appears solid, but its material is often porous. This structure, which helps it withstand extreme heat, also allows it to absorb moisture from the atmosphere during shipping and storage. The tempering process addresses the hidden dangers this moisture creates.
The Hidden Danger: Trapped Moisture
Crucible materials like clay and graphite act like a sponge, absorbing humidity from the air. When you heat the crucible rapidly, this trapped water turns to steam.
This steam expands with explosive force inside the crucible's walls. This rapid, internal pressure is the leading cause of cracks and fractures in new crucibles.
Preventing Catastrophic Thermal Shock
A crucible is designed to handle immense heat, but it is still vulnerable to sudden temperature changes—a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
Tempering is a form of controlled pre-heating. It gradually raises the crucible's temperature, allowing internal stresses to normalize and ensuring the entire vessel is prepared for the rapid heating required for melting metal.
The Correct Tempering Process
Following the correct procedure is simple but essential for conditioning your crucible properly. Always perform this process on an empty crucible.
Step 1: The Low-Temperature Bake
Begin by gently heating the empty crucible to approximately 500°F (or about 260°C).
Hold it at this temperature for at least 20 minutes. This initial, low-heat stage is what safely evaporates the trapped moisture.
Step 2: The High-Temperature Conditioning
After the low-temperature hold, gradually increase the heat until the crucible glows a dull red.
This second stage conditions the material itself, ensuring it is fully prepared for the thermal demands of a real melt.
Step 3: The Slow Cool-Down
Once the crucible has reached red heat, turn off your furnace or forge.
Leave the crucible inside to cool down as slowly as possible with the furnace. Do not remove it or attempt to cool it with water, as this would induce the very thermal shock you are trying to prevent.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The consequences of improper crucible preparation can range from a ruined tool to a dangerous workshop accident. Understanding common mistakes is key to preventing them.
Skipping the Process Entirely
The most common mistake is assuming a new crucible is ready to use out of the box. This puts the crucible at an extremely high risk of failure on its very first run, potentially spilling molten metal.
Heating Too Quickly
Even during the tempering process, patience is key. Ramping up the heat too fast can cause the moisture to boil and expand before it has a chance to gently steam out, defeating the purpose of the low-temperature bake.
Improper Storage After Use
A tempered crucible is not permanently immune to moisture. If you store your crucible in a damp or humid environment, it will reabsorb water over time. It is best practice to briefly pre-heat your crucible before every use to ensure it is completely dry.
Applying This to Your Work
Proper preparation is not a shortcut you can afford to skip. It is a fundamental step that dictates the safety and success of your operation.
- If your primary focus is safety: Tempering is your most important defense against a crucible failure that could lead to a dangerous spill of molten metal.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: A crucible that is properly tempered and cared for will survive far more thermal cycles, saving you the cost and frustration of frequent replacement.
- If your primary focus is a successful melt: Starting with a stable, conditioned crucible eliminates a major variable that could otherwise ruin your material or end your work session unexpectedly.
Ultimately, taking 30 minutes to properly temper your crucible is a foundational investment in the safety, reliability, and success of your craft.
Summary Table:
| Tempering Step | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Bake | Evaporate trapped moisture | Heat to 500°F (260°C) for 20+ minutes |
| High-Temperature Conditioning | Prepare crucible material | Gradually heat until crucible glows dull red |
| Slow Cool-Down | Prevent thermal shock | Let cool inside the furnace; do not remove |
Ensure every melt is safe and successful with the right equipment from KINTEK.
A properly tempered crucible is your first line of defense against dangerous failures. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable crucibles designed for rigorous use. Our experts can help you select the right tools and understand the best practices for your specific laboratory or workshop needs.
Ready to enhance your safety and efficiency? Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK solutions can support your craft.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is a PTFE crucible preferred for plasma etching? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Targeted Action
- Can a crucible withstand heat? Yes, with the right material and thermal properties.
- Why crucible is used during heating? Essential Guide for High-Temperature Containment
- What is the best type of crucible? The Answer Depends on Your Application's Needs
- What are 2 uses of crucible? Mastering High-Temperature Melting and Analysis



















