Brazing is a metal-joining process that requires specific conditions to ensure strong, clean, and reliable joints. One of the critical factors in brazing is the atmosphere in which the process takes place. Oxygen, in particular, is detrimental to the brazing process because it can cause oxidation, scaling, and poor wetting of the filler material. Instead, brazing typically requires an atmosphere devoid of oxygen and other oxidants, such as water vapor. Common atmospheres used include inert gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, or dissociated ammonia, as well as vacuum environments. These conditions help prevent oxidation and ensure proper flow and adhesion of the filler material. Below, the key points related to the role of oxygen in brazing are explained in detail.

Key Points Explained:
-
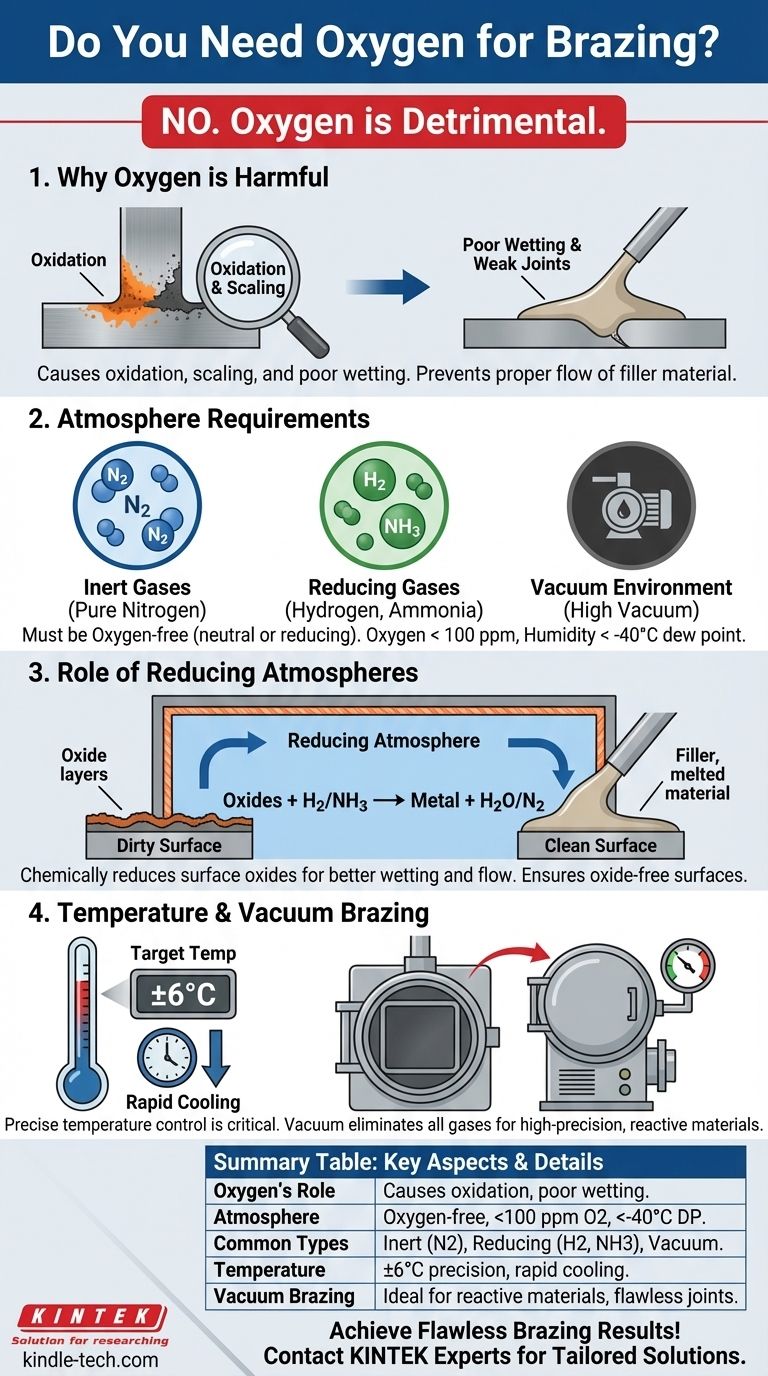
Oxygen is Harmful in Brazing
- Oxygen causes oxidation on the surfaces of the metals being joined, which prevents the filler material from properly wetting and bonding to the base metals.
- Oxidation can also lead to scaling and carbon buildup, which weaken the joint and reduce its mechanical properties.
- For this reason, brazing requires an atmosphere that is free of oxygen and other oxidants, such as water vapor.
-
Atmosphere Requirements for Brazing
- The atmosphere must be neutral or reducing, meaning it should not contain oxygen or other reactive gases.
- Common atmospheres include:
- Inert gases: Pure nitrogen is often used because it is chemically inert and prevents oxidation.
- Reducing gases: Hydrogen and dissociated ammonia are used to chemically reduce surface oxides, creating an oxide-free surface for better wetting and flow of the filler material.
- Vacuum: High vacuum environments are used in vacuum brazing to eliminate all gases, including oxygen, ensuring a clean and oxidation-free joint.
- Specific atmospheric conditions include:
- Oxygen content < 100 ppm (parts per million).
- Humidity < -40°C dew point to ensure minimal water vapor.
-
Role of Reducing Atmospheres
- In reducing atmosphere furnace brazing, the atmosphere chemically reduces surface oxides on the metals being joined.
- This process ensures that the surfaces are clean and free of oxides, which is essential for proper wetting and flow of the molten filler material.
- Reducing atmospheres are typically maintained in continuous conveyor furnaces lined with heat-resisting alloys to contain the atmosphere and prevent contamination.
-
Importance of Temperature Control
- Brazing requires precise control of temperature and time to ensure proper melting and flow of the filler material.
- The furnace used for brazing must have a reliable temperature control system, with deviations kept within ±6℃ of the target brazing temperature.
- Rapid cooling capabilities are also important to achieve the desired mechanical properties of the joint.
-
Vacuum Brazing as an Alternative
- Vacuum brazing is a specialized process that eliminates the need for a gas atmosphere by using high vacuum and temperature.
- This method is particularly effective for materials that are highly reactive or prone to oxidation.
- Vacuum brazing ensures a clean, oxidation-free joint, making it suitable for high-precision applications.
-
Practical Considerations for Equipment and Consumables
- When selecting equipment for brazing, ensure that the furnace or brazing system can maintain the required atmosphere (inert, reducing, or vacuum) and temperature control.
- Consumables, such as filler materials, should be chosen based on their compatibility with the base metals and the brazing atmosphere.
- For reducing atmospheres, ensure the availability of high-purity gases like hydrogen or dissociated ammonia.
- For vacuum brazing, invest in a high-quality vacuum furnace with rapid cooling capabilities.
In summary, oxygen is not needed for brazing and is, in fact, detrimental to the process. Brazing requires an atmosphere free of oxygen and other oxidants to ensure clean, strong, and reliable joints. The choice of atmosphere—whether inert, reducing, or vacuum—depends on the base materials and the specific requirements of the brazing project. Proper temperature control and equipment selection are also critical to achieving high-quality brazed joints.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Oxygen's Role | Causes oxidation, scaling, and poor wetting of filler material. |
| Atmosphere Requirements | Oxygen-free (neutral or reducing) with <100 ppm oxygen and < -40°C dew point. |
| Common Atmospheres | Inert gases (nitrogen), reducing gases (hydrogen, ammonia), or vacuum. |
| Temperature Control | ±6℃ precision, rapid cooling for optimal joint properties. |
| Vacuum Brazing | Eliminates gases, ideal for reactive materials and high-precision joints. |
| Equipment & Consumables | Choose furnaces and filler materials compatible with the brazing atmosphere. |
Achieve flawless brazing results—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization



















