Yes, induction furnaces are not only compatible with aluminum but are often the preferred technology for melting it. They are used across a wide range of applications, from large-scale industrial smelters converting alumina into pure aluminum to specialized foundries creating high-performance alloys. The process is valued for its speed, energy efficiency, and the high degree of control it offers.
The core advantage of using an induction furnace for aluminum is not just its ability to melt the metal, but its capacity to do so with exceptional efficiency and precision, leading to higher quality alloys and better process control compared to traditional fuel-fired methods.

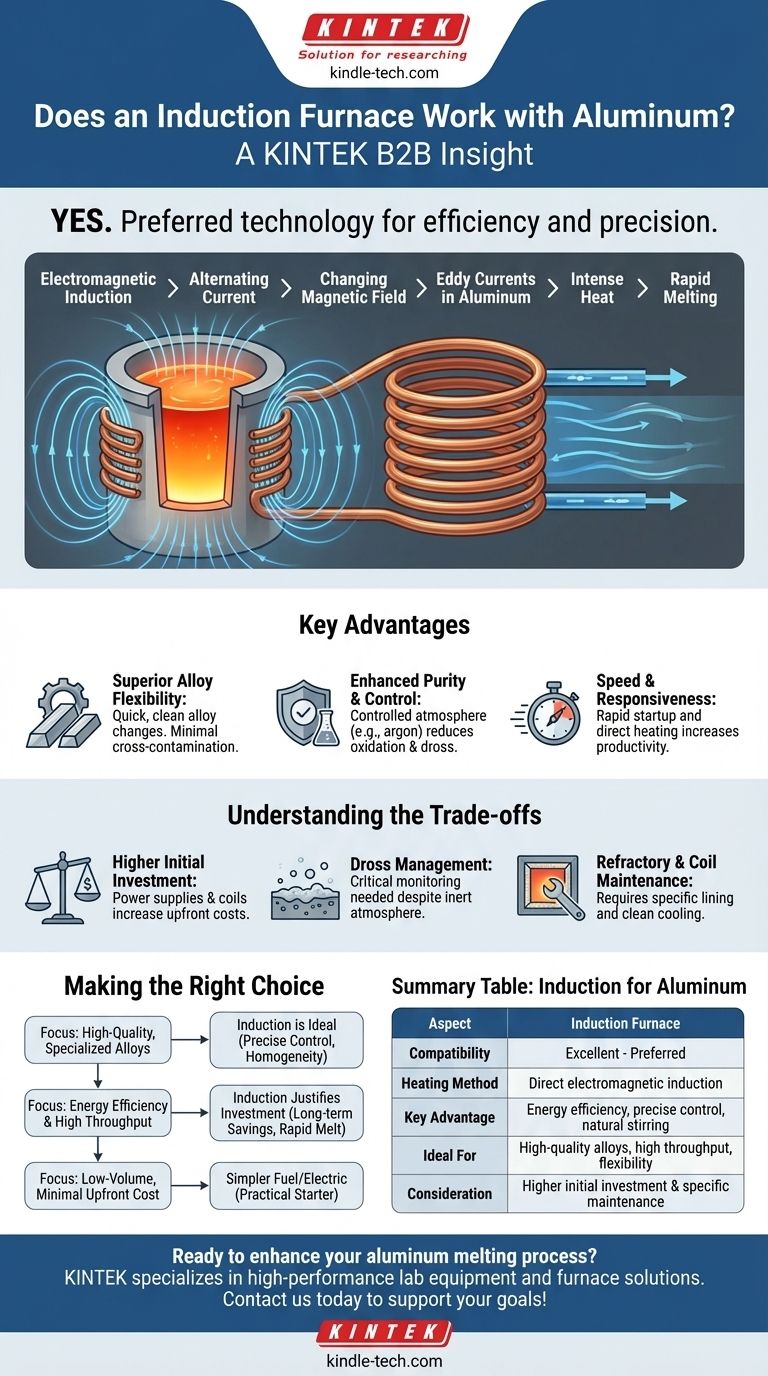
How Induction Heating Works for Aluminum
The effectiveness of an induction furnace stems from its unique method of generating heat directly within the metal itself, rather than transferring it from an external source.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a coil of water-cooled copper tubing. When a powerful alternating current flows through this coil, it creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field. This magnetic field penetrates the aluminum placed inside the furnace, inducing powerful electrical currents—known as eddy currents—within the metal. The natural electrical resistance of the aluminum causes these currents to generate intense heat, leading to rapid melting.
Inherent Energy Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly inside the aluminum charge, energy loss to the surrounding environment is minimized. This makes the process significantly more energy-efficient than fuel-fired furnaces, where a large portion of the heat is lost through the furnace walls and exhaust gases. This efficiency is critical in aluminum processing, which is notoriously energy-intensive.
The Benefit of Electromagnetic Stirring
A unique feature of induction melting is the natural stirring action created by the magnetic fields. This movement ensures the molten aluminum bath has a uniform temperature and that any added alloying elements are mixed in thoroughly and evenly. This results in a more homogeneous and consistent final product.
Key Advantages for Aluminum Processing
For applications demanding high quality and flexibility, coreless induction furnaces offer several distinct benefits.
Superior Alloy Flexibility
Induction furnaces allow for very quick and clean changes between different aluminum alloys. Since there is no combustion and the furnace can be completely emptied, the risk of cross-contamination between batches is minimal. This is ideal for foundries producing a variety of specialized materials.
Enhanced Purity and Control
The process allows for melting under a controlled atmosphere. By using an inert gas cover (like argon), the molten aluminum can be protected from oxygen in the air. This drastically reduces the formation of oxides, or "dross," improving metal cleanliness and yield—a critical factor for demanding applications in aerospace and commercial casting.
Speed and Responsiveness
Induction furnaces can be started and stopped very quickly. The direct heating method brings the metal to temperature much faster than furnaces that need to heat up a large refractory chamber first. This operational speed increases productivity and flexibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction technology presents its own set of considerations that must be managed for optimal results.
Higher Initial Investment
The primary drawback of induction furnace systems is their upfront capital cost. The power supplies, control systems, and water-cooled coils make them more expensive to purchase and install compared to simpler gas or resistance-based furnaces.
Dross Management is Still Critical
Although an inert atmosphere helps, aluminum's high affinity for oxygen means dross management is always a concern. The vigorous stirring action, while beneficial for mixing, can increase the surface area exposed to any residual oxygen, potentially accelerating dross formation if the process is not carefully controlled.
Refractory and Coil Maintenance
The furnace's internal lining (the refractory) must be specifically chosen to resist chemical attack from molten aluminum. Likewise, the copper induction coil is a critical component that requires clean cooling water and regular inspection to prevent failure, which can be costly and dangerous.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use an induction furnace depends on balancing cost against performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality, specialized aluminum alloys: An induction furnace is the ideal choice due to its precise temperature control, alloy homogeneity, and options for atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and high throughput at an industrial scale: The long-term operational savings and rapid melt rates of induction technology often justify the initial investment.
- If your primary focus is low-volume melting with minimal upfront cost: A simpler fuel-fired or electric resistance furnace may be a more practical starting point, though it will lack the advanced control and efficiency of induction.
By understanding these factors, you can determine if an induction furnace is the right strategic tool to achieve your specific aluminum melting objectives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Furnace for Aluminum |
|---|---|
| Compatibility | Excellent - Preferred for many applications |
| Heating Method | Direct internal heating via electromagnetic induction |
| Key Advantage | Energy efficiency, precise control, and natural stirring |
| Ideal For | High-quality alloy production, high throughput, and flexibility |
| Consideration | Higher initial investment and specific maintenance needs |
Ready to enhance your aluminum melting process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnace solutions tailored for laboratory and foundry needs. Our expertise ensures you get the efficiency, control, and purity required for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific aluminum processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















