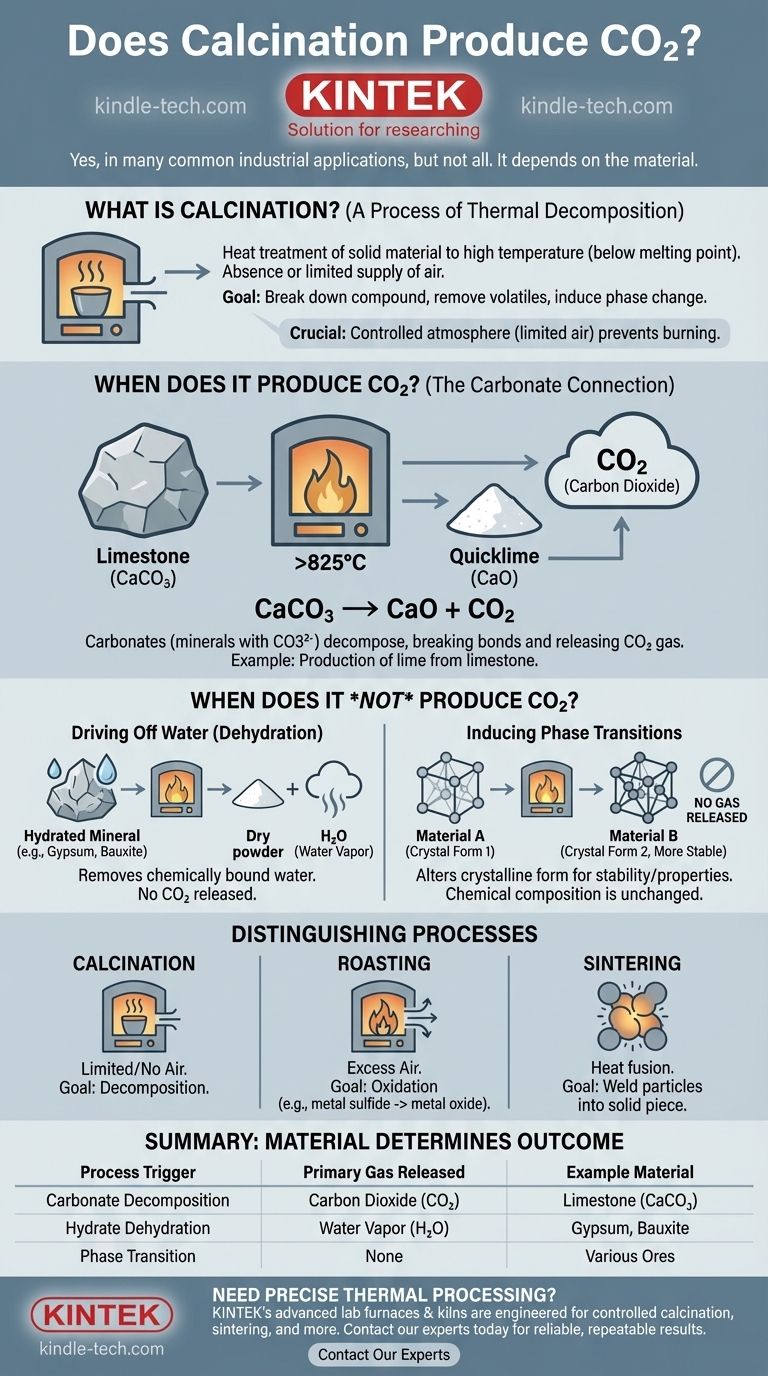
In many common industrial applications, yes. Calcination is a heating process, and when applied to carbonate-containing materials like limestone, it causes a chemical breakdown that releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2). The production of lime from limestone is a primary example of this reaction.
The critical point to understand is that calcination is a process, not a single specific reaction. Whether it produces CO2 depends entirely on the chemical makeup of the material being heated.

What is Calcination Fundamentally?
A Process of Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a heat treatment process where a solid material is heated to a high temperature, but below its melting point. This is done in the absence of, or with a very limited supply of, air.
The primary purpose is to induce thermal decomposition, which means breaking down the compound using heat.
The Goal: Inducing Change
The goal of calcination isn't always the same. It can be used to:
- Remove a volatile substance, like CO2 from limestone or water from a hydrated mineral.
- Remove impurities from an ore.
- Cause a phase transition, changing the material's crystal structure and properties.
The Role of the Atmosphere
The controlled atmosphere (limited air) is crucial. It prevents the material from burning or oxidizing, distinguishing calcination from other heat treatments like roasting.
When Does Calcination Produce CO2?
The Carbonate Connection
Calcination produces carbon dioxide when the raw material is a carbonate. Carbonates are minerals that contain the carbonate ion (CO3²⁻).
When heated, these minerals decompose, breaking their chemical bonds and releasing the carbon and oxygen atoms as CO2 gas.
Example: Producing Lime from Limestone
The most classic example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃).
When heated to over 825°C (1517°F), it decomposes into calcium oxide (CaO), also known as quicklime, and releases carbon dioxide. The chemical reaction is: CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂.
Other Carbonate Ores
This principle applies to other carbonate ores as well, such as magnesite (MgCO₃) or dolomite (CaMg(CO₃)₂), which also release CO2 upon heating.
When Does Calcination Not Produce CO2?
Driving Off Water (Dehydration)
Many minerals are calcined simply to drive off water (H₂O) that is chemically bound within their crystal structure.
For example, the calcination of bauxite ore to produce alumina (aluminum oxide) or the heating of gypsum to produce plaster of Paris both release water vapor, not carbon dioxide.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Sometimes, a material is calcined simply to alter its crystalline form. This can make it more stable, more reactive, or give it different physical properties.
In these cases, the chemical composition doesn't change, and no gas is released.
Distinguishing Calcination from Similar Processes
Calcination vs. Roasting
Roasting is heating an ore in the presence of excess air. Its goal is typically oxidation, such as converting a metal sulfide into a metal oxide. Calcination occurs in limited or no air to cause decomposition.
Calcination vs. Sintering
Sintering uses heat to fuse small particles into a single, solid piece, often after impurities have already been removed. Calcination breaks a material down; sintering welds it together.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the starting material is the key to predicting the outcome.
- If your material is a carbonate (like limestone or dolomite): Expect significant CO2 production as a primary outcome of the process.
- If your material is a hydrate (like bauxite or gypsum): The primary emission will be water vapor (steam), not CO2.
- If your goal is to change a material's crystal structure: The process may not release any gases at all.
Ultimately, calcination is a versatile tool defined by heat and a controlled atmosphere, while its specific results are dictated by chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Process Trigger | Primary Gas Released | Example Material |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonate Decomposition | Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Limestone (CaCO₃) |
| Hydrate Dehydration | Water Vapor (H₂O) | Gypsum, Bauxite |
| Phase Transition | None | Various Ores |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK's advanced lab furnaces and kilns are engineered for controlled calcination, sintering, and more. Whether you're processing carbonates, hydrates, or other materials, our equipment ensures accurate temperature control and atmosphere management for reliable, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the purpose of pre-treating coal samples? Ensure Accurate Pyrolysis with Nitrogen Drying
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing



















