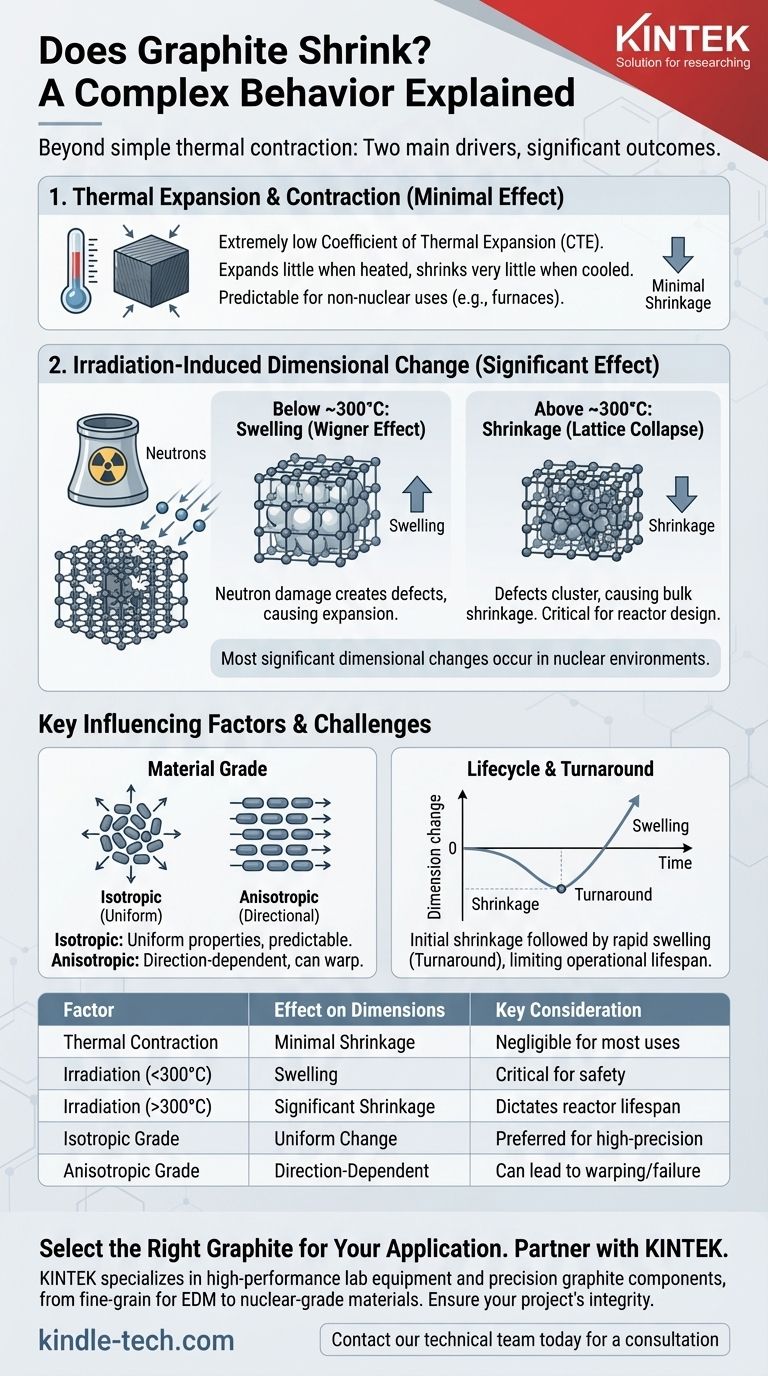
In short, yes, graphite can shrink, but its behavior is far more complex than simple thermal contraction. While all materials shrink when cooled, the most dramatic and significant shrinkage in graphite is not caused by temperature changes alone. It is primarily driven by exposure to intense neutron irradiation at specific temperatures, a phenomenon critical in nuclear applications.
The central takeaway is this: while graphite is prized for its excellent thermal stability, its most significant dimensional changes are caused by its operating environment. For most uses, shrinkage is negligible; for nuclear applications, it is a primary design constraint that dictates the material's lifespan.

The Two Drivers of Dimensional Change
To understand graphite shrinkage, you must separate its behavior into two distinct categories: standard thermal effects and the more complex irradiation-induced effects.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Graphite is renowned for its extremely low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). This means it expands very little when heated and, consequently, shrinks very little when cooled.
The reason for this stability lies in its atomic structure. Strong covalent bonds within the graphene layers resist expansion, making the material dimensionally stable.
For most applications outside of a nuclear reactor—such as in furnaces, crucibles, or EDM electrodes—thermal contraction is the only form of shrinkage you will encounter. It is minimal, predictable, and rarely a design issue.
Irradiation-Induced Dimensional Change
This is the most critical and complex factor. When used in a nuclear reactor, graphite is bombarded with high-energy neutrons. This bombardment knocks carbon atoms out of their crystal lattice positions, creating defects.
This damage, often called the Wigner effect, causes significant changes to the material's volume and shape. The outcome depends heavily on the operating temperature.
At temperatures below approximately 300°C, the accumulation of these defects primarily causes the graphite to expand, or swell.
However, at the higher operating temperatures of most modern reactors (above 300°C), a competing effect occurs. The atomic vacancies become mobile and cluster together, causing a collapse of the crystal lattice planes. This results in a bulk shrinkage of the graphite component.
Why Not All Graphite Is Created Equal
The specific grade of graphite profoundly impacts its response to these conditions. You cannot treat all graphite as a single material.
Isotropic vs. Anisotropic Grades
During manufacturing, graphite's crystalline particles can be aligned in a specific direction (anisotropic) or oriented randomly (isotropic).
Anisotropic graphite, often formed by extrusion, will shrink and expand differently along different axes. This can lead to warping.
Isotropic graphite, which is molded, has uniform properties in all directions. It shrinks and swells more predictably, making it the preferred choice for most high-performance nuclear applications.
The Role of Crystallite Size
The manufacturing process also determines the size and perfection of the graphite crystallites. Materials with fine, well-ordered crystals are generally more resistant to irradiation damage and exhibit more predictable dimensional changes than less-ordered grades.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing with graphite requires acknowledging its complex nature. What makes it uniquely suited for some environments also creates challenges.
The Challenge of Predictability
Modeling irradiation-induced shrinkage is not straightforward. It depends on neutron dose (fluence), temperature, and the specific grade of graphite. Engineers must rely on extensive empirical data gathered from testing programs for the exact material they intend to use.
Lifetime and "Turnaround"
The initial phase of high-temperature shrinkage does not last forever. After reaching a point of maximum density, the graphite will "turn around" and begin to swell rapidly as new microcracks form. This late-stage swelling is often the factor that limits the operational lifetime of a graphite component in a reactor.
Cost vs. Performance
Nuclear-grade isotropic graphite, engineered for maximum dimensional stability, is significantly more expensive than standard industrial grades. Using a cheaper, less-characterized grade in a critical application can lead to premature and unpredictable failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach to graphite must be dictated by its intended environment. There is no one-size-fits-all answer.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature thermal stability (e.g., furnace components, crucibles): You can rely on graphite's exceptionally low thermal contraction, which will be minimal and predictable.
- If your primary focus is performance in a radiation environment (e.g., nuclear reactor moderation): You must design for significant initial shrinkage followed by late-life swelling, selecting a specific nuclear-grade isotropic graphite with well-documented performance data.
- If your primary focus is high-precision machining (e.g., EDM electrodes): Select a fine-grain isotropic grade for its uniformity, as its minimal thermal changes will ensure the highest dimensional accuracy during use.
By understanding the mechanisms that govern graphite's behavior, you can select the correct material and engineer a robust and reliable system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Graphite Dimensions | Key Application Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Contraction | Minimal shrinkage on cooling (low CTE) | Negligible for most furnace/heating uses |
| Irradiation (Below 300°C) | Swelling (Wigner effect) | Critical for reactor design and safety |
| Irradiation (Above 300°C) | Significant shrinkage (lattice collapse) | Dictates component lifespan in reactors |
| Material Grade (Isotropic) | Uniform, predictable dimensional change | Preferred for high-precision/nuclear applications |
| Material Grade (Anisotropic) | Direction-dependent, can warp | Can lead to unpredictable failure in critical systems |
Select the Right Graphite for Your Demanding Application
Understanding the complex shrinkage behavior of graphite is essential for the success and safety of your high-temperature or nuclear project. The wrong material choice can lead to premature failure, unpredictable performance, and significant costs.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision graphite components. We provide the expertise and material grades—from fine-grain isotropic graphite for EDM electrodes to nuclear-grade materials for research reactors—to ensure your system's dimensional stability and longevity.
Let our experts help you:
- Select the optimal graphite grade for your specific temperature and environmental conditions.
- Access detailed material data on irradiation behavior and thermal properties.
- Source high-precision components manufactured to your exact specifications.
Ensure your project's integrity. Contact our technical team today for a consultation on your graphite needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres
- What happens to graphite at high temperatures? Unlock its Extreme Heat Resistance
- What is the thermal conductivity of graphite at high temperatures? A Guide to Thermal Management in Extreme Heat
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















