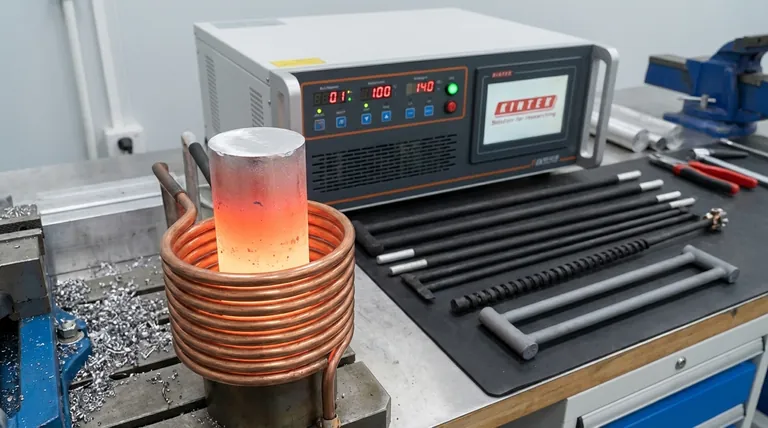
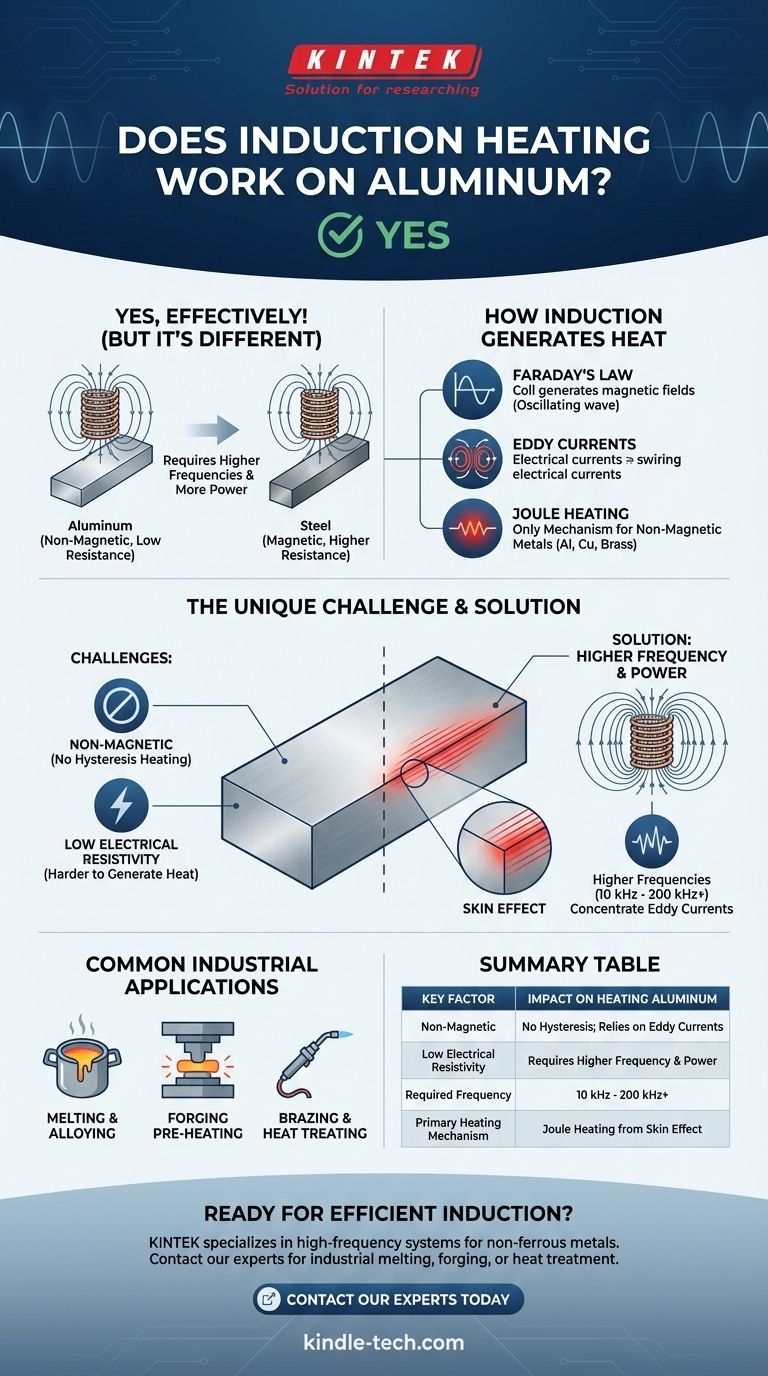
Yes, induction heating works very effectively on aluminum, but the physics behind it are different and more demanding than when heating magnetic metals like iron and steel. While it is a standard industrial process for melting, forging, and treating aluminum, success depends entirely on using the right equipment and understanding the material's unique properties.
The core challenge is that aluminum is non-magnetic and has very low electrical resistance. To heat it efficiently, induction systems must use significantly higher frequencies and more power to generate the intense eddy currents required for heating.

How Induction Generates Heat
To understand why aluminum behaves differently, we first need to review the two phenomena that induction heating relies on.
The Power of Eddy Currents
All induction heating relies on a principle called Faraday's Law of Induction. An induction coil generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field.
When a conductive material like aluminum is placed in this field, small, swirling electrical currents—called eddy currents—are induced within the metal.
Heat from Resistance (Joule Heating)
These eddy currents are not just flowing freely; they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This friction on an atomic level generates precise and rapid heat.
This is the only mechanism that heats non-magnetic materials like aluminum, copper, and brass.
The Unique Challenge of Heating Aluminum
Steel heats exceptionally well with induction because it benefits from a second, powerful heating effect and has higher electrical resistance. Aluminum lacks these advantages.
Aluminum is Non-Magnetic
Ferrous metals like iron and steel are magnetic. When subjected to the rapidly changing magnetic field, their magnetic domains rapidly flip back and forth. This internal friction creates a massive amount of heat called hysteresis heating.
This effect is extremely efficient but disappears once the steel passes its Curie temperature (around 770°C or 1420°F) and loses its magnetism. Since aluminum is never magnetic, it gets zero heating from this powerful effect.
Aluminum's Low Electrical Resistivity
The more significant factor is aluminum's very low electrical resistivity. It is an excellent electrical conductor, which is why it's used for power lines.
According to the principle of Joule heating, the heat generated is proportional to the material's resistance. Because aluminum's resistance is so low, it is inherently more difficult to generate heat within it using eddy currents compared to steel.
The Solution: Higher Frequency and Power
To overcome low resistance, we must induce much stronger eddy currents. The most effective way to do this is by increasing the frequency of the alternating magnetic field.
A higher frequency concentrates the eddy currents in a thin layer near the surface of the material (a phenomenon known as the skin effect), intensifying the heating effect. This is why systems designed for aluminum must operate at higher frequencies and deliver more power than those designed for steel.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While induction is an excellent choice for aluminum, it comes with specific engineering and cost considerations.
Equipment Requirements
An induction power supply and coil designed for steel may perform poorly or fail entirely when used on aluminum.
Equipment for aluminum must be specifically engineered to handle the higher frequencies (often 10 kHz to 200 kHz or higher, depending on the application) and the greater power (kW) needed to achieve the target temperature in a reasonable time.
Energy Efficiency in Context
Induction furnaces are indeed an energy-efficient method for melting aluminum when compared to alternatives like gas-fired reverberatory furnaces. This is because the heat is generated directly within the metal, minimizing energy loss to the environment.
However, heating a piece of aluminum to 600°C will always require more energy and power than heating an identically sized piece of steel to the same temperature via induction.
Common Industrial Applications
The properties of induction—fast, clean, and precise heating—make it ideal for high-volume, controlled processes. It is widely used for melting pure aluminum ingots to create specific aluminum alloys in large induction furnaces.
It is also used for pre-heating aluminum billets for forging and extrusion, as well as for localized brazing and heat-treating applications in manufacturing.
Is Induction Right for Your Aluminum Application?
Choosing the right technology depends entirely on your goal, scale, and budget.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial melting or alloying: Induction furnaces are the industry standard, offering unmatched speed, metallurgical control, and efficiency compared to fossil fuel methods.
- If your primary focus is high-speed forging or heat treating: A properly specified high-frequency induction system provides the precise, repeatable heating necessary for high-quality manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or hobbyist work: Be cautious. Many lower-cost induction heaters are designed for steel and will struggle to heat aluminum effectively, if at all. Verify that the equipment's frequency and power output are suitable for non-ferrous metals.
Ultimately, heating aluminum with induction is a solved problem in engineering, but it requires applying the correct principles and using equipment designed for the task.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Heating Aluminum |
|---|---|
| Non-Magnetic | No hysteresis heating; relies solely on eddy currents. |
| Low Electrical Resistivity | Requires higher frequency and power to generate sufficient heat. |
| Required Frequency | Typically 10 kHz to 200 kHz+ (much higher than for steel). |
| Primary Heating Mechanism | Joule heating from intense eddy currents concentrated by the skin effect. |
Ready to implement precise, efficient induction heating for your aluminum processes? KINTEK specializes in high-frequency induction heating systems engineered specifically for non-ferrous metals like aluminum. Whether your application is industrial melting, forging, or heat treatment, our expertise ensures you get the power and control you need for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of induction furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between an induction furnace and an arc furnace? Choosing the Right Melting Technology
- What advantages does gas-blown induction heating (GBIH) offer for titanium nitriding over traditional systems?
- Can you melt aluminum in an induction furnace? Yes, with the right high-frequency equipment.
- What materials can be used for induction heating? A Guide to Efficient and Effective Material Selection
- What is the concept of an induction furnace? Unlock Fast, Clean, and Efficient Metal Melting
- Can you melt metal to reuse it? Unlock the Secrets of Metal Casting and Recycling
- What is the mechanism of induction furnace heating? Discover Efficient, Precise Metal Melting














