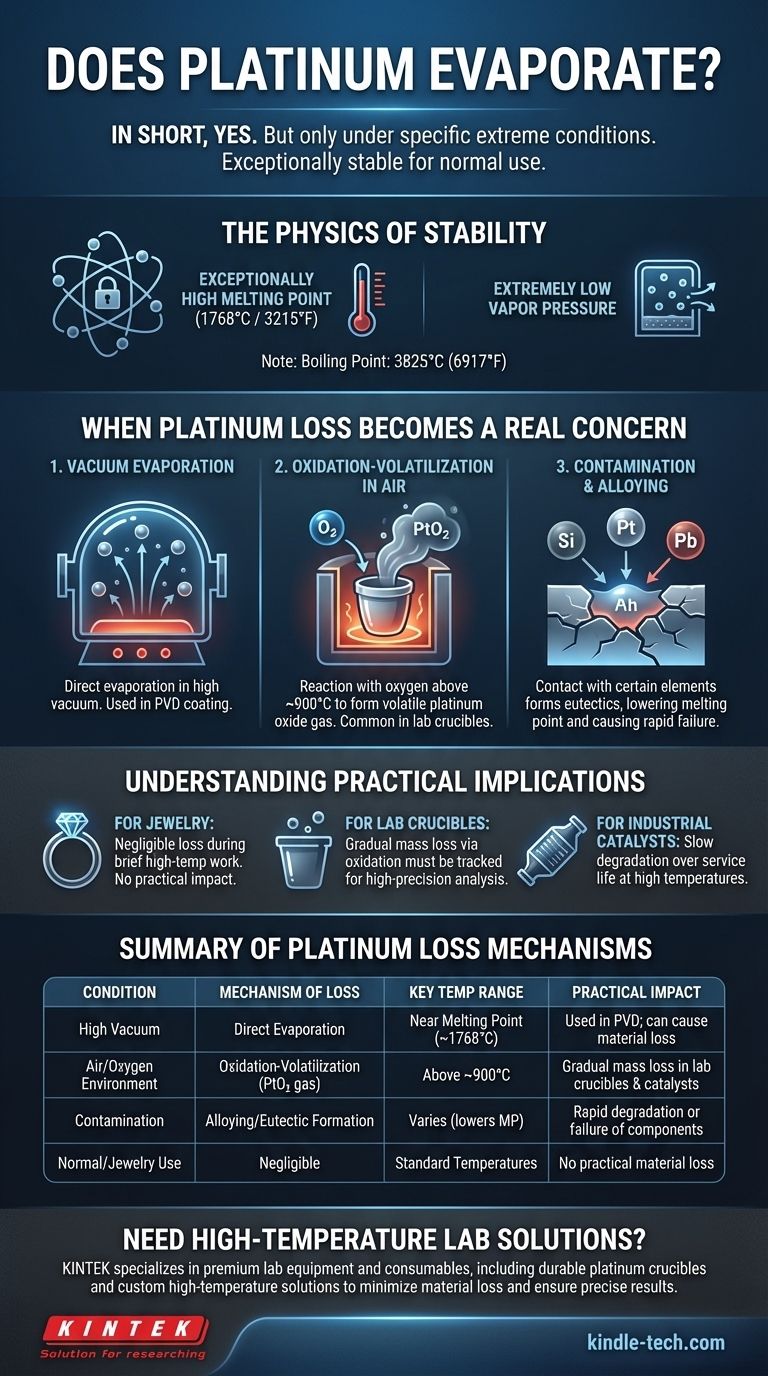
In short, yes, platinum does evaporate, but this only becomes a practical concern under very specific and extreme conditions. For any normal application, including jewelry, platinum is exceptionally stable. The process requires immense heat, typically near its melting point of 1768°C (3215°F), and is most significant in a vacuum.
The critical distinction is between pure evaporation and high-temperature oxidation. While direct evaporation of platinum is rare, a more common cause of material loss in real-world, high-heat applications is a chemical reaction with oxygen that forms a volatile platinum oxide gas.

The Physics of Platinum's Stability
To understand why platinum is so resistant to evaporating, we need to look at its fundamental properties.
### Exceptionally High Melting Point
Evaporation is the process of atoms on a material's surface gaining enough energy to escape into a gaseous state. Platinum's melting point is an extremely high 1768°C (3215°F).
This high temperature is a direct indicator of the immense energy required to loosen the strong metallic bonds holding its atoms together.
### Extremely Low Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure is a measure of a substance's tendency to transition into a gas. Even at high temperatures, platinum has an exceptionally low vapor pressure.
This means very few platinum atoms have enough energy to escape the surface, even when the metal is glowing red-hot. For context, its boiling point is a staggering 3825°C (6917°F).
When Platinum Loss Becomes a Real Concern
While stable, there are three primary scenarios where platinum mass loss is a genuine factor that must be managed.
### 1. Evaporation in a Vacuum
In high-vacuum environments, there is no air pressure to keep the platinum atoms contained. As the metal is heated close to its melting point, atoms will begin to evaporate directly from the surface.
This principle is used intentionally in industrial processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) to create ultra-thin platinum coatings on electronics and other components.
### 2. Oxidation-Volatilization in Air
This is the most common mechanism for platinum loss in practical applications like laboratory crucibles or industrial sensors operating in air.
At temperatures above approximately 900°C (1650°F), platinum can react with oxygen in the air to form gaseous platinum dioxide (PtO₂). This gas can then travel away from the surface, causing a gradual loss of material. This is not true evaporation, but a chemical transport process that has a similar result.
### 3. Contamination and Alloying
Contact with certain other elements at high temperatures can cause significant damage. Elements like silicon, lead, arsenic, or phosphorus can form alloys, or eutectics, with platinum.
These alloys have much lower melting points than pure platinum, which can lead to rapid degradation or catastrophic failure of the component. This is why handling platinum labware with clean, non-contaminating tools is critical.
Understanding the Practical Implications
The significance of platinum evaporation or loss is entirely dependent on the application. What is a negligible effect in one context is a critical failure in another.
### For Jewelry
For jewelers and wearers, this is not a concern. The temperatures used in soldering and casting are applied for very short periods. The amount of platinum lost is minuscule and has no practical impact on the piece.
### For Laboratory Crucibles
For scientists using platinum crucibles for high-precision analysis (like thermogravimetric analysis, or TGA), this is a major factor. The slow loss of mass due to oxidation-volatilization over many heating cycles in an air furnace must be tracked and accounted for to ensure accurate measurements.
### For Industrial Catalysts
In applications like catalytic converters or chemical processing, the high operating temperatures can cause slow degradation of the platinum catalyst over its service life, partly through these same volatilization mechanisms.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the specific mechanism of platinum loss is key to managing it in your application.
- If your primary focus is jewelry making or daily wear: You can consider platinum perfectly stable, as any material loss from routine work or use is functionally zero.
- If you use platinum labware in high-temperature air: Be aware that slow, steady mass loss via oxidation is inevitable and must be factored into your experimental procedure for accurate results.
- If you work in a high-vacuum, high-temperature environment: Recognize that direct evaporation is a real phenomenon that can be harnessed for coating or must be managed to prevent unwanted material loss.
Ultimately, platinum's resistance to evaporation and chemical attack is precisely what makes it one of our most valuable and enduring materials.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Mechanism of Loss | Key Temperature Range | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum | Direct Evaporation | Near Melting Point (1768°C) | Used in PVD coating; can cause material loss |
| Air/Oxygen Environment | Oxidation-Volatilization (Forms PtO₂ gas) | Above ~900°C | Gradual mass loss in lab crucibles & catalysts |
| Contamination (e.g., Si, Pb) | Alloying/Eutectic Formation | Varies (lowers melting point) | Rapid degradation or failure of components |
| Normal/Jewelry Use | Negligible | Standard Temperatures | No practical material loss |
Need High-Temperature Lab Solutions?
Managing platinum's behavior under extreme heat is critical for accuracy and longevity in your laboratory. KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including durable platinum crucibles and custom high-temperature solutions designed to minimize material loss and ensure precise results.
Let our experts help you select the right tools for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your lab's needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your research reliability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity



















