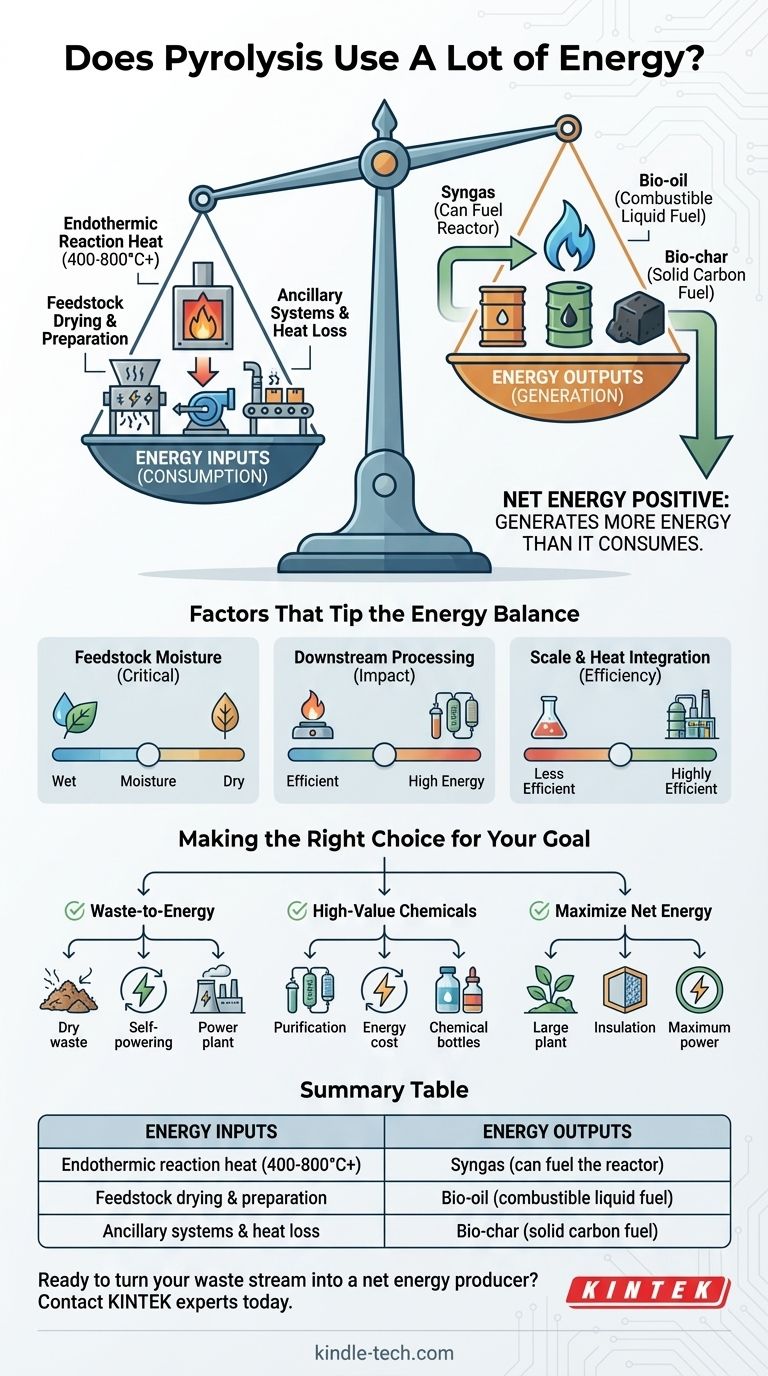
Yes, pyrolysis requires a significant initial energy input to start, as it is an endothermic process that needs heat to break down materials in the absence of oxygen. However, the process is often net energy positive, meaning it generates more energy than it consumes by converting feedstock into valuable energy products like syngas and bio-oil, which can then be used to create heat and power.
The critical question is not simply how much energy pyrolysis uses, but rather its net energy balance. A properly designed system often produces more energy in its outputs (syngas, bio-oil, bio-char) than is required to heat the reactor and prepare the feedstock.

The Energy Input: What Does Pyrolysis Consume?
To understand the energy balance, we must first account for all the energy inputs. These are the primary costs on the energy ledger.
The Endothermic Reaction Itself
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials. Breaking the chemical bonds within the feedstock requires a constant supply of external heat, typically ranging from 400°C to 800°C or higher, depending on the desired products.
Feedstock Preparation
Raw feedstock is rarely ready for the reactor. It often requires significant energy for drying to remove moisture, as well as shredding or grinding to achieve the optimal particle size for efficient heat transfer.
Ancillary Systems and Heat Loss
A pyrolysis plant is more than just a reactor. Energy is consumed by conveyors, pumps, sensors, and control systems. Furthermore, no system is perfectly insulated; some thermal energy is always lost to the environment, a factor known as process-specific heat loss.
The Energy Output: Where Does the Value Come From?
The energy consumed is an investment to unlock the chemical energy stored within the feedstock. The outputs of pyrolysis are where the energy return is generated.
Syngas (Synthesis Gas)
This mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane is a flammable gas. A key feature of efficient pyrolysis plants is their ability to use a portion of this syngas to fuel the reactor, creating a self-sustaining loop that dramatically reduces or eliminates the need for external fuel once the process is running.
Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil)
This liquid product is a dense form of chemical energy. While it often requires upgrading before being used as a transportation fuel, it can be burned directly in industrial furnaces or boilers to generate heat and electricity, displacing the need for fossil fuels.
Bio-char
The solid carbon-rich remnant, bio-char, also has energy value and can be burned as a fuel. Its energy content is a direct contributor to the positive side of the energy balance calculation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Factors That Tip the Energy Balance
Whether a specific pyrolysis operation is a net energy producer or consumer depends entirely on system design and operational discipline.
Feedstock Moisture is Critical
The single largest variable in energy consumption is often the moisture content of the feedstock. Using energy to boil water is highly inefficient. A system fed with dry biomass will have a vastly more favorable energy balance than one fed with wet organic waste.
The Impact of Downstream Processing
Simply burning the raw syngas for heat is energy-efficient. However, if the goal is to produce a pure product, like industrial-grade hydrogen from methane pyrolysis, the energy costs rise significantly. Purification, separation, and compression all require substantial energy inputs.
Scale and Heat Integration
Large, continuous-process industrial plants are far more energy-efficient than small-batch lab units. They have a lower surface-area-to-volume ratio, which minimizes heat loss, and can better integrate heat from the outputs to preheat the incoming feedstock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating the energy profile of pyrolysis requires you to define your objective first.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: Prioritize dry feedstock and design the system to use its own syngas for power, which can make it a highly effective, self-sufficient energy generator.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value chemicals: Be prepared for a less favorable energy balance and budget for the significant energy required for purification, compression, and handling.
- If your primary focus is maximizing net energy production: Invest in a large-scale, continuous, and highly insulated system to minimize heat loss and maximize the capture of energy from all outputs.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis as an energy transformation process, not just a consumer, is the key to evaluating its true potential.
Summary Table:
| Energy Inputs | Energy Outputs |
|---|---|
| Endothermic reaction heat (400-800°C+) | Syngas (can fuel the reactor) |
| Feedstock drying & preparation | Bio-oil (combustible liquid fuel) |
| Ancillary systems & heat loss | Bio-char (solid carbon fuel) |
Ready to turn your waste stream into a net energy producer?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for developing and optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you're focused on waste-to-energy, chemical production, or maximizing efficiency, our solutions help you achieve a positive energy balance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can support your pyrolysis R&D and scale-up goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity



















