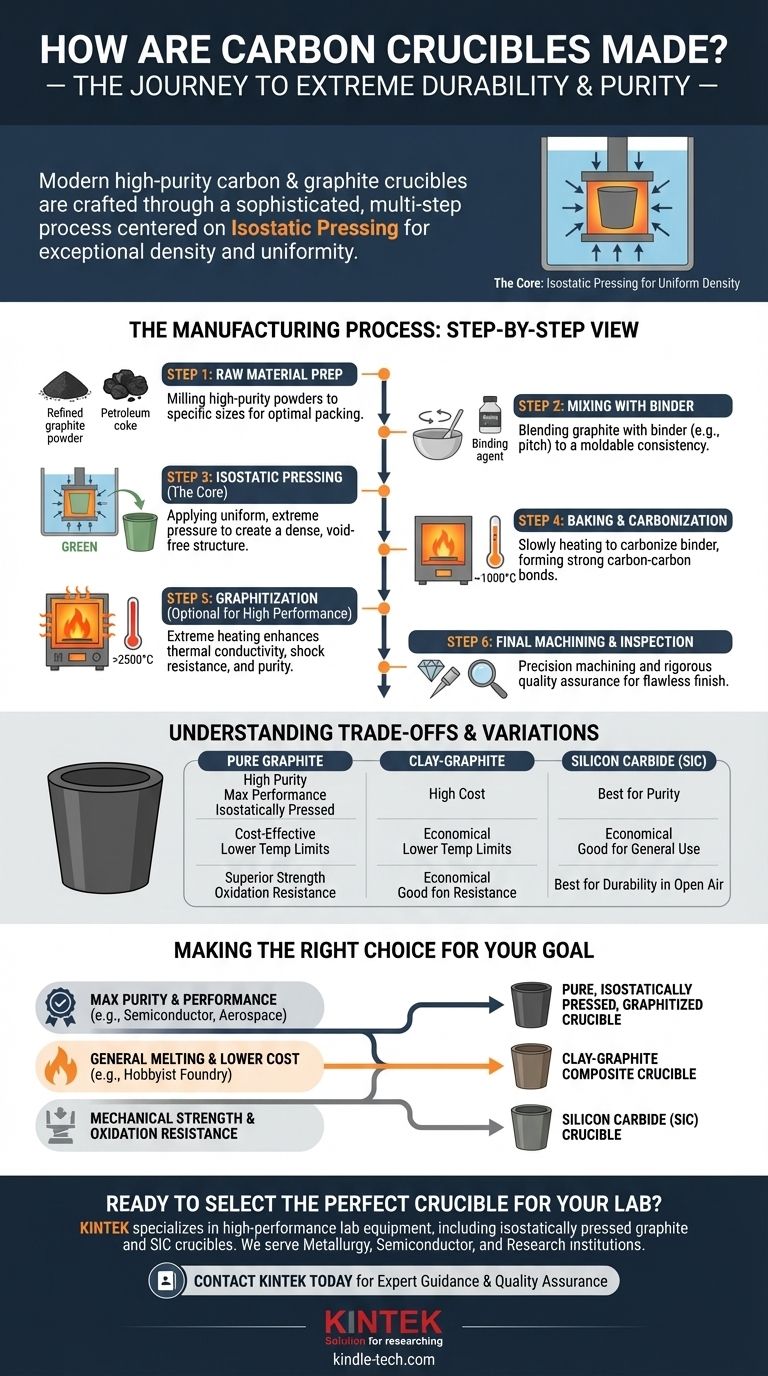
To be direct, modern high-purity carbon and graphite crucibles are made through a multi-step process centered on isostatic pressing. This method involves placing a mixture of refined graphite powder and a binding agent into a flexible mold, which is then submerged in a fluid and subjected to extreme, uniform pressure. This process compacts the raw materials into a highly dense and uniform shape, which is then baked at high temperatures to solidify it into its final, durable form.
The core takeaway is that the manufacturing process is not simple molding, but a sophisticated engineering method designed to create a product with extreme density and structural uniformity. This uniformity is the single most important factor in a crucible's ability to withstand immense thermal shock and prevent catastrophic failure.

The Modern Manufacturing Process: A Step-by-Step View
Understanding how a carbon crucible is made reveals why certain types are superior for demanding applications. The process is precise and energy-intensive, directly translating to the crucible's final performance characteristics.
Step 1: Selecting and Preparing Raw Materials
The process begins with high-purity raw materials, typically petroleum coke or synthetic graphite powder. The purity of these initial ingredients is critical, as any contaminants can leach into the final melt.
These powders are milled to a specific particle size distribution to ensure optimal packing during the molding stage.
Step 2: Mixing with a Binder
The graphite powder is then thoroughly mixed with a binding agent, such as coal tar pitch or a phenolic resin. This binder acts as a temporary glue, giving the mixture a moldable, clay-like consistency.
Step 3: The Core of the Process: Isostatic Pressing
This is the most critical manufacturing step. The graphite-binder mixture is sealed in a flexible, watertight mold shaped like the desired crucible.
This mold is then placed into a high-pressure chamber filled with a liquid (usually water or oil). The liquid is pressurized, applying equal force from all directions onto the mold. This isostatic pressure compacts the powder far more evenly than a traditional mechanical press.
The result of this step is a "green" (unfired) crucible with exceptional density and no internal voids, which are common points of failure.
Step 4: Baking and Carbonization
The green crucible is carefully removed from its mold and placed in a furnace. It is slowly heated in an oxygen-free atmosphere to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F).
During this baking phase, the binder decomposes and carbonizes, forming a strong carbon-carbon bond with the graphite particles. This permanently locks the crucible into its solid, hardened state.
Step 5: Graphitization and Purification
For the highest-performance crucibles, a final heating step called graphitization is performed. The crucible is heated to extremely high temperatures, often above 2500°C (4532°F).
This intense heat converts any remaining amorphous carbon into a more ordered, crystalline graphite structure. This process dramatically increases the crucible's thermal conductivity and shock resistance while vaporizing almost all remaining impurities.
Step 6: Final Machining and Inspection
The finished crucible blank is a hard, strong ceramic-like material. It can now be machined with diamond tooling to achieve precise dimensions and a smooth surface finish.
Finally, every high-quality crucible undergoes rigorous quality assurance, including visual and ultrasonic inspections, to detect any microscopic cracks or flaws that could lead to failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
Not all crucibles are created equal. The manufacturing method and material composition create a clear hierarchy of performance and cost.
Pure Graphite vs. Clay-Graphite
Historically, and for many hobbyist applications today, graphite is mixed with clay. Clay-graphite crucibles are cheaper to produce but have significantly lower temperature limits and thermal shock resistance compared to pure, isostatically pressed graphite.
The Role of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) crucibles are manufactured using the same isostatic pressing and high-temperature firing techniques. They are not a "lesser" material but offer a different set of properties. SiC provides superior physical strength and better resistance to oxidation in open-air environments.
The Cost Factor
The multi-stage, high-temperature process, especially graphitization, is incredibly energy-intensive. This is why high-purity, isostatically pressed graphite crucibles are significantly more expensive than their clay-bonded counterparts. The cost reflects the complex engineering required to ensure reliability under extreme conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a crucible is a technical decision that should be based entirely on the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: You must use a high-purity, isostatically pressed, and graphitized crucible. This is non-negotiable for semiconductor, aerospace, or specialty alloy applications.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose melting at a lower cost: A clay-graphite composite crucible is a viable and economical choice for less sensitive metals and hobbyist foundry work.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and oxidation resistance: A silicon carbide (SiC) crucible, made via the same advanced pressing methods, is often the superior technical choice.
Ultimately, understanding how a crucible is made empowers you to select a tool engineered for the specific thermal and chemical challenges of your work.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Step | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Prep | Milling high-purity graphite/coke | Ensure optimal particle packing and purity |
| 2. Mixing | Combining powder with binder (e.g., pitch) | Achieve moldable consistency |
| 3. Pressing | Isostatic pressing in flexible mold | Create uniform, dense structure without voids |
| 4. Baking | Heating to ~1000°C in inert atmosphere | Carbonize binder, form solid structure |
| 5. Graphitization | Heating above 2500°C (optional) | Enhance thermal conductivity and purity |
| 6. Finishing | Machining and quality inspection | Ensure precise dimensions and flaw-free finish |
Ready to Select the Perfect Crucible for Your Lab?
Understanding the manufacturing process is key to choosing a crucible that won't fail under extreme conditions. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including isostatically pressed graphite and silicon carbide crucibles designed for maximum thermal shock resistance, purity, and durability.
We serve laboratories and industries where precision and reliability are non-negotiable, such as:
- Metallurgy & Alloy Development: For melting high-purity metals and specialty alloys without contamination.
- Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing: Where material purity is critical.
- Research & Academic Institutions: Requiring consistent, repeatable results.
By partnering with KINTEK, you gain:
- Expert Guidance: Our team helps you select the right crucible material and type for your specific application, saving you time and preventing costly errors.
- Quality Assurance: Every crucible we supply meets rigorous standards for density, purity, and structural integrity.
- Enhanced Lab Efficiency: Reduce downtime and improve the safety of your high-temperature processes.
Don't compromise on your results. Let our experts help you make the right choice.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and get a recommendation for the ideal crucible solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
People Also Ask
- How does a magnetron sputtering work? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the effects of magnetron sputtering? Achieve High-Quality, Durable Thin Films for Your Lab
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the fundamental of magnetron sputtering? Master High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















