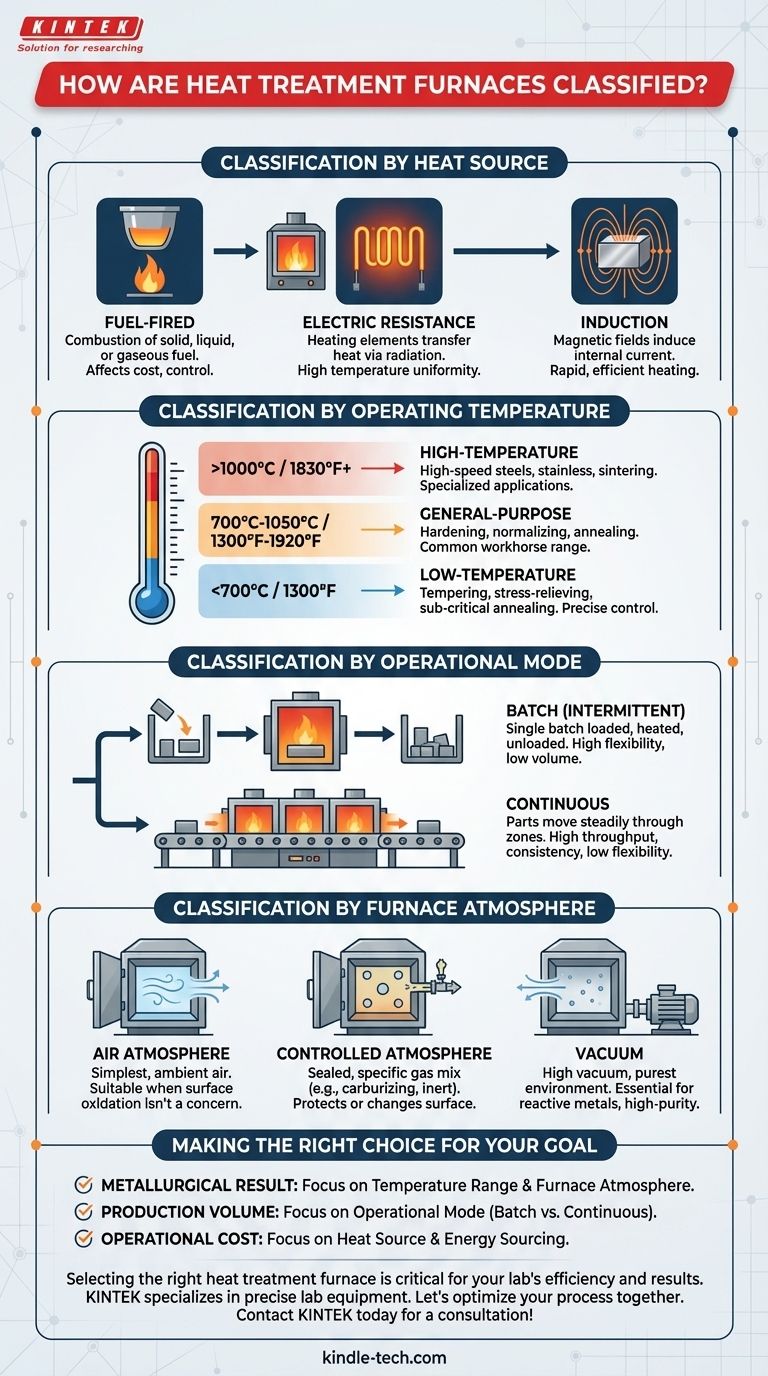
Ultimately, there is no single way to classify a heat treatment furnace. Instead, they are categorized based on several distinct criteria, each answering a different technical or operational question. The most common methods of classification are by the source of heat, the furnace's maximum operating temperature, its mode of operation (batch or continuous), and the type of atmosphere it can maintain.
The most effective way to classify a furnace is to align the classification method with your primary objective. Focusing on the metallurgical process demands classification by temperature and atmosphere, while focusing on production economics requires classifying by heat source and operational mode.

Classification by Heat Source
The method used to generate heat is a fundamental differentiator, impacting operational costs, temperature control, and the types of processes a furnace can perform.
Fuel-Fired Furnaces
These furnaces generate heat through the combustion of fuel. They are often sub-classified by the type of fuel used, such as solid (coal, coke), liquid (kerosene, oil), or gaseous (natural gas, producer gas). The choice is heavily dependent on local fuel availability and cost.
Electric Resistance Furnaces
These furnaces use specialized heating elements that glow hot when a high electric current passes through them, transferring heat primarily through radiation. They offer excellent temperature uniformity and control. They can be further classified by their heating element material, such as nichrome wire, silicon carbide rods, or molybdenum disilicide rods, which determines their maximum temperature.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use powerful, high-frequency magnetic fields to induce an electric current directly within the metal part itself. This internal current generation (eddy currents) causes the material to heat rapidly and efficiently from the inside out. They are often classified by operating frequency, such as medium frequency (500Hz-10kHz) or high frequency (70-200kHz).
Classification by Operating Temperature
The temperature range of a furnace dictates the metallurgical processes it can execute. This is one of the most common ways to categorize furnaces for specific applications.
Low-Temperature Furnaces (up to 700°C / 1300°F)
These furnaces are designed for processes like tempering, stress-relieving, and sub-critical annealing. They provide precise control in a range where steel's properties are modified without changing its core crystal structure.
General-Purpose Furnaces (700°C to 1050°C / 1300°F to 1920°F)
This is the workhorse range for many common heat treatments, including hardening, normalizing, and annealing of most carbon and alloy steels.
High-Temperature Furnaces (1000°C to 1400°C+ / 1830°F to 2550°F+)
Required for specialized applications, these furnaces handle the treatment of high-speed steels, some stainless steels, and sintering of powdered metals. Furnaces with silicon molybdenum elements or induction heating are common in this range.
Classification by Operational Mode
This classification focuses on how material is processed through the furnace, which has major implications for production volume, flexibility, and automation.
Intermittent (Batch) Furnaces
In a batch furnace, a single part or a "batch" of parts is loaded, heated for the required time, and then unloaded. These are highly flexible and ideal for low-volume production, one-off jobs, or processes with varying requirements. A common example is a box furnace.
Continuous Furnaces
In a continuous furnace, parts move steadily through different heating and cooling zones. These are designed for high-volume, standardized production where the same process is repeated constantly. They offer high throughput and consistency but lack the flexibility of batch furnaces.
Classification by Furnace Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is critical for preventing unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation (scaling), or for intentionally changing the surface chemistry of a part.
Air Atmosphere Furnaces
These are the simplest type, where the part is heated in the ambient air. They are suitable only for processes or materials where surface oxidation is not a concern. A typical muffle furnace is often an air atmosphere furnace.
Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces
These furnaces are sealed and filled with a specific gas or mixture of gases to create a controlled chemical environment. This is used for processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or carbonitriding (adding carbon and nitrogen), or simply to provide an inert atmosphere (e.g., argon, nitrogen) to protect the part's surface.
Vacuum Furnaces
For the most sensitive materials that react even with trace amounts of gases, vacuum furnaces are used. The air is pumped out to create a high vacuum, providing the purest possible environment for heat treatment. This is essential for reactive metals like titanium or for high-purity brazing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or specifying a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. No single furnace type is best for every situation.
Cost vs. Precision
Fuel-fired furnaces often have lower operational energy costs but can be harder to control precisely and may introduce combustion byproducts. Electric furnaces offer superior temperature uniformity and a clean environment but may have higher energy costs.
Throughput vs. Flexibility
Continuous furnaces are unmatched for high-volume, repeatable production runs, delivering low per-piece costs. However, they are expensive to install and inflexible. Batch furnaces offer maximum flexibility for varied parts and processes but have lower overall throughput.
Capability vs. Complexity
Adding atmosphere or vacuum control dramatically increases a furnace's capability, but it also adds significant cost, complexity, and maintenance requirements. A simple air furnace is easy to operate, while a vacuum furnace requires specialized knowledge and equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The lens through which you classify a furnace should directly reflect your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific metallurgical result: Classify first by temperature range and furnace atmosphere to ensure the material's requirements are met.
- If your primary focus is production volume and efficiency: Classify by operational mode (batch vs. continuous) to match your manufacturing strategy.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and energy sourcing: Classify by heat source (fuel, electric, induction) to align with your budget and available utilities.
By understanding these distinct classification frameworks, you can evaluate a furnace based on its direct suitability for your specific technical and operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Classification Method | Key Categories | Primary Application Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Fuel-Fired, Electric Resistance, Induction | Operational Cost & Energy Sourcing |
| Operating Temperature | Low-Temp (<700°C), General-Purpose (700-1050°C), High-Temp (>1000°C) | Metallurgical Process Requirements |
| Operational Mode | Batch (Intermittent), Continuous | Production Volume & Flexibility |
| Furnace Atmosphere | Air, Controlled Atmosphere, Vacuum | Material Surface Integrity & Purity |
Selecting the right heat treatment furnace is critical for your lab's efficiency and results. The classification framework shows that the best choice depends on your specific goals: metallurgical outcome, production volume, or operational cost.
KINTEK specializes in providing precise lab equipment and consumables. Whether you need a batch furnace for flexible R&D or a high-temperature vacuum furnace for sensitive materials, our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs and identify the ideal solution for your laboratory's unique challenges.
Let's optimize your heat treatment process together. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the magnetron sputtering technique? A Guide to High-Speed, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of sturdy construction in ultra-low freezers? Ensure Long-Term Sample Security and Reliability
- What are the two uses of a laboratory oven? Drying and Sterilizing with Precision
- What are the methods of XRF? Choosing Between Lab Precision and Field Speed
- What is benefit of sintering? Achieve Superior Material Performance & Complex Part Manufacturing
- How does concentration affect IR? Master Quantitative Analysis and Spectral Interpretation
- How does a constant-temperature laboratory shaker support microbial toxicity testing? Ensure Accurate Nanocomposite Data
- What is the role of a laboratory stirrer or homogenizer in waste paper pretreatment? Maximize Fermentation Yields



















