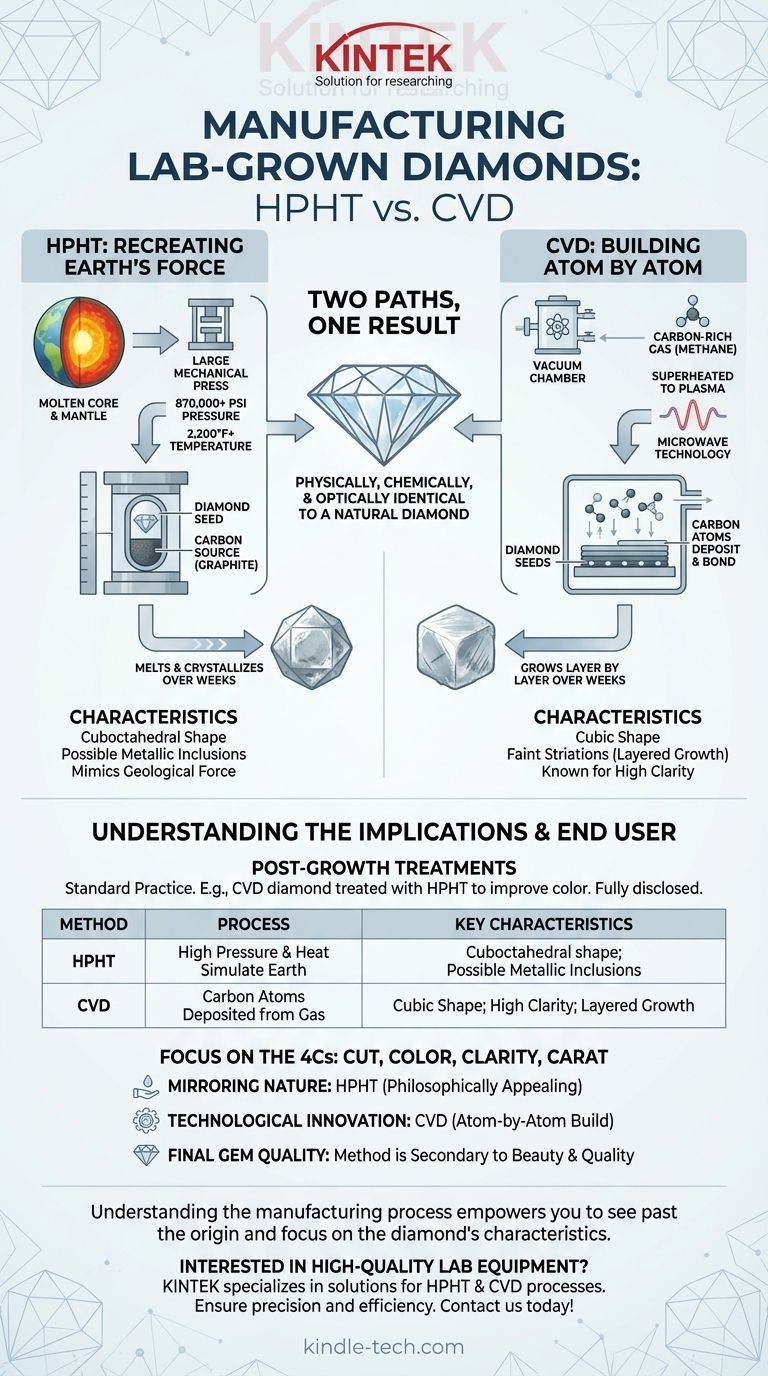
Lab-grown diamonds are created using one of two highly advanced technological processes: High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The HPHT method simulates the immense force found deep within the Earth, while the CVD method "grows" a diamond atom-by-atom from a gas. Crucially, both methods produce a final stone that is physically, chemically, and optically identical to a natural diamond.
While the manufacturing methods differ significantly—one mimicking geological force and the other precisely layering atoms—the final product is a true diamond. The distinction lies in its origin, not in its fundamental properties.

The Two Paths to a Diamond: HPHT vs. CVD
Understanding the two creation processes is key to understanding the lab-grown diamond industry. Each method starts with a "seed"—a tiny sliver of a pre-existing diamond—that acts as the foundation for new crystal growth.
The HPHT Method: Recreating the Earth's Force
The High-Pressure, High-Temperature method is the original process for creating diamonds and directly replicates the conditions of the Earth’s mantle.
A diamond seed is placed in a large mechanical press along with a source of pure carbon, such as graphite.
The press applies immense pressure—over 870,000 pounds per square inch—while simultaneously heating the capsule to temperatures exceeding 2,200°F (1,200°C).
Under these extreme conditions, the carbon source melts and crystallizes around the diamond seed, forming a larger, rough diamond over several days or weeks.
The CVD Method: Building a Diamond Atom by Atom
The Chemical Vapor Deposition method is a newer technique that builds a diamond in layers, akin to how they form in interstellar gas clouds.
Diamond seeds are placed inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is then filled with a carbon-rich gas, like methane.
This gas is superheated into a plasma using technology similar to microwaves. This process breaks the gas molecules apart, releasing carbon atoms.
These carbon atoms "rain down" onto the diamond seeds and bond to the existing crystal structure, growing the diamond layer by layer over a period of several weeks.
Understanding the Implications of Each Method
While the end products are chemically identical, the growth process for each method can leave subtle traces that a trained gemologist can identify. These are not flaws, but rather markers of origin.
Growth Patterns and Inclusions
HPHT diamonds grow in a cuboctahedral shape and may sometimes contain tiny metallic inclusions from the press environment. These are typically invisible to the naked eye.
CVD diamonds grow in a cubic shape, and their layered growth can sometimes result in faint striations. They are generally known for producing diamonds with very high clarity.
Post-Growth Treatments
It is common for both HPHT and CVD diamonds to undergo post-growth treatments to improve their color. For example, a CVD diamond might be treated with the HPHT process to enhance its quality.
This practice is standard and fully disclosed, highlighting how these technologies can even be used together to produce the final gem.
What This Means for the End User
The manufacturing process does not determine whether one diamond is "better" than another. The quality of any diamond, whether mined or lab-grown, is judged by the classic 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat.
- If your primary focus is mirroring nature: The HPHT method, which replicates the intense pressure and heat of the Earth's mantle, might be more philosophically appealing.
- If your primary focus is technological innovation: You might find the CVD method, which builds a diamond atom-by-atom from a gas, more fascinating.
- If your primary focus is simply the final gem: Recognize that both methods produce a diamond that is identical to a mined diamond, making the method secondary to the stone's beauty and quality.
Ultimately, understanding the manufacturing process empowers you to see past the origin and focus on the characteristics of the diamond itself.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT | High pressure and heat simulate Earth's mantle | Grows in cuboctahedral shape; may contain metallic inclusions |
| CVD | Carbon atoms deposited from gas onto a diamond seed | Grows in cubic shape; known for high clarity and layered growth |
Interested in high-quality lab equipment for your diamond research or production? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your needs. Whether you're working with HPHT or CVD processes, our solutions ensure precision and efficiency. Contact us today to learn how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques



















