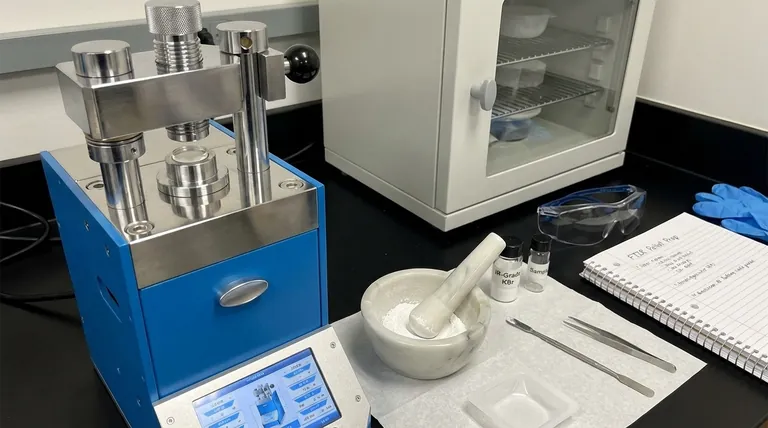
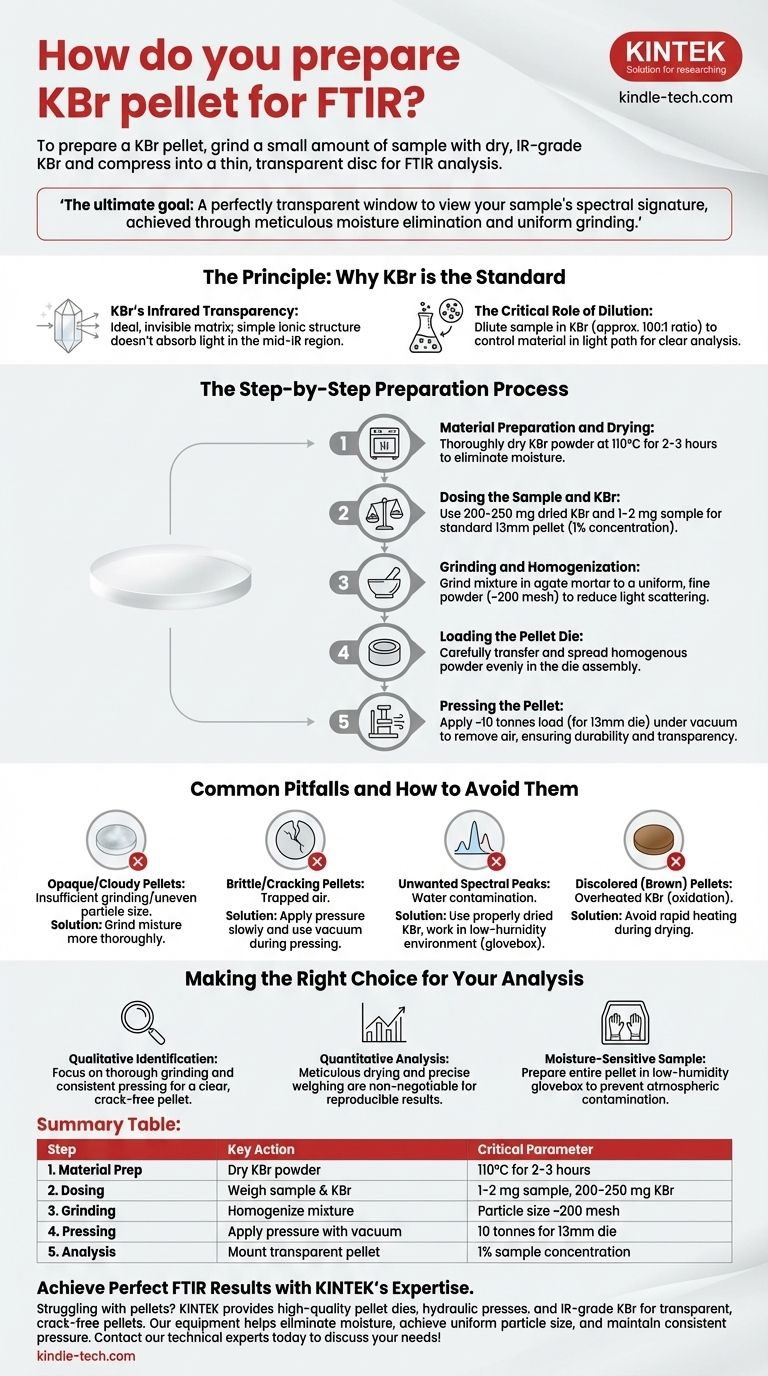
To prepare a KBr pellet for FTIR, you must grind a small amount of your solid sample with dry, IR-grade potassium bromide, and then use a hydraulic press to compress the fine powder mixture into a thin, transparent disc. This process dilutes the sample in an infrared-transparent medium, allowing the spectrometer's IR beam to pass through for analysis.
The ultimate goal is not just to make a solid disc, but to create a perfectly transparent window to view your sample's spectral signature. Success hinges on meticulously eliminating moisture and achieving a uniform, finely ground mixture before applying pressure.

The Principle: Why KBr is the Standard
KBr's Infrared Transparency
Potassium bromide (KBr) is the most common choice for this technique because its simple ionic structure does not absorb light in the mid-infrared region. This makes it an ideal, invisible matrix to hold your sample.
The Critical Role of Dilution
A pure, solid sample is typically too dense and will absorb or scatter the entire IR beam, resulting in a useless spectrum.
By diluting the sample in KBr, usually at a ratio of about 100:1 (KBr:sample), you control the precise amount of material in the light path, ensuring a clear, high-quality analysis.
The Step-by-Step Preparation Process
Step 1: Material Preparation and Drying
Moisture is the primary enemy of a good KBr pellet, as water has strong IR absorption bands that can obscure your sample's data.
KBr powder must be thoroughly dried before use. A standard practice is to heat it at approximately 110°C for at least two to three hours and store it in a desiccator.
Step 2: Dosing the Sample and KBr
For a standard 13 mm (or ½ inch) diameter pellet, you will need 200-250 mg of your dried KBr powder.
You only need a very small amount of your sample, typically just 1-2 mg, to achieve the desired 1% concentration.
Step 3: Grinding and Homogenization
Combine the KBr and sample in a mortar and pestle, preferably made of agate to minimize contamination and ensure a smooth surface.
Grind the mixture until it becomes a uniform, fine powder with a consistency similar to flour. Proper grinding is essential to reduce light scattering and produce a transparent pellet. The target particle size is typically around 200 mesh.
Step 4: Loading the Pellet Die
Carefully transfer the homogenous powder into the pellet die assembly. Ensure the powder is spread evenly across the surface of the die base to promote a pellet of uniform thickness.
Step 5: Pressing the Pellet
Place the loaded die into a hydraulic press. For a 13 mm die, a load of around 10 tonnes is a widely accepted rule of thumb.
If your die set allows for it, apply a vacuum during pressing. This degassing step removes trapped air and residual moisture, which is critical for creating a durable, transparent pellet.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
The Problem: Opaque or Cloudy Pellets
A cloudy pellet is typically caused by insufficient grinding or uneven particle size. This leads to excessive scattering of the infrared beam, weakening your signal. The solution is to grind the mixture more thoroughly.
The Problem: Brittle or Cracking Pellets
Pellets that break easily are almost always the result of trapped air. Applying pressure too quickly or, more importantly, failing to apply a vacuum during pressing can cause this.
The Problem: Unwanted Spectral Peaks
The appearance of broad peaks around 3400 cm⁻¹ and a sharp peak near 1630 cm⁻¹ is a classic sign of water contamination. This underscores the absolute necessity of using properly dried KBr and, if possible, working in a low-humidity environment like a glovebox.
The Problem: Discolored (Brown) Pellets
If your KBr powder turns brown, it has likely been overheated during the drying process, causing some of it to oxidize into potassium bromate (KBrO₃). Avoid rapid heating to prevent this discoloration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
- If your primary focus is routine qualitative identification: Your main goal is a clear, crack-free pellet; ensure thorough grinding and consistent pressing pressure.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Meticulous drying of KBr and precise, repeatable weighing of your sample are non-negotiable for achieving reproducible results.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a moisture-sensitive sample: Preparing the entire pellet inside a low-humidity glovebox is the most effective strategy to prevent atmospheric water contamination.
Mastering this technique transforms a simple powder into a clear window for precise molecular analysis.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Critical Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Prep | Dry KBr powder | 110°C for 2-3 hours |
| 2. Dosing | Weigh sample & KBr | 1-2 mg sample, 200-250 mg KBr |
| 3. Grinding | Homogenize mixture | Particle size ~200 mesh |
| 4. Pressing | Apply pressure with vacuum | 10 tonnes for 13mm die |
| 5. Analysis | Mount transparent pellet | 1% sample concentration |
Achieve Perfect FTIR Results with KINTEK's Expertise
Struggling with cloudy pellets or water contamination in your FTIR analysis? KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory professionals with high-quality pellet dies, hydraulic presses, and IR-grade potassium bromide that ensure transparent, crack-free pellets every time.
Our equipment and consumables are designed to help you:
- Eliminate moisture contamination with proper drying protocols
- Achieve uniform particle size for clear spectral windows
- Maintain consistent pressure for reproducible quantitative analysis
Whether you're performing routine qualitative identification or precise quantitative measurements, KINTEK has the solutions to enhance your FTIR workflow.
Contact our technical experts today to discuss your specific FTIR pellet preparation needs and discover how our lab equipment can improve your analytical results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in testing solid-state electrolytes? Optimize Your Material Density
- What role do laboratory hydraulic presses play in HPHT diamond synthesis? Powering Extreme Carbon Transformation
- Why is it necessary to process nickel ore powder into pellets? Optimize Gas Permeability for Reductive Roasting
- Why KBr is used as material for pellets formation in IR-spectroscopy? The Ideal Matrix for Clear, Accurate Analysis
- What kind of press is used for forging? The Definitive Guide to Hydraulic Forging Presses
- What is the primary function of a laboratory uniaxial hydraulic press in LLZO processing? Optimize Your Green Pellets
- What are the advantages of press forging in comparison to drop forging? Superior Control and Material Integrity
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in molecular sieve catalyst preparation? Achieve Optimal Pelleting



















