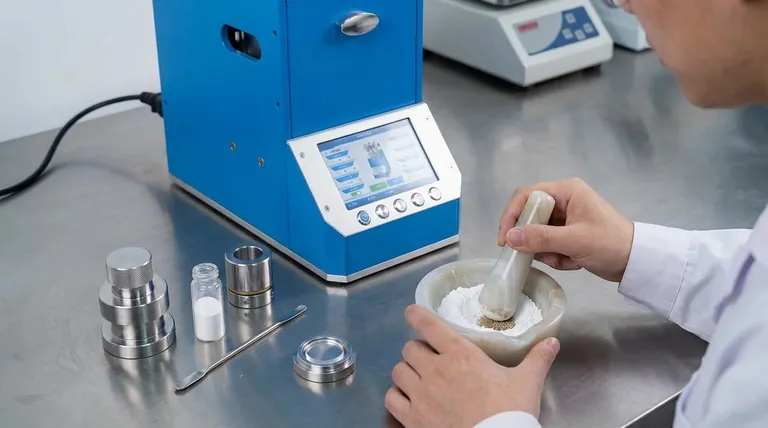
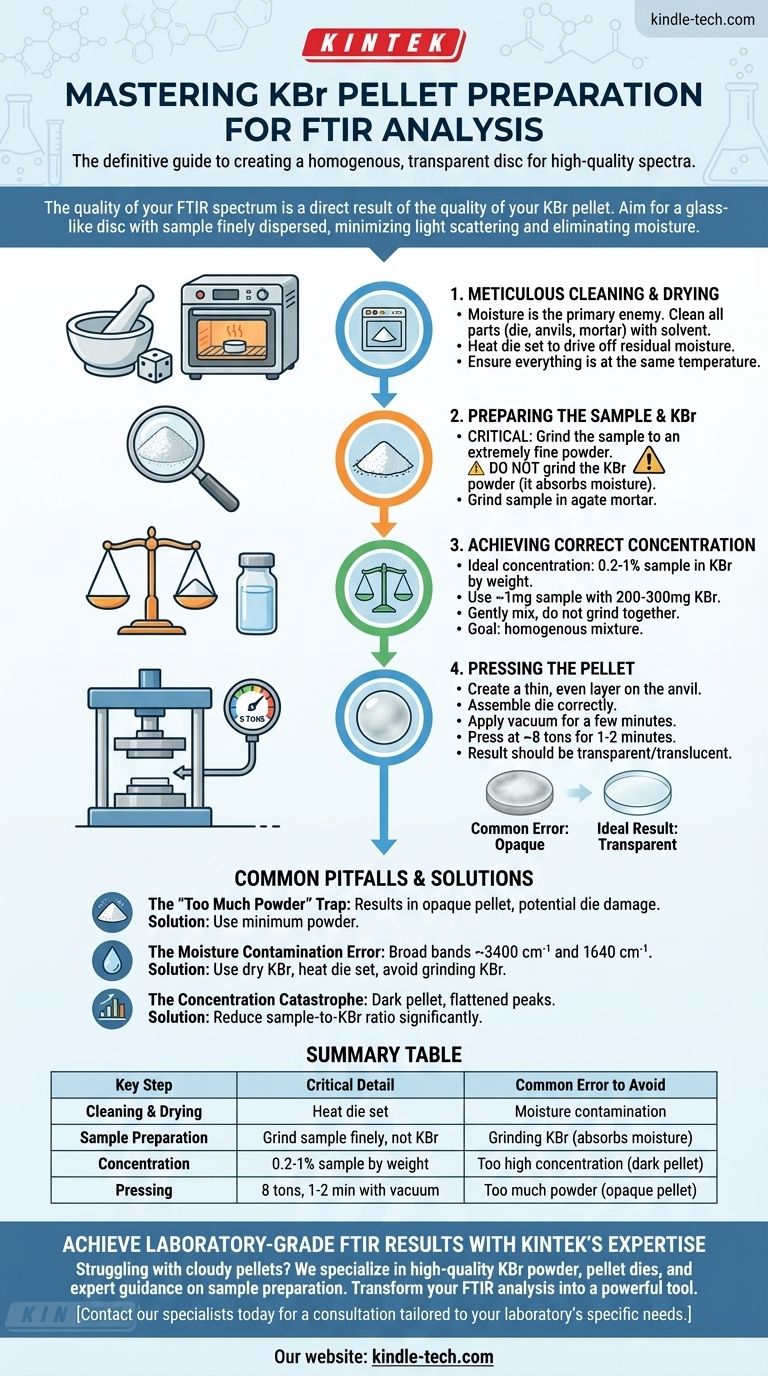
The definitive method for preparing a KBr pellet involves meticulously grinding your sample, mixing a tiny fraction of it (0.2-1%) into dry KBr powder, and pressing the mixture in a die under high pressure. The key is to create a homogenous, glass-like disc that is transparent to the infrared beam, which requires scrupulously clean and dry equipment and a minimal amount of material.
The quality of your FTIR spectrum is a direct result of the quality of your KBr pellet. The goal is not simply to press a disc, but to create an optically clear medium where your sample is finely dispersed, minimizing light scattering and eliminating moisture contamination.

The Foundation: Why KBr Works
Potassium Bromide (KBr) is the standard for solid-state FTIR analysis because it is transparent to infrared radiation across the typical mid-IR range (4000-400 cm⁻¹). It acts as a perfect "window" for the analysis.
The Goal: A Solid-State "Solution"
Think of the KBr pellet as a solid-state version of a solution. Your solid sample is the "solute," and the KBr powder is the "solvent."
The objective is to grind the sample into particles so small they don't scatter the IR beam and disperse them evenly throughout the KBr matrix. A poorly mixed or cloudy pellet will scatter light, creating a noisy and unreliable spectrum.
Step-by-Step Pellet Preparation
Following these steps methodically will prevent the most common sources of error and lead to high-quality, reproducible spectra.
1. Meticulous Cleaning and Drying
Moisture is the primary enemy of good KBr pellets, as water has strong IR absorption bands.
First, clean all parts of your pellet die (anvils and body) and your mortar and pestle. Use a solvent like acetone or chloroform, then wipe completely dry with a tissue.
For the highest quality, gently heat the die set and anvils in an oven before use to drive off any residual moisture. Ensure all equipment and the KBr powder are at the same temperature before pressing.
2. Preparing the Sample and KBr
This is the most critical step and a common source of error. Grind the sample, not the KBr.
Use an agate mortar and pestle to grind a small amount of your solid sample into an extremely fine powder. The finer the particle size, the less light scattering will occur.
Do not grind the KBr powder. KBr is a crystalline salt. Grinding it opens up new crystal facets that aggressively absorb atmospheric moisture, which will contaminate your spectrum.
3. Achieving the Correct Concentration
A pellet is much thicker than a typical liquid sample film, so a very low concentration is required.
The ideal concentration of your sample in KBr is between 0.2% and 1% by weight. A common starting point for a 13mm die is 1 mg of sample mixed with 200-300 mg of KBr powder.
Add your finely ground sample to the KBr powder in the mortar and gently but thoroughly mix them together with the pestle. The goal is a perfectly homogenous mixture without any further aggressive grinding.
4. Pressing the Pellet
Use just enough of the KBr/sample mixture to create a thin, even layer on the face of the die's anvil.
Assemble the die set correctly. If using a vacuum die, which helps remove trapped air and moisture, ensure the seals are good and apply a vacuum for a few minutes before pressing.
Apply pressure according to the die manufacturer's instructions. A typical load for a 13mm die is around 8 tons. Hold the pressure for a minute or two to allow the KBr to flow and form a clear disc. The result should be a transparent or translucent pellet, like a small piece of glass.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced analysts can make mistakes. Understanding these pitfalls is key to troubleshooting.
The "Too Much Powder" Trap
This is the most frequent mistake. Using too much of the KBr mixture results in an opaque, white pellet. It also requires excessive force to press, which can crack the pellet, damage the die, or cause the pellet to become permanently wedged.
Solution: Use the minimum powder necessary to thinly coat the anvil face.
The Moisture Contamination Error
Moisture contamination is immediately obvious in a spectrum as broad absorption bands around 3400 cm⁻¹ and a sharp band near 1640 cm⁻¹. This can obscure important sample peaks.
Solution: Always use dry KBr, heat your die set, and never grind the KBr itself. For highly sensitive work or in humid environments, prepare pellets inside a glovebox.
The Concentration Catastrophe
If the pellet appears dark or the resulting spectrum has flattened, broad peaks (total absorption), your sample concentration is too high. If the spectral baseline is very noisy and sloped, it is likely due to light scattering from either a cloudy pellet or poorly ground sample particles.
Solution: Reduce the sample-to-KBr ratio significantly. Ensure the sample is ground to a flour-like consistency before mixing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your preparation can be tailored to your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is routine qualitative analysis: Prioritize consistency. Focus on avoiding the main pitfalls of using too much powder and ensuring your equipment is dry.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity quantitative analysis: Precision is paramount. Carefully weigh your sample and KBr, ensure homogenous mixing, and use a vacuum die to eliminate moisture and trapped air for the clearest possible pellet.
- If you are consistently getting cloudy pellets: The problem is almost certainly either particle size or concentration. Re-evaluate your sample grinding technique and drastically reduce the amount of sample used.
Mastering this technique is a fundamental skill that transforms FTIR from a simple measurement into a powerful analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Critical Detail | Common Error to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning & Drying | Heat die set to remove moisture | Moisture contamination (3400 cm⁻¹ band) |
| Sample Preparation | Grind sample finely, not KBr | Grinding KBr (absorbs moisture) |
| Concentration | 0.2-1% sample in KBr by weight | Too high concentration (dark pellet) |
| Pressing | 8 tons for 1-2 minutes with vacuum | Too much powder (opaque pellet) |
Achieve laboratory-grade FTIR results with KINTEK's expertise.
Struggling with cloudy pellets or inconsistent spectra? Our team specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise analytical preparation. We provide:
- High-quality KBr powder and pellet dies
- Expert guidance on sample preparation techniques
- Solutions for moisture-sensitive applications
Let KINTEK help you transform your FTIR analysis from a simple measurement into a powerful, reliable tool. Contact our specialists today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is a BARS press? Discover the Engineering Secrets to Growing Large, Gem-Quality Diamonds
- What is a 100 ton press used for? A Guide to Industrial Bending, Forming, and Assembly
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to MIC testing? Ensure Precision in Stainless Steel Specimens
- What are the advantages of power press? Achieve High-Speed, Low-Cost Mass Production
- How are laboratory hydraulic presses applied in neural implant manufacturing? Precision Tools for Neural Electrodes
- What are the two applications of a hydraulic press? From Industrial Forging to Lab Analysis
- What is the function of a laboratory uniaxial hydraulic press in battery assembly? Unlock High-Performance Cells
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in preparing solid model materials? Standardize for Precise Data.



















