To start a pyrolysis plant, you must begin with a strategic planning phase that includes conducting a thorough feasibility study, securing a consistent feedstock supply, and navigating the complex landscape of local regulations and permits. Only after these foundational business and legal elements are in place can you proceed to the technical design, construction, and safe operation of the facility.
Success in launching a pyrolysis plant hinges less on the reactor technology itself and more on meticulously planning the entire ecosystem around it—from the sourcing of waste materials to the final market for your end products.

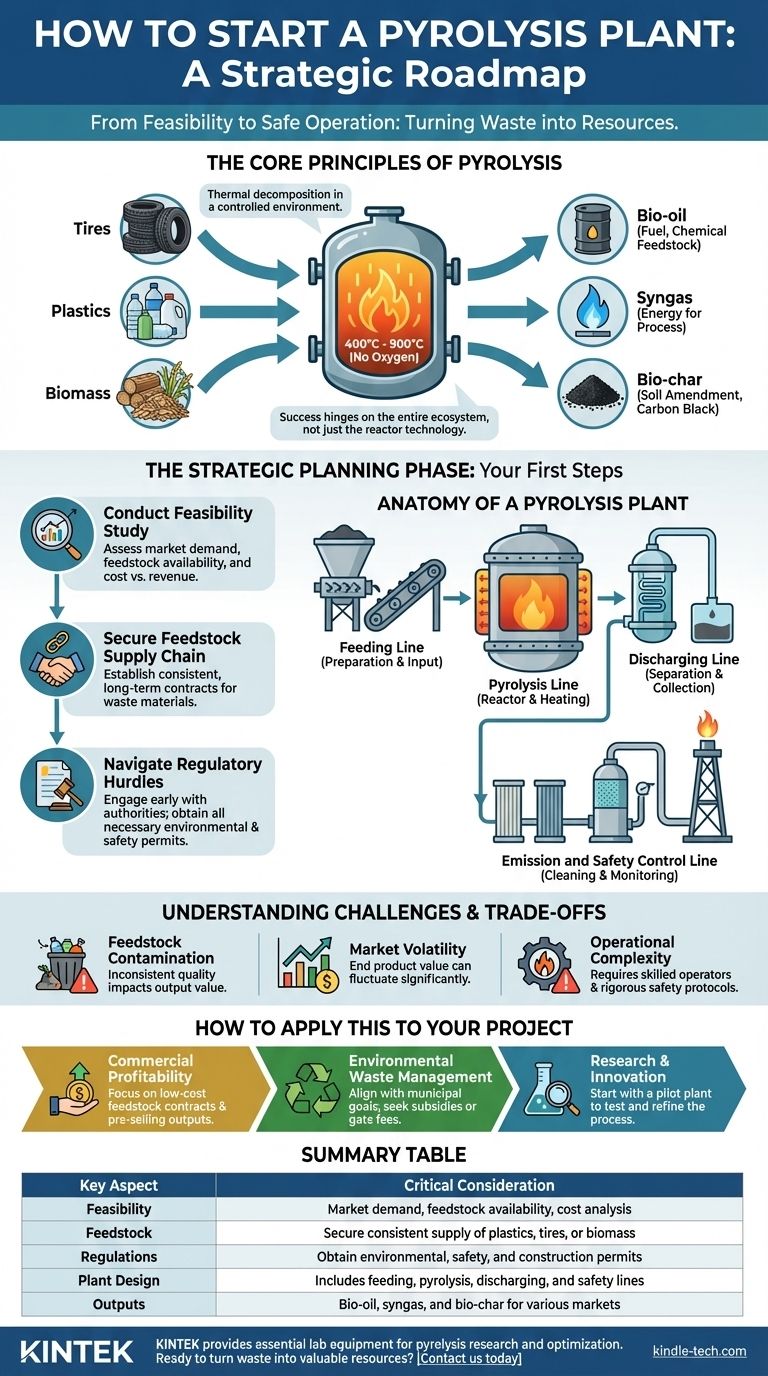
The Core Principles of Pyrolysis
Before diving into the business logistics, it's critical to understand the fundamental process. Pyrolysis is a form of thermal decomposition that operates in a specific, controlled environment.
The Process: Heat Without Oxygen
A pyrolysis plant works by feeding organic materials, such as plastics, tires, or biomass, into a sealed reactor. This material is then heated to very high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 900°C.
Crucially, this process occurs in the near or total absence of oxygen. This prevents combustion (burning) and instead causes the long-chain molecules within the feedstock to break down, or "crack," into smaller, more valuable components.
Key Inputs (Feedstock)
The viability of your plant is directly tied to your feedstock. While many organic materials can be used, common inputs include:
- Waste plastics
- End-of-life tires
- Biomass (wood waste, agricultural residue)
- Textile and rubber scraps
The type and purity of your feedstock will determine the characteristics and quality of your outputs.
Primary Outputs
The thermal decomposition process yields three primary products, each with its own potential market:
- Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil): A liquid fuel that can be refined or used in boilers and furnaces.
- Syngas (Synthesis Gas): A mixture of combustible gases that can be used to power the plant itself, making the process more energy-efficient.
- Bio-char (or Carbon Black): A solid, carbon-rich material used as a soil amendment, for producing activated carbon, or as a solid fuel.
The Strategic Planning Phase: Your First Steps
The most common point of failure is not in the technology, but in the preliminary planning. Rushing this stage is a critical error.
Step 1: Conduct a Feasibility Study
Before any investment, you must assess the viability of your project. This study should objectively analyze the availability of feedstock, the local market demand for the end products, and your projected operational costs versus potential revenue.
Step 2: Secure Your Feedstock Supply Chain
Your entire operation depends on a steady, reliable, and affordable source of waste material. You must secure contracts or firm agreements for collecting materials like waste tires or plastics.
The consistency of this supply is as important as the quantity. Fluctuations in the type or contamination level of your feedstock can significantly impact plant efficiency and output quality.
Step 3: Navigate Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles
A pyrolysis plant is an industrial facility subject to strict environmental and safety regulations. Engaging with local environmental agencies and municipal authorities from the very beginning is non-negotiable.
You will need to obtain numerous permits covering emissions, waste handling, and construction. Consulting with environmental experts and legal advisors is essential to ensure full compliance.
Anatomy of a Pyrolysis Plant
While designs vary based on feedstock and scale, most plants are comprised of four primary operational lines.
The Feeding Line
This is the system that prepares and inputs the raw material into the reactor. It may include shredders to reduce the size of the feedstock and a conveyor or screw system to feed it into the sealed chamber.
The Pyrolysis Line
This is the heart of the plant, containing the pyrolysis reactor. The reactor is heated externally, and its design is critical for ensuring even heat distribution and preventing oxygen from entering.
The Discharging Line
Once the process is complete, the outputs must be safely separated and removed. This includes systems to condense and collect the bio-oil, pipe off the syngas, and discharge the solid bio-char.
The Emission and Safety Control Line
This system is paramount for safe and compliant operation. It includes equipment to clean the syngas before it's used or flared and comprehensive safety controls to monitor temperature, pressure, and other critical operational parameters.
Understanding the Challenges and Trade-offs
Building a pyrolysis plant is a complex undertaking with significant challenges that must be anticipated.
Feedstock Contamination and Consistency
Mixed plastics or dirty feedstock can introduce contaminants that lower the quality of your bio-oil and bio-char. A consistent, clean feedstock stream is ideal but often difficult and more expensive to secure.
Market for End Products
Producing bio-oil is only half the battle; you must have a market to sell it. The value of pyrolysis products can fluctuate, and you may need to invest in refining or upgrading them to meet buyer specifications.
Operational Complexity and Safety
These are not "set-it-and-forget-it" facilities. They require skilled operators to manage the process and sophisticated control systems to maintain safety. Handling high temperatures and flammable gases presents inherent operational risks that must be managed professionally.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your approach should be dictated by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is commercial profitability: Prioritize securing long-term feedstock contracts at a low cost and pre-selling your end products to establish a stable market.
- If your primary focus is environmental waste management: Engage with municipal authorities early to align your plant's capabilities with their waste reduction goals, potentially securing subsidies or gate fees.
- If your primary focus is research and innovation: Start with a smaller-scale pilot plant to test different feedstocks and refine the process before considering industrial scaling.
Ultimately, a successful pyrolysis plant is a carefully orchestrated system where technology, logistics, and market demand are perfectly aligned.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|
| Feasibility | Market demand, feedstock availability, cost analysis |
| Feedstock | Secure consistent supply of plastics, tires, or biomass |
| Regulations | Obtain environmental, safety, and construction permits |
| Plant Design | Includes feeding, pyrolysis, discharging, and safety lines |
| Outputs | Bio-oil, syngas, and bio-char for various markets |
Ready to turn waste into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for pyrolysis research, process optimization, and quality control. Whether you're testing feedstock, analyzing bio-oil, or scaling up your operation, our reliable tools help ensure accuracy and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your pyrolysis project from pilot to production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why are high-strength alloy tube reactors critical for HHIP? Ensuring Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Environments
- Why must SCWG reactors maintain a specific heating rate? Protect Your High-Pressure Vessels from Thermal Stress
- Why are high-precision pressure sensors and temperature control systems critical for hydrothermal reaction equilibrium?
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- What are the technical characteristics of PTFE (Teflon) lined hydrothermal reactors? Comparing α-ZrP Synthesis Methods


















