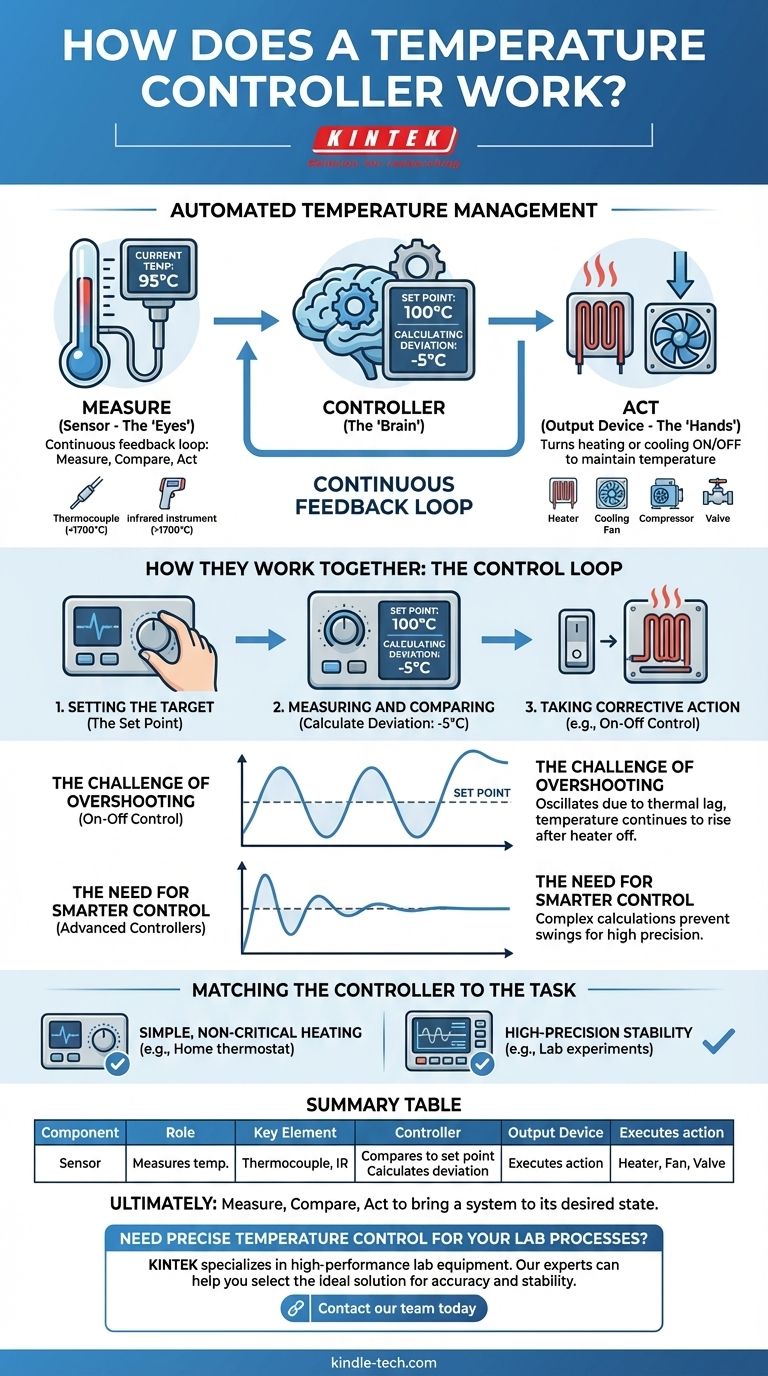
At its core, a temperature controller is a device that automates temperature management. It works by continuously comparing the actual temperature from a sensor to a desired temperature, or "set point." Based on the difference between these two values, it turns a heating or cooling device on or off to maintain the desired temperature automatically.
The fundamental principle behind any temperature controller is a simple, continuous feedback loop: Measure the current temperature, Compare it to the target, and Act to correct any deviation.

The Three Core Components of Temperature Control
To understand how a controller functions, it's best to think of it as a system with three distinct parts working in unison.
The Sensor (The "Eyes")
The sensor is the component that measures the actual temperature of the process. It acts as the system's eyes, providing the raw data the controller needs.
Different sensors are used for different temperature ranges, such as a thermocouple for temperatures below 1700°C or an infrared instrument for even higher temperatures.
The Controller (The "Brain")
The controller is the central processing unit of the system. Its primary job is to constantly compare the real-time temperature data from the sensor with the set point that has been programmed by a user.
The difference between the actual temperature and the set point is known as the deviation or error. The controller uses this value to decide what to do next.
The Output Device (The "Hands")
The output device is the equipment that the controller manages to actually alter the temperature. This could be a heater, a cooling fan, a compressor, or a valve.
The controller sends a signal to this device, telling it when to turn on or off to bring the process temperature back toward the set point.
How They Work Together: The Control Loop
The real power of a temperature controller comes from the continuous loop these three components create.
Setting the Target (The Set Point)
First, an operator defines the desired temperature. This could be done by turning a dial or entering a value on a digital interface. This value is the set point.
Measuring and Comparing
Once active, the controller receives a constant signal from the sensor. It immediately subtracts this measured value from the set point to calculate the deviation.
For example, if the set point is 100°C and the sensor reads 95°C, the deviation is -5°C.
Taking Corrective Action
The controller then acts based on this deviation. In the simplest type of control, called On-Off control, the logic is straightforward.
If the temperature drops below the set point, the controller sends a signal to turn the heater on. When the temperature rises to meet the set point, the controller cuts power to the heater.
This cycle repeats indefinitely to automatically hold the temperature around the desired value.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While simple and effective for many tasks, the basic On-Off control method has inherent limitations.
The Challenge of Overshooting
Because of thermal lag, a simple On-Off system will often overshoot the set point. The temperature will continue to rise for a short time even after the heater is turned off, and it will fall below the set point before the heater can bring it back up.
This results in a temperature that constantly oscillates above and below the target rather than holding steady.
The Need for Smarter Control
For processes requiring high precision, more advanced controllers are needed. These devices perform more complex calculations based on the deviation, as well as how quickly it's changing.
This allows them to apply heat more intelligently—for example, by reducing power as the temperature approaches the set point—to prevent overshooting and maintain a much more stable temperature.
Matching the Controller to the Task
Choosing the right type of control depends entirely on the requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is simple, non-critical heating (like a home thermostat or basic appliance): A simple On-Off controller is sufficient, reliable, and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-precision stability (like in industrial manufacturing or a scientific lab): You need a more advanced controller capable of sophisticated calculations to avoid temperature swings.
Ultimately, every temperature controller operates on the same fundamental principle of measure, compare, and act to bring a system to its desired state.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role | Key Element |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor | Measures the current temperature | Thermocouple, Infrared Instrument |
| Controller | Compares measurement to set point | Calculates deviation (error) |
| Output Device | Executes the heating/cooling action | Heater, Cooling Fan, Valve |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the ideal temperature control solution to ensure accuracy, stability, and efficiency in your experiments. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in hot-pressing sintering? Achieve Precision in Silicon Nitride Ceramic
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- How long does a heat press machine last? Maximize Your Investment with the Right Choice
- What is a good mini heat press? Achieve Professional Results on Small, Complex Items



















