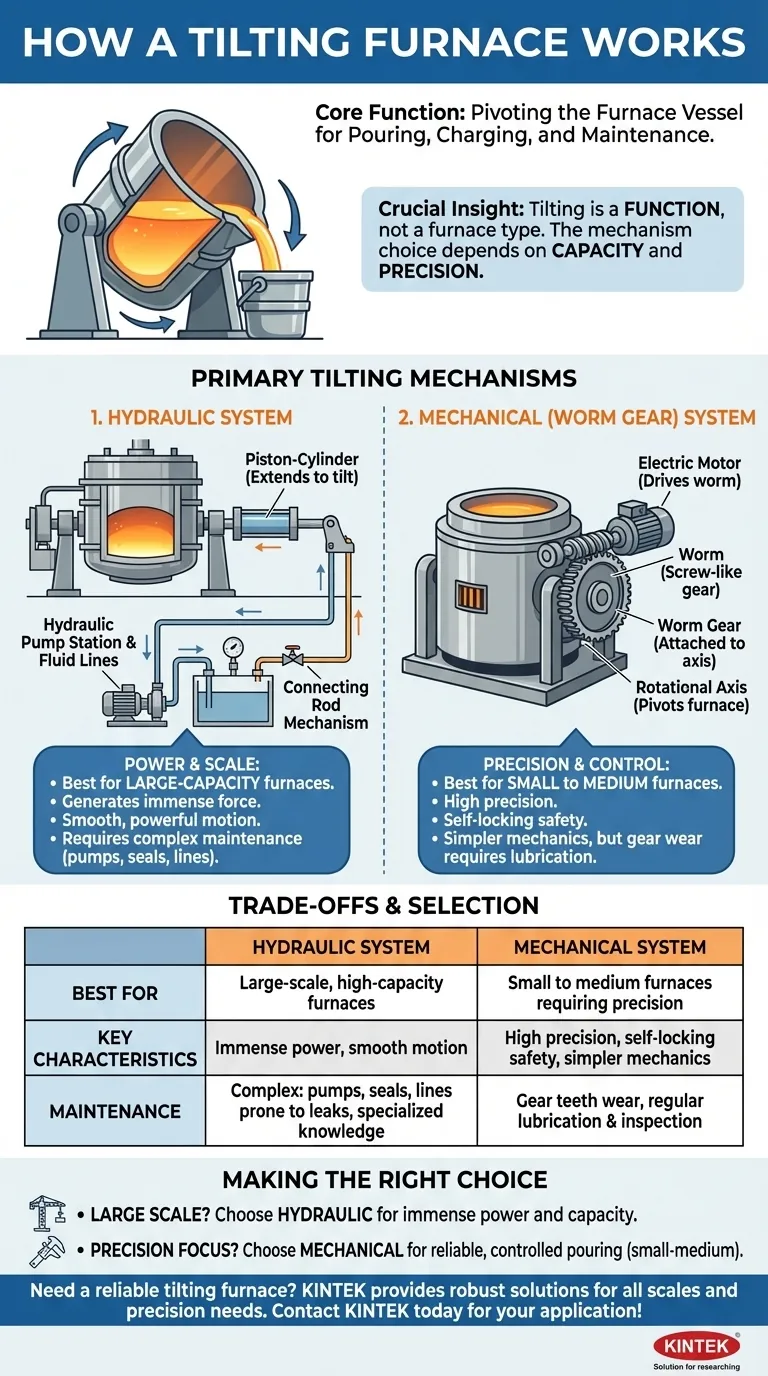
At its core, a tilting furnace works by physically pivoting the main vessel of the furnace. This is accomplished using a powerful actuation system, most commonly hydraulic pistons or a motor-driven gear mechanism. The entire furnace body rotates on a horizontal axis, allowing for the precise and controlled pouring of molten metal into a ladle or mold, as well as facilitating charging and maintenance.
The essential takeaway is that "tilting" is a function, not a single type of furnace. The choice between the two primary mechanisms—hydraulic and mechanical gear-driven—is dictated by the furnace's capacity and the level of precision required for the operation.

The Core Function of a Tilting Furnace
Before examining the mechanisms, it's crucial to understand why tilting is a fundamental requirement in many metallurgical operations. The ability to tilt the furnace serves several critical purposes.
Purpose 1: Pouring Molten Metal
The primary and most obvious function is tapping, or pouring the molten metal out of the furnace once it has reached the desired temperature and composition. A controlled tilt ensures a smooth, safe pour with minimal splashing and turbulence.
Purpose 2: Aiding in Charging and Maintenance
Tilting can also be used to position the furnace for easier charging (loading raw materials) or for maintenance tasks like electrode removal and replacement in an electric arc furnace.
Primary Tilting Mechanisms Explained
While the goal is simple—to tilt the furnace—the engineering to accomplish it for a vessel holding tons of molten metal is significant. Two designs dominate the industry.
Hydraulic Tilting Systems
A hydraulic tilting system uses the power of pressurized fluid to move the furnace. It consists of a high-pressure pump station, pipelines, and one or more hydraulic piston-cylinders connected to the furnace body.
When activated, the pump forces hydraulic fluid into the cylinders, extending the pistons. This linear force is transferred through a connecting rod mechanism, which rotates the furnace smoothly and powerfully. This method is common for larger furnaces where immense force is required.
Mechanical (Worm Gear) Tilting Systems
This mechanism relies on a motor and a specialized gear set. An electric motor drives a worm (a screw-like gear), which meshes with a large worm gear attached to the furnace's rotational axis.
As the motor turns the worm, the worm gear rotates very slowly but with tremendous torque, tilting the furnace with high precision. This system is often favored for small to medium-sized induction furnaces, typically in the 1 to 3-ton capacity range.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hydraulic vs. Mechanical
Choosing between a hydraulic and a mechanical system involves clear engineering trade-offs related to power, control, and maintenance.
Power and Scale
Hydraulic systems generate immense force, making them the standard for large-capacity furnaces where the weight of the vessel and its contents is substantial.
Mechanical gear systems are highly effective but are generally limited to smaller-scale applications where the required torque is lower.
Precision and Control
The worm gear mechanism is naturally self-locking, meaning it cannot be driven in reverse. This provides an inherent safety feature and allows for extremely precise, non-slipping positional control during a pour.
Hydraulic systems offer very smooth and powerful motion but require more complex control valves and systems to achieve the same level of fine-tuned positioning.
Maintenance and Complexity
Hydraulic systems involve pumps, high-pressure lines, and seals that can be prone to leaks over time. Maintenance often requires specialized knowledge of hydraulic circuits.
Mechanical systems are generally simpler, but the gear teeth are subject to significant wear and require regular lubrication and inspection to prevent failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The selection of a tilting mechanism is not arbitrary; it is a direct consequence of the furnace's intended scale and operational demands.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production: A hydraulic system is the necessary choice to handle the immense weight and provide the raw power needed to tilt high-capacity furnaces safely.
- If your primary focus is precision for small to medium furnaces: A motor-driven worm gear system offers excellent, reliable control with simpler mechanics and inherent safety features.
Ultimately, the right tilting system is the one that safely and reliably matches the physical demands of the furnace it is designed to move.
Summary Table:
| Tilting Mechanism | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic System | Large-scale, high-capacity furnaces | Immense power, smooth motion, complex maintenance |
| Mechanical (Worm Gear) System | Small to medium furnaces requiring precision | High precision, self-locking safety, simpler mechanics |
Need a reliable tilting furnace for your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust furnaces tailored to your specific metallurgical processes. Whether you require the immense power of a hydraulic system for large-scale production or the precise control of a mechanical gear system for smaller batches, our experts can help you select the right equipment to ensure safe, efficient, and controlled pouring.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the perfect tilting furnace solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















