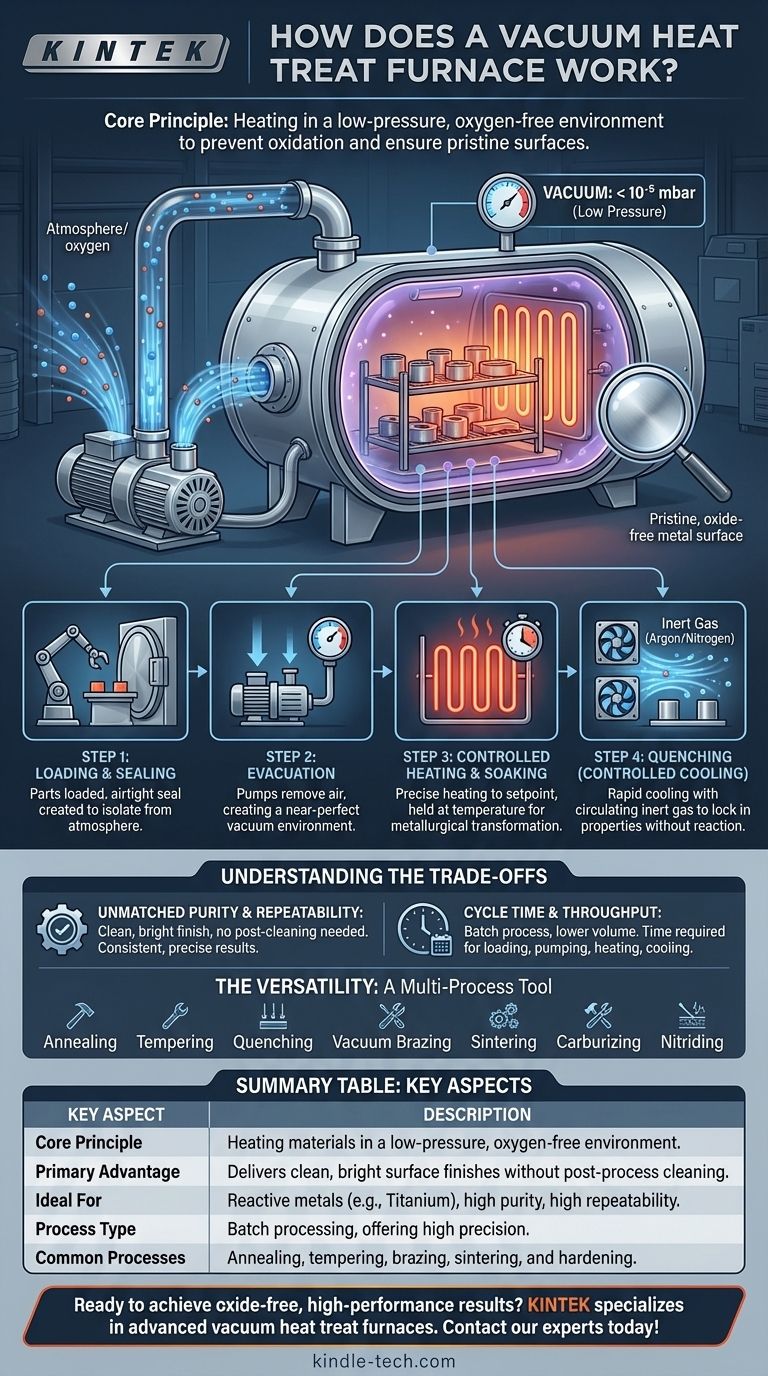
At its core, a vacuum heat treat furnace works by removing the atmosphere from a sealed chamber before heating a material to a specific temperature. This process uses a vacuum system to pump out reactive gases like oxygen, followed by precise heating and controlled cooling cycles. This method gives metallurgists exceptional control over the final properties of the material.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum furnace is not simply to heat material, but to do so in a chemically non-reactive environment. By eliminating oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants, it prevents oxidation and ensures the material's surface remains pristine, enabling metallurgical outcomes that are impossible in a conventional furnace.

The Fundamental Principle: Controlling the Atmosphere
A vacuum furnace is a comprehensive technology that integrates vacuum and heat treatment principles. Its primary advantage comes from manipulating the environment in which the thermal process takes place.
What is a "Vacuum" Environment?
The term "vacuum" refers to any atmospheric pressure below standard sea-level pressure. It does not mean a perfect void.
Vacuum furnaces operate in environments ranging from low to ultra-high vacuum, depending on the material and process requirements. The key is reducing the number of gas molecules, particularly oxygen, that can interact with the parts.
The Primary Goal: Eliminating Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals readily react with oxygen in the air. This reaction, called oxidation, forms a layer of scale on the part's surface.
By pumping the air out of the chamber, the furnace removes the oxygen. This allows the material to be heated, soaked, and cooled without forming an oxide layer, resulting in a clean, bright surface finish that often requires no secondary cleaning.
The Step-by-Step Operational Cycle
A vacuum furnace operates as a batch furnace, meaning it processes one load of parts at a time. The entire cycle must be completed before the next batch can be loaded.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
Parts, components, or tools are loaded into the furnace chamber. The furnace door is then closed and an airtight seal is created, isolating the chamber from the outside atmosphere.
Step 2: Evacuation (Creating the Vacuum)
A system of vacuum pumps is activated to remove the air from the sealed chamber. This process continues until the desired low-pressure level (the "vacuum") is achieved, ensuring virtually all oxygen has been evacuated.
Step 3: Controlled Heating and Soaking
Once the vacuum is stable, the furnace's internal heating elements are energized. A sophisticated temperature control system raises the temperature of the parts to a precise setpoint at a controlled rate.
The parts are then held at this temperature for a specified period, known as "soaking," to allow the desired metallurgical transformations to occur throughout the material.
Step 4: Quenching (Controlled Cooling)
After soaking, the parts must be cooled rapidly to lock in the new material properties. This is called quenching.
In a vacuum furnace, this is typically done by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity, inert gas like argon or nitrogen. Powerful fans circulate this gas to cool the parts quickly and uniformly without causing any chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not the solution for every application. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Repeatability
The primary benefit is the exceptionally clean, bright finish of the parts, which eliminates the need for post-process cleaning. Furthermore, the precise digital control over the vacuum level, temperature, and cooling rates ensures that the process is highly repeatable, delivering consistent results from batch to batch.
The Limitation: Cycle Time and Throughput
Because it is a batch process, a vacuum furnace has a lower throughput than continuous, atmospheric furnaces. Each cycle involves time for loading, pumping down, heating, soaking, cooling, and unloading, which can make it a slower option for high-volume production.
The Versatility: A Multi-Process Tool
A single vacuum furnace can be used for a vast array of thermal processes. This includes standard treatments like annealing, tempering, and quenching, as well as more advanced processes like vacuum brazing, sintering, carburizing, and nitriding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and purity: Vacuum treatment is the superior choice, as it prevents oxidation and delivers clean, bright parts directly from the furnace.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive materials: For metals like titanium, zirconium, or certain superalloys, a vacuum environment is non-negotiable to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and precision: A vacuum furnace offers unparalleled digital control over the entire thermal cycle, ensuring extremely consistent and predictable results.
Understanding how a vacuum furnace controls the processing atmosphere empowers you to achieve specific, high-performance material properties that are otherwise unattainable.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heating materials in a low-pressure, oxygen-free environment to prevent oxidation. |
| Primary Advantage | Delivers clean, bright surface finishes without post-process cleaning. |
| Ideal For | Reactive metals (e.g., titanium), applications requiring high purity and repeatability. |
| Process Type | Batch processing, offering high precision but lower throughput than continuous furnaces. |
| Common Processes | Annealing, tempering, brazing, sintering, and hardening (quenching). |
Ready to achieve oxide-free, high-performance results with your materials?
KINTEK specializes in advanced vacuum heat treat furnaces for laboratories and production facilities. Our equipment provides the precise, contaminant-free environment essential for working with reactive metals and achieving superior material properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a vacuum furnace can enhance your R&D or manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why Use a Vacuum Furnace with a Titanium Trap for Pre-Annealing? Protect Substrates & Prevent LSCF Coating Cracks
- What is the mechanism of a carbonization furnace in TiC sol-gel synthesis? Achieve Superior Molecular Uniformity
- What advantages do fast-heating furnaces provide when brazing manganese-nickel alloys? Precision Thermal Control Guide
- What are the conditions in heat treatment? Mastering Temperature, Time, and Cooling for Superior Metal Properties
- What materials are used in quenching? Choosing the Right Quenchant for Hardness & Toughness
- What are the primary advantages of using a Vacuum Plasma Arc Melting Furnace for U-Zr-Nb? Superior Alloy Preparation
- What are the problems with heat treating? Master Internal Stress to Avoid Failure
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of oil as a quenching medium? Achieve Superior Hardening with Minimal Distortion



















