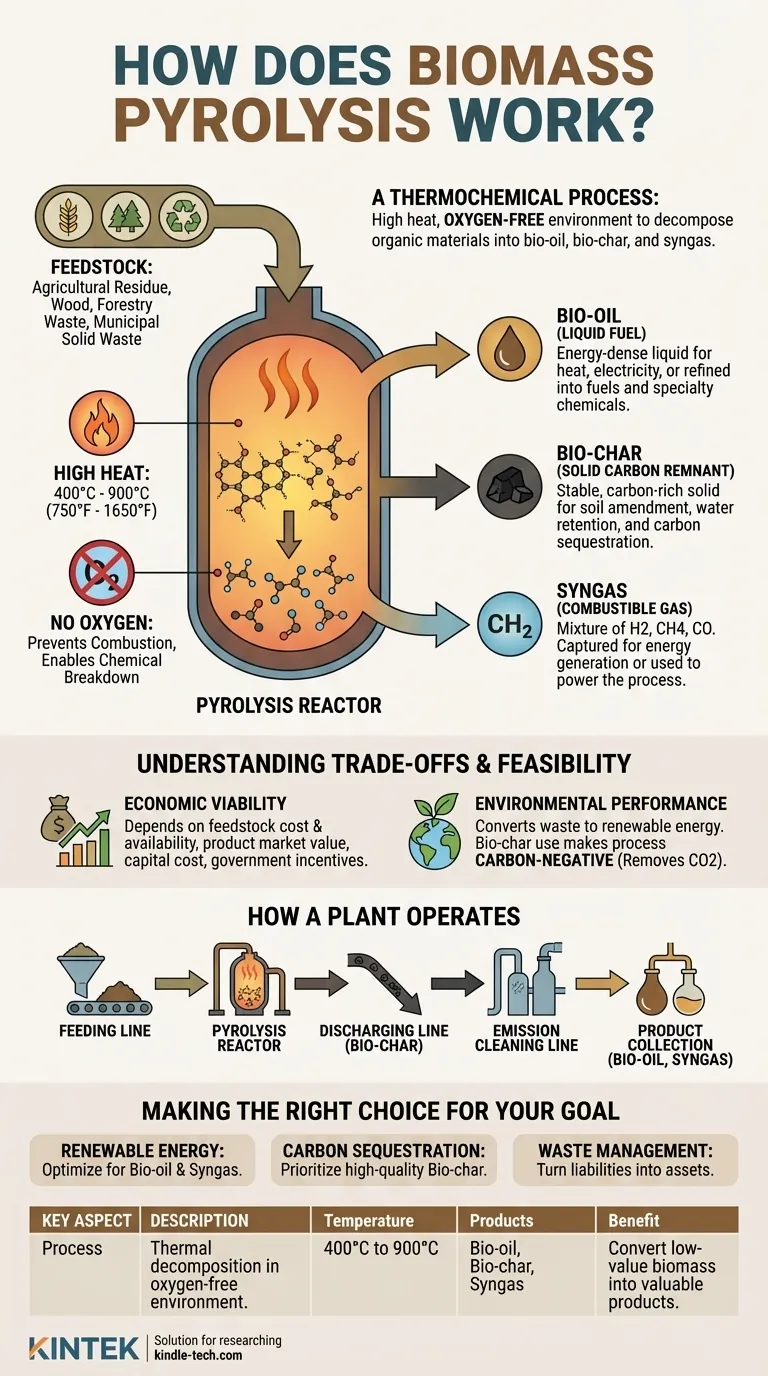
In essence, biomass pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that uses high heat in an oxygen-free environment to decompose organic materials like wood, agricultural residue, or even tires. Instead of burning the material, this process breaks it down into three valuable outputs: a liquid known as bio-oil, a solid called bio-char, and a combustible gas called syngas. The primary goal is to upgrade low-value biomass into stable, energy-dense, and useful products.
Pyrolysis is not about burning; it's about a controlled thermal breakdown. By removing oxygen, you prevent combustion and instead chemically transform the biomass into a suite of valuable, carbon-rich products.

Deconstructing the Core Process
To truly understand pyrolysis, you must see it as a precise chemical transformation rather than simple heating. The entire system is engineered to control what the biomass becomes.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The defining feature of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When you heat biomass with oxygen present, it combusts, releasing most of its energy as immediate heat and producing ash, CO2, and water.
By heating the material inside a sealed reactor, you prevent this combustion. The energy from the heat, instead of burning the material, breaks down the complex organic polymers (like cellulose and lignin) into smaller, more stable molecules.
The Key Inputs: Feedstock
The process begins with a "feedstock," which is simply the raw organic material being processed.
Common feedstocks include agricultural residues like corn stover, forestry waste like wood chips, and even specific streams of municipal solid waste. The key is that the material is carbon-based.
The Transformation: Applying High Heat
Inside the reactor, the feedstock is heated to temperatures typically ranging from 400°C to 900°C (750°F to 1650°F).
This intense heat, without oxygen, causes the material to decompose rapidly. The complex hydrocarbons vaporize and break apart, initiating the chemical change.
The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
The output of pyrolysis isn't a single substance but a portfolio of products. These vapors are collected and then cooled, causing them to separate into liquid, solid, and gaseous forms.
Bio-char: The Solid Carbon Remnant
Bio-char is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the process. It looks very similar to common charcoal.
Its primary uses are as a soil amendment to improve water retention and fertility, or for carbon sequestration. By burying bio-char, you are effectively locking atmospheric carbon into the ground for centuries.
Bio-oil: The Liquid Fuel
As the hot gases cool, a significant portion condenses into a dark, thick liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
This liquid is energy-dense and can be used to generate heat and electricity. With further refining, it can also be upgraded into transportation fuels or used as a feedstock for producing specialty chemicals.
Syngas: The Non-Condensable Gas
The gases that do not condense into liquid are called synthesis gas or syngas. This is a mixture of combustible gases like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
Syngas is typically not wasted. It is often captured and looped back into the system to provide the very heat needed to run the pyrolysis reactor, making the process more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Feasibility
While technically robust, the practical implementation of biomass pyrolysis depends on a careful balance of economic and environmental factors. It is not a universally perfect solution.
Economic Viability
The business case for a pyrolysis plant hinges on several variables. The cost and availability of feedstock is paramount.
Furthermore, the profitability is dictated by the market value of the end products (bio-char, bio-oil), the initial capital cost of the technology, and the availability of government incentives or carbon credits.
Environmental Performance
Pyrolysis offers significant environmental benefits. It provides a method for converting waste streams into renewable energy.
Most importantly, when the bio-char is used for soil application, the process becomes carbon-negative. It removes more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it produces, making it a powerful tool for climate change mitigation.
How a Plant Operates
A typical pyrolysis plant is an integrated system. It includes a feeding line to get biomass into the reactor, the pyrolysis line where the reaction occurs, a discharging line to safely remove the hot bio-char, and an emission cleaning line to handle any pollutants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying pyrolysis technology effectively requires aligning the process with a specific strategic objective.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy generation: Optimize the process to maximize the yield and quality of bio-oil and syngas for electricity or heating.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil health: Prioritize the production of high-quality, stable bio-char for agricultural application or burial.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Use pyrolysis as a value-add technology to process agricultural, forestry, or municipal solid waste, turning a liability into an asset.
Ultimately, biomass pyrolysis offers a powerful and flexible platform for converting organic matter into stable forms of energy and carbon.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition of biomass in an oxygen-free environment. |
| Temperature Range | 400°C to 900°C (750°F to 1650°F). |
| Primary Products | Bio-oil (liquid fuel), Bio-char (solid carbon), Syngas (combustible gas). |
| Main Benefit | Converts low-value biomass into stable, energy-dense products. |
Ready to transform your biomass or waste streams into valuable products?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for researching and optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you are developing new biofuels, studying bio-char for carbon sequestration, or analyzing syngas composition, our precise and reliable tools are designed to support your innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve your renewable energy and sustainability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















