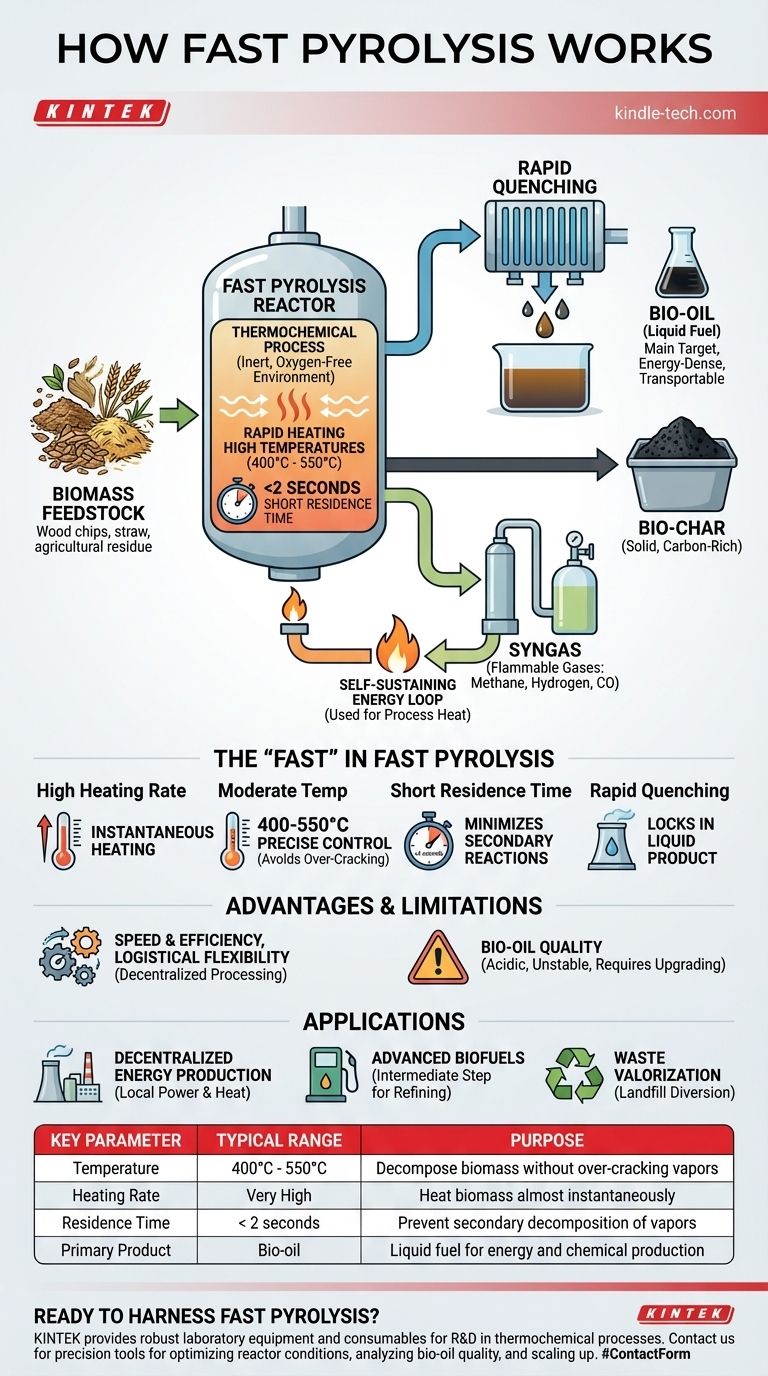
In essence, fast pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that uses high temperatures and extreme speed to decompose organic material, like biomass, in an environment without oxygen. This rapid heating and short reaction time are precisely controlled to maximize the production of a liquid fuel known as bio-oil, effectively converting solid biomass into a more energy-dense and transportable liquid form.
The core principle is to heat biomass so quickly that its complex organic structures don't have time to fully break down into gas or solid char. Instead, they vaporize and are then rapidly cooled, condensing into a liquid bio-oil before they can decompose further.
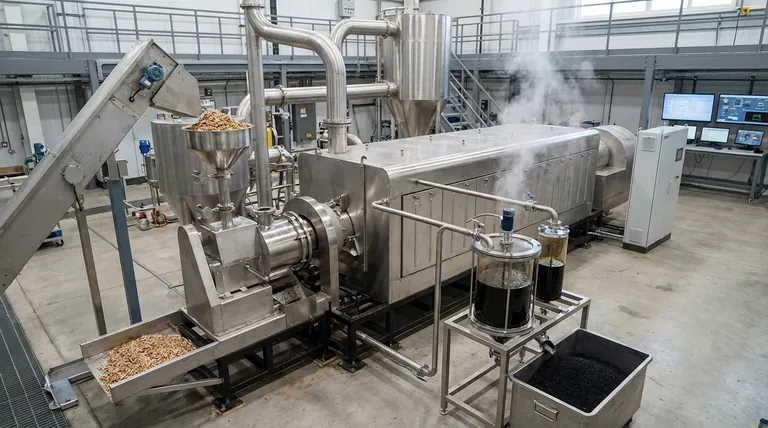

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition Without Combustion
Heating in an Inert Atmosphere
The entire process happens in the absence of oxygen. This is the critical difference between pyrolysis and burning (combustion).
Without oxygen, the material cannot ignite. Instead of burning away, the intense heat forces the chemical bonds within the biomass to break apart, a process known as lysis. The word pyrolysis itself comes from the Greek pyro (fire) and lysis (separation).
The Three Primary Products
This controlled decomposition yields three distinct products:
- Bio-oil: A dark, liquid fuel that is the main target of fast pyrolysis.
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal.
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases like methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide.
The Self-Sustaining Energy Loop
A key advantage of the process is that the syngas produced can be captured and burned.
This provides the necessary heat to run the reactor, creating a partially self-sustaining system that reduces the need for external energy inputs once it is operational.
What Makes "Fast" Pyrolysis Unique?
The "fast" in fast pyrolysis refers to a specific set of operating conditions designed to favor liquid production over solids or gases. The process hinges on precise control over temperature, speed, and time.
High Heating Rate
Biomass feedstock is subjected to an extremely high heating rate. The goal is to raise the material's temperature to the target range almost instantaneously.
Moderate Temperature Control
The process operates within a carefully controlled temperature window, typically between 400°C and 550°C.
This temperature is hot enough to rapidly decompose the biomass but not so hot that it "over-cracks" the valuable vapors into less desirable permanent gases, which is what happens in gasification.
Short Residence Time
The biomass material and its resulting vapors are only inside the hot reactor for an incredibly short period—often less than two seconds.
This short residence time is crucial. It ensures the vapors are removed from the heat before they can undergo secondary reactions and break down further into gas and char.
Rapid Quenching
Immediately after leaving the reactor, the hot vapors are quenched, or cooled down very quickly.
This rapid cooling forces the vapors to condense into the liquid bio-oil, effectively "locking in" the desired product. This final step is essential for achieving high liquid yields.
Understanding the Advantages and Limitations
Fast pyrolysis is a promising technology, but like any process, it involves trade-offs that are important to understand.
Advantage: Speed and Efficiency
As the name implies, the process is extremely quick. It can convert large volumes of biomass into bio-oil with high efficiency, utilizing all components of the feedstock with minimal waste.
Advantage: Logistical Flexibility
Pyrolysis reactors can be built on a relatively small, even mobile, scale. This allows for decentralized processing, converting bulky, low-density biomass into energy-dense bio-oil near its source. The liquid is then much cheaper and easier to transport to a central upgrading facility.
Limitation: Bio-oil Quality
The primary challenge is the quality of the raw bio-oil. It is not a direct "drop-in" replacement for crude oil.
Raw bio-oil is acidic, unstable over time, and contains a significant amount of water and oxygen. It typically requires substantial secondary processing, or upgrading, before it can be used as a transportation fuel or in a conventional refinery.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding fast pyrolysis allows you to see its strategic fit in different value chains, from waste management to renewable energy production.
- If your primary focus is decentralized energy production: Fast pyrolysis is an excellent technology for converting scattered, low-value biomass (like agricultural or forest residues) into a transportable liquid energy carrier.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced biofuels: View fast pyrolysis as the crucial first step in a longer process, where the raw bio-oil serves as an intermediate feedstock for a specialized upgrading facility.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization: This process offers a powerful method to transform organic waste streams that would otherwise go to a landfill into valuable fuels and chemical precursors.
Ultimately, fast pyrolysis is a powerful tool for rapidly transforming low-density solid biomass into a high-density liquid intermediate.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Typical Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 400°C - 550°C | Decompose biomass without over-cracking vapors |
| Heating Rate | Very High | Heat biomass almost instantaneously |
| Residence Time | < 2 seconds | Prevent secondary decomposition of vapors |
| Primary Product | Bio-oil | Liquid fuel for energy and chemical production |
Ready to harness the power of fast pyrolysis for your biomass conversion or renewable energy project?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables essential for research and development in thermochemical processes like pyrolysis. Whether you're optimizing reactor conditions, analyzing bio-oil quality, or scaling up your process, our precision tools can help you achieve accurate and reliable results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can support your laboratory's needs in advancing renewable energy technologies.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















