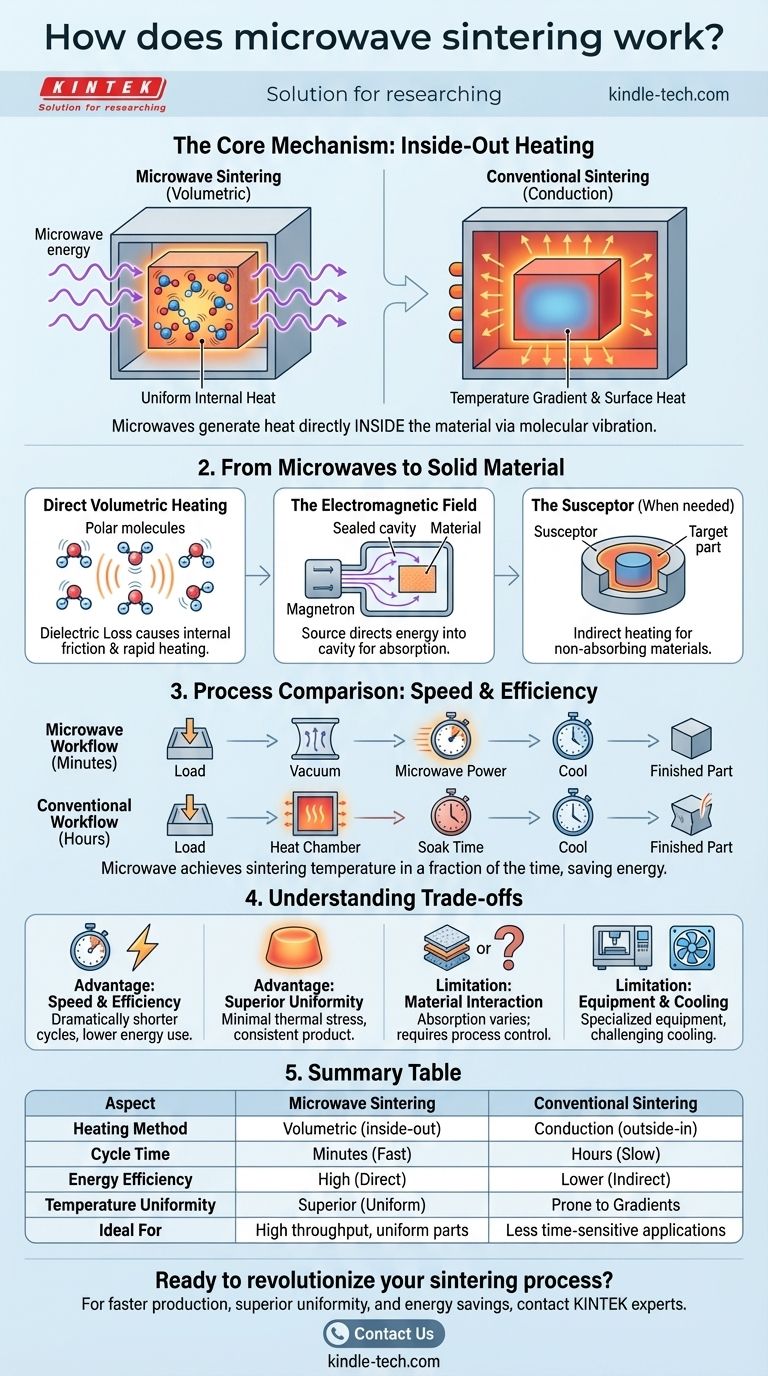
Microwave sintering fundamentally changes how materials are heated. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats from the outside-in, this process uses microwave energy to generate heat directly inside the material itself. This "volumetric heating" occurs as the electromagnetic waves cause the material's internal molecules and ions to vibrate rapidly, creating uniform heat throughout the entire part almost instantly.
The critical distinction of microwave sintering is its "inside-out" heating mechanism. By heating the entire volume of the material simultaneously, it achieves faster, more uniform results and significant energy savings compared to traditional methods that heat from the surface inward.

The Core Mechanism: From Microwaves to Solid Material
The effectiveness of microwave sintering lies in its unique method of energy transfer. It bypasses the slow, indirect process of conduction and convection used in conventional furnaces.
Direct Volumetric Heating
The process relies on a material's dielectric loss. As microwaves pass through the ceramic or powder, they interact with its molecular structure, forcing polar molecules and ions to rapidly oscillate.
This intense internal friction is the source of heat. Because the microwaves penetrate the material, this heating occurs everywhere at once, from the core to the surface.
The Electromagnetic Field
A microwave sintering furnace consists of a microwave source (like a magnetron), a sealed heating cavity, and a system to handle the material.
The source generates and directs microwave energy into the cavity. The material placed inside absorbs this energy, rapidly raising its temperature to the point of sintering, where individual particles bond together to form a dense solid.
When Materials Don't Cooperate: The Susceptor
Not all materials readily absorb microwave energy. Some, like monoclinic zirconia, are effectively transparent to microwaves at lower temperatures.
In these cases, a susceptor material is used. This is a secondary material that strongly absorbs microwave energy and converts it into heat. The target material is then heated indirectly by the hot susceptor, combining the speed of microwaves with conventional thermal transfer.
A Step-by-Step Process Comparison
The operational workflow for microwave sintering highlights its primary advantage: speed.
The Microwave Sintering Workflow
The process is direct and fast. A typical cycle involves loading the material, creating a vacuum (if required for the material), and applying microwave power.
The material heats to the sintering temperature in a fraction of the time required by a conventional furnace. After a brief holding period to ensure densification, the part is cooled.
Contrast with Conventional Sintering
Conventional sintering is a much slower process. The furnace chamber itself must first be heated.
This heat then slowly soaks into the material from the outside, creating a significant temperature gradient between the hot surface and the cooler core. This process takes much longer and consumes far more energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to its successful application.
Advantage: Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The most significant benefit is speed. Heating cycles can be reduced from many hours to mere minutes. Because energy is focused solely on heating the material and not the entire furnace chamber, it is also highly energy-efficient.
Advantage: Superior Uniformity
By heating volumetrically, microwave sintering nearly eliminates the internal temperature gradients common in conventional methods. This reduces thermal stress, minimizes warping, and results in a more uniform and consistent final product.
Limitation: Material Interaction
The primary challenge is that a material's ability to absorb microwave energy can change with its temperature and composition. This requires careful process control and, in some cases, the use of susceptors, which adds a layer of complexity.
Limitation: Equipment and Cooling
Specialized equipment is required to generate and contain the microwave field safely. Furthermore, while the heating is rapid, efficiently cooling the equipment after a cycle, especially in large-scale production, can be a challenge and may require auxiliary cooling systems.
Is Microwave Sintering Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right sintering method depends entirely on your project's priorities, from production speed to final material properties.
- If your primary focus is rapid production and high throughput: Microwave sintering's dramatically shorter cycle times offer a clear and compelling advantage.
- If your primary focus is material quality and uniformity: The volumetric heating minimizes thermal gradients, reducing internal stresses and improving final product consistency.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and cost reduction: This method is inherently more efficient as it heats the part directly, not the entire furnace chamber.
- If you are working with novel or temperature-sensitive materials: The precise control and potential for lower sintering temperatures can be a critical enabler for advanced material development.
By understanding its unique inside-out heating principle, you can effectively leverage microwave sintering to achieve results that are often impossible with traditional furnaces.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Microwave Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Volumetric (inside-out) | Conduction (outside-in) |
| Cycle Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Energy Efficiency | High (heats material directly) | Lower (heats entire chamber) |
| Temperature Uniformity | Superior (reduces gradients) | Prone to gradients and stress |
| Ideal For | High throughput, uniform parts | Less time-sensitive applications |
Ready to revolutionize your sintering process? If your lab needs faster production cycles, superior material uniformity, and significant energy savings, KINTEK has the solution. Our specialized microwave sintering equipment is designed for laboratories seeking to enhance throughput and material quality. Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can optimize your sintering applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















