At its core, molybdenum increases corrosion resistance by stabilizing and reinforcing the protective passive film on the surface of an alloy. When added to materials like stainless steel, molybdenum makes this passive layer more resilient, particularly against localized attacks from chlorides, which are a primary cause of pitting and crevice corrosion.
The primary value of molybdenum is not that it is inherently corrosion-proof itself, but that it acts as a powerful enhancer for the protective oxide layer of the base metal, typically chromium in stainless steel. It makes this "shield" tougher, more stable, and faster to repair when damaged.
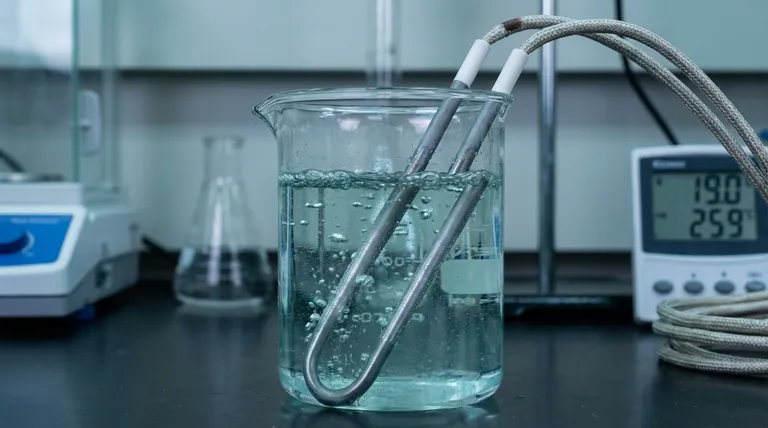

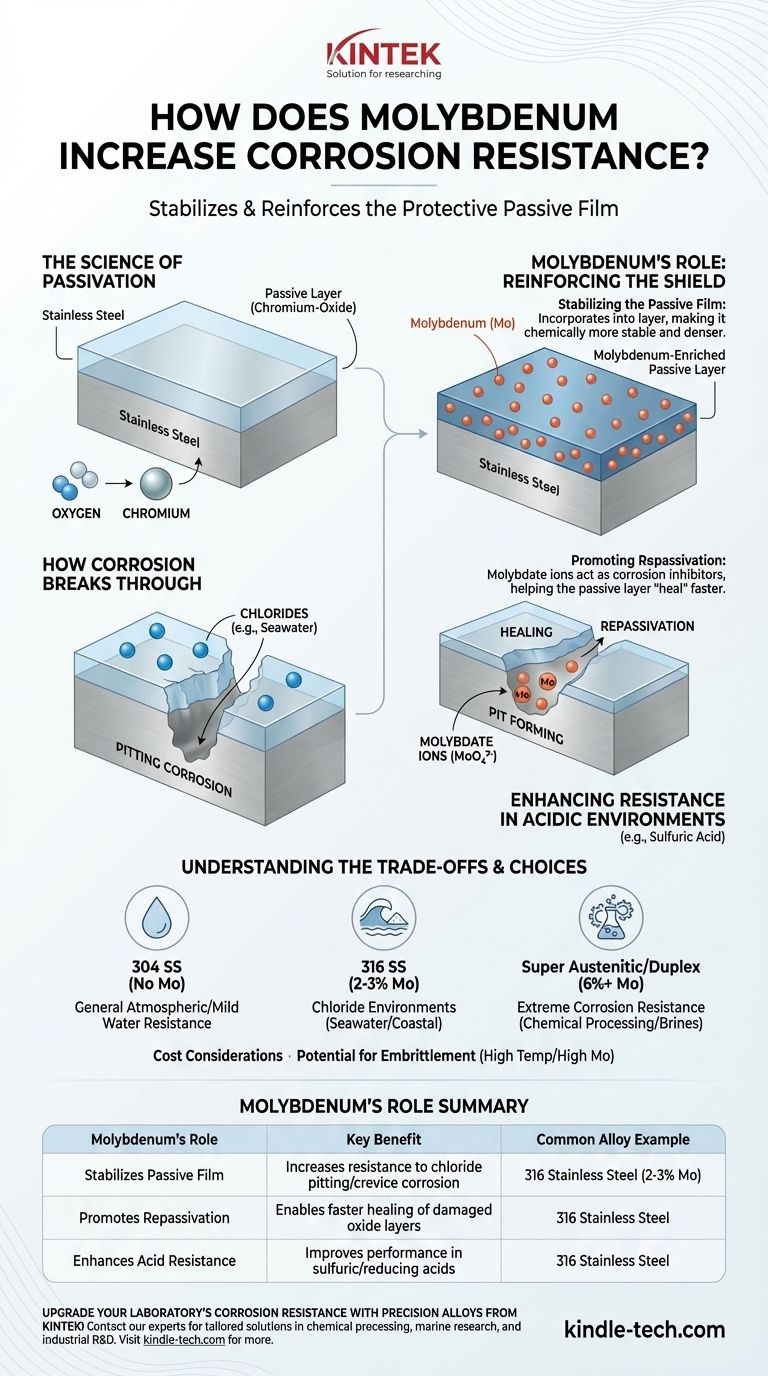
The Science of Passivation: An Alloy's First Line of Defense
To understand molybdenum's role, we first need to understand the mechanism that protects stainless steel in the first place.
What is a Passive Layer?
Most stainless steels are not inherently inert. Their corrosion resistance comes from a very thin, invisible, and durable surface film.
This film, called the passive layer, is formed when chromium in the alloy reacts with oxygen in the environment. It creates a stable chromium-oxide "shield" that protects the underlying iron from corroding.
How Corrosion Breaks Through
This passive layer is effective, but it can be compromised. Aggressive ions, most notably chlorides (found in seawater, de-icing salts, and many industrial chemicals), can locally break down this film.
When the film is breached at a specific point, corrosion can rapidly accelerate underneath, creating a small hole or "pit." This is known as pitting corrosion, a particularly damaging form of localized corrosion.
Molybdenum's Role: Reinforcing the Shield
Molybdenum is added to alloys specifically to combat the breakdown of the passive layer. It intervenes in several critical ways.
Stabilizing the Passive Film
When molybdenum is present in the alloy, its oxidized ions become incorporated into the chromium-oxide passive layer. This makes the film chemically more stable and denser.
A molybdenum-enriched passive layer is significantly more resistant to being broken down by chlorides, preventing pits from forming in the first place.
Promoting Repassivation
If a pit does begin to form, molybdenum provides a crucial secondary defense. Inside the acidic, low-oxygen environment of a new pit, molybdenum dissolves and forms stable molybdate ions (MoO₄²⁻).
These ions act as corrosion inhibitors within the pit itself. They help neutralize the acidic conditions and make it much easier for the passive layer to "heal" or repassivate over the damaged area, effectively stopping the pit from growing.
Enhancing Resistance in Acidic Environments
Beyond chlorides, molybdenum also significantly improves an alloy's resistance to non-oxidizing or reducing acids, such as sulfuric acid. It helps maintain the stability of the passive film in environments where it would otherwise dissolve.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding molybdenum is not a universal solution and comes with important considerations that engineers must balance.
The Impact of Cost
Molybdenum is a relatively expensive alloying element. This is why 316 stainless steel (which contains Mo) is consistently more expensive than 304 stainless steel (which does not). The cost must be justified by the demands of the service environment.
Potential for Embrittlement
In certain grades of steel, and under specific high-temperature conditions, high concentrations of molybdenum can promote the formation of brittle intermetallic phases (like sigma phase).
This can reduce the alloy's toughness and ductility. Proper material selection and heat treatment are critical to manage this risk in high-molybdenum alloys.
Not a Cure-All
While exceptional against chloride pitting, molybdenum does not improve resistance to all forms of corrosion equally. For example, in some highly oxidizing acid environments, its benefits may be minimal or even detrimental compared to other alloying strategies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of alloy should be driven by a clear understanding of the operational environment and the primary corrosion risk.
- If your primary focus is general atmospheric or mild water resistance: A standard austenitic like 304 stainless steel (no Mo) is often a cost-effective and sufficient choice.
- If your primary focus is resisting chloride environments (seawater, coastal areas, de-icing salts): An alloy with 2-3% molybdenum, like 316 stainless steel, is the industry standard and provides a significant performance upgrade.
- If your primary focus is extreme corrosion resistance (chemical processing, harsh marine, or high-chloride brines): A super austenitic or duplex stainless steel with higher molybdenum content (e.g., 6% or more) is necessary to ensure long-term integrity.
Ultimately, selecting a molybdenum-bearing alloy is a strategic investment in durability where the risk of localized corrosion is high.
Summary Table:
| Molybdenum's Role | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Stabilizes Passive Film | Increases resistance to chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion |
| Promotes Repassivation | Enables faster healing of damaged oxide layers, stopping pit growth |
| Enhances Acid Resistance | Improves performance in sulfuric acid and other reducing acids |
| Common Alloy Example | 316 Stainless Steel (contains 2-3% Mo) |
Upgrade your laboratory's corrosion resistance with precision alloys from KINTEK!
Struggling with equipment failure due to pitting or chloride attack? KINTEK specializes in supplying high-performance lab equipment and consumables crafted from molybdenum-enhanced alloys like 316 stainless steel. We help laboratories in chemical processing, marine research, and industrial R&D achieve superior durability and longevity.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your specific environment and get a tailored solution that maximizes your investment in material integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three-Section Clamp
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere



















