At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated vacuum-coating process that transforms a solid metal into a vapor, which then condenses onto a target object as a thin, high-performance film. This atom-by-atom deposition occurs within a high-temperature vacuum chamber, creating a new surface layer that is molecularly bonded to the original material, or substrate.
PVD coating isn't a simple paint or plating; it's a micro-scale manufacturing process. By turning a solid material into a vapor within a vacuum and letting it re-solidify atom-by-atom onto a surface, it creates a bonded layer with properties far superior to the original material.
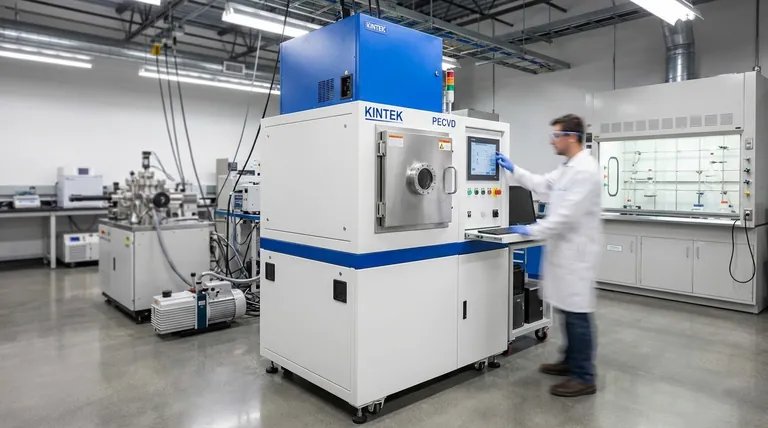

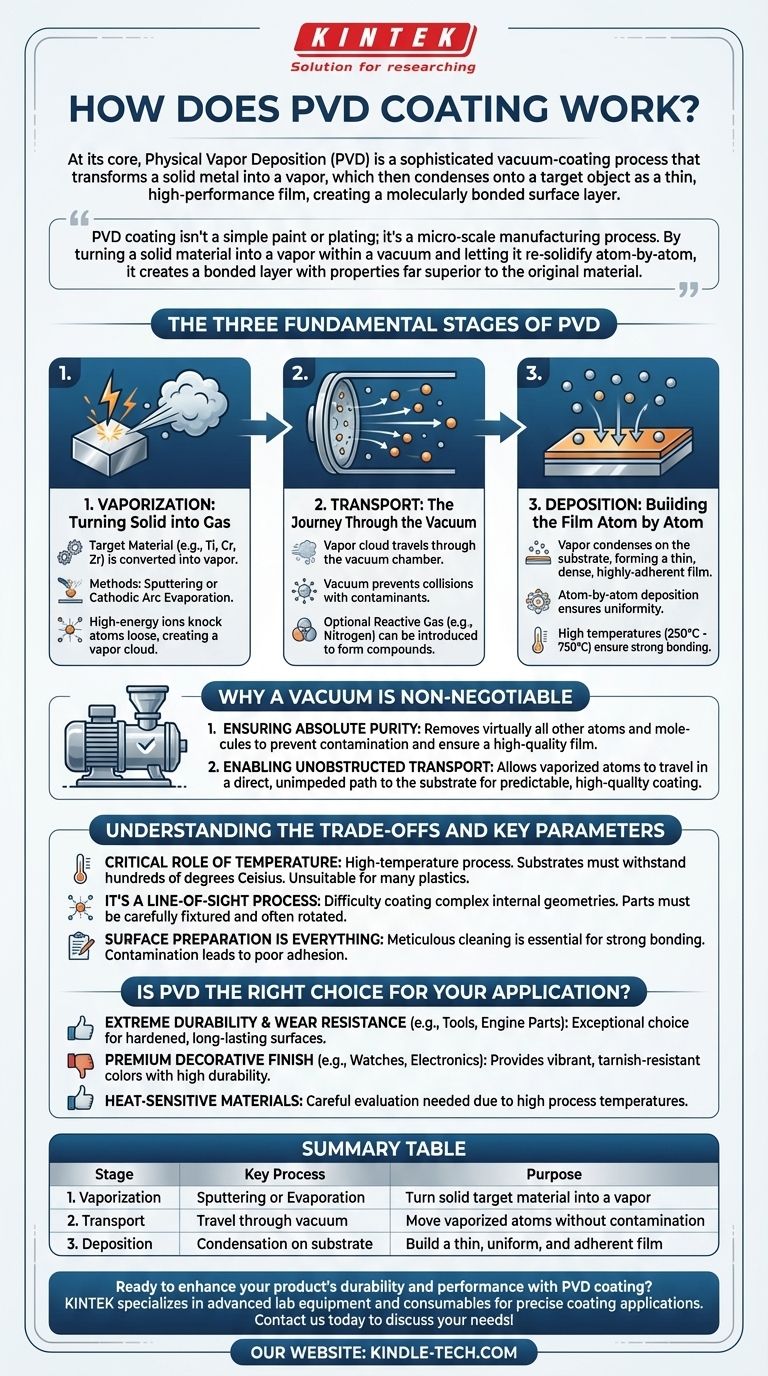
The Three Fundamental Stages of PVD
The entire PVD process can be broken down into a sequence of three critical stages, each occurring under highly controlled conditions within a vacuum chamber.
Stage 1: Vaporization - Turning Solid into Gas
The process begins with a solid, high-purity coating material known as a "target." This target (e.g., titanium, chromium, zirconium) must be converted into a vapor.
This is the "Physical" part of PVD, and it is typically achieved through methods like sputtering or cathodic arc evaporation. In simple terms, the target is bombarded with high-energy ions, which knock atoms loose from the solid material, effectively turning it into a cloud of vapor.
Stage 2: Transport - The Journey Through the Vacuum
Once vaporized, the cloud of metal atoms and ions travels through the vacuum chamber. This journey is crucial, as the vacuum environment ensures the particles do not collide with or react to contaminants like oxygen or water vapor in the air.
At this stage, a reactive gas, such as nitrogen, can be strategically introduced into the chamber. This allows the metal vapor to react and form a new ceramic compound (like Titanium Nitride), altering the final coating's properties and color.
Stage 3: Deposition - Building the Film Atom by Atom
The vaporized material finally reaches the substrate—the part being coated. It condenses on the surface, forming a thin, dense, and highly-adherent film.
Because this deposition happens one atom at a time, the resulting layer is exceptionally uniform and can precisely replicate the original surface texture. The high temperatures (ranging from 250°C to 750°C) help ensure the coating is tightly bonded to the substrate, making it extremely durable and difficult to remove.
Why a Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
The vacuum chamber is the defining feature of the PVD process. Without it, the technique would be impossible for two key reasons.
Ensuring Absolute Purity
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove virtually all other atoms and molecules from the chamber. This prevents the vaporized coating material from reacting with contaminants, which would create an impure, weak, and ineffective film.
Enabling Unobstructed Transport
In a vacuum, the vaporized atoms can travel in a straight, unimpeded path from the target to the substrate. This direct line-of-sight travel is essential for creating a predictable and high-quality coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
While powerful, the PVD process is not universally applicable. Understanding its operational requirements is key to using it effectively.
The Critical Role of Temperature
PVD is a high-temperature process. Substrates must be able to withstand temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius without deforming or losing their structural integrity. This makes it unsuitable for many plastics or other heat-sensitive materials.
It's a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, PVD has difficulty coating complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes. The parts must be carefully fixtured and often rotated during the process to ensure even coverage on all exposed surfaces.
Surface Preparation is Everything
The final coating is only as good as its bond to the substrate. The part to be coated must be meticulously cleaned, dried, and sometimes pre-treated. Any surface contamination will lead to poor adhesion and potential coating failure.
Is PVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
The decision to use PVD coating depends entirely on your end goal. It excels where performance and durability are paramount.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: PVD is an exceptional choice for components like cutting tools, industrial parts, and engine components, as it creates a hardened surface that dramatically extends component life.
- If your primary focus is a premium decorative finish: For products like watches, faucets, and high-end electronics, the process provides vibrant, tarnish-resistant colors with a durability that far exceeds traditional plating.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: You must carefully evaluate the specific PVD process temperature, as the high heat can damage substrates that are not thermally stable.
Ultimately, understanding the PVD process empowers you to leverage its unique capabilities for creating products that are both beautiful and incredibly resilient.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vaporization | Sputtering or Evaporation | Turn solid target material into a vapor |
| 2. Transport | Travel through vacuum | Move vaporized atoms without contamination |
| 3. Deposition | Condensation on substrate | Build a thin, uniform, and adherent film |
Ready to enhance your product's durability and performance with PVD coating? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise coating applications. Our expertise ensures your laboratory achieves superior results with reliable, high-performance solutions. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific coating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















