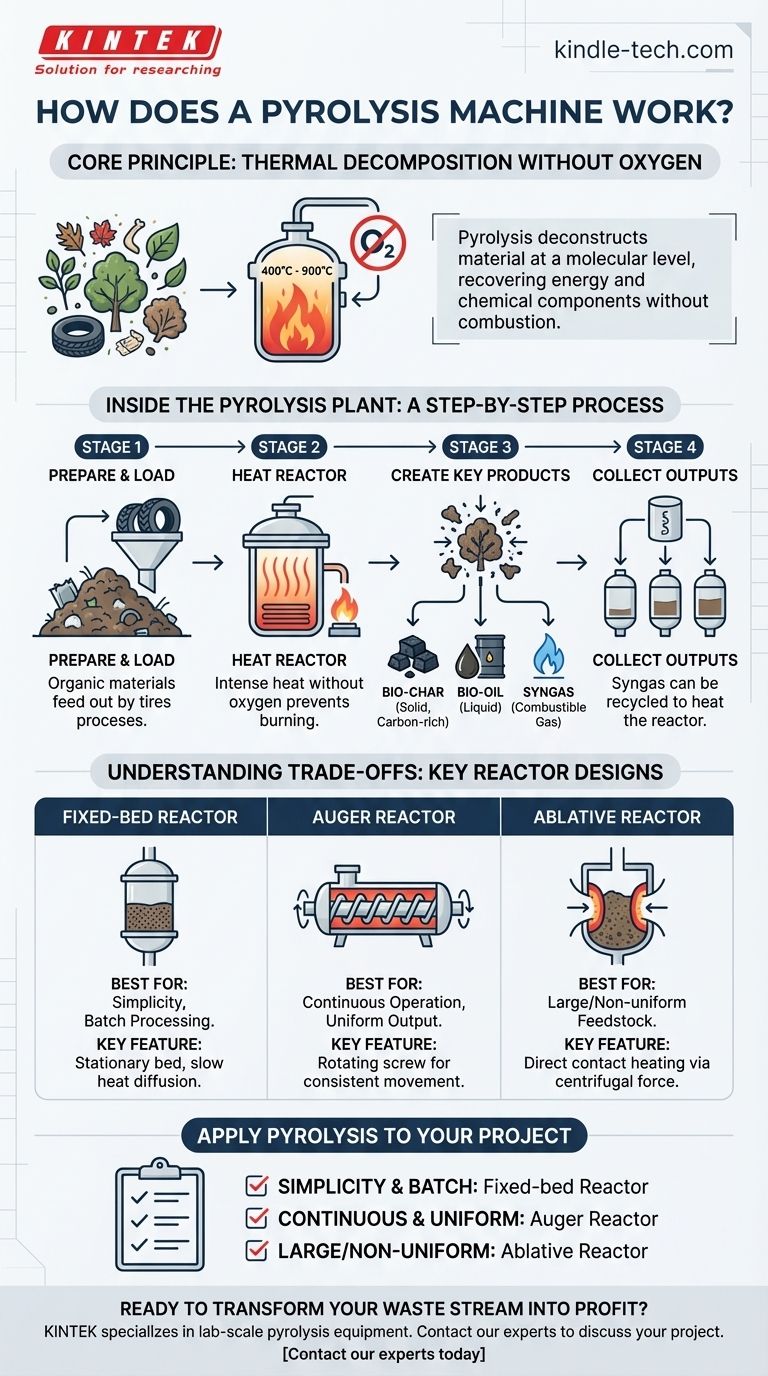
At its core, a pyrolysis machine works by intensely heating organic materials in a completely oxygen-free environment. This process, called pyrolysis, is not burning; it is a controlled thermal decomposition. The extreme heat breaks down the chemical bonds within the material, deconstructing it at a molecular level into valuable solid, liquid, and gaseous byproducts.
The critical distinction to understand is that pyrolysis deconstructs material rather than destroying it. By eliminating oxygen, the machine prevents combustion and instead enables the recovery of energy and chemical components locked within the original feedstock.

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical treatment that applies high heat to carbon-based materials like biomass, plastics, or old tires. It is fundamentally a process of chemical and physical separation into different molecules.
The Role of High Temperature
Inside a pyrolysis machine's reactor, materials are heated to temperatures typically ranging from 400°C to 900°C. This intense heat provides the energy needed to overcome the limited thermal stability of the material's chemical bonds, causing them to break apart.
Why the Absence of Oxygen is Critical
In the presence of oxygen, high heat would simply cause the material to burn (combust), producing mostly ash, carbon dioxide, and other emissions. By operating in a sealed, oxygen-free system, the machine ensures that decomposition occurs instead of combustion.
Inside the Pyrolysis Plant: A Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Feedstock is Prepared and Loaded
Organic materials are fed into the machine. This feedstock can range from agricultural waste and wood to end-of-life plastics and tires.
Step 2: The Reactor Heats the Material
The heart of the machine is the pyrolysis reactor, a closed vessel where the material is heated externally. The system is designed to maintain high temperatures while preventing any oxygen from entering.
Step 3: Decomposition Creates Three Key Products
As the feedstock breaks down, it separates into three distinct outputs:
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich residue similar to charcoal.
- Bio-oil: A liquid mixture of various organic compounds, also known as pyrolysis oil.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases, including hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Step 4: Outputs are Collected
These three products are then separated and collected. The syngas is often recycled to provide the energy needed to heat the reactor, making the process partially self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Reactor Designs
The specific mechanism for heating and moving material defines the reactor type. Each design has different strengths and is suited for different kinds of feedstock.
The Fixed-Bed Reactor
This is a simple design where the feedstock is placed on a stationary bed inside the reactor. Heat is applied to the vessel's walls and slowly diffuses inward to decompose the material. Its simplicity is its primary advantage.
The Auger Reactor
This design uses a large, rotating screw mechanism (an auger) to continuously move the feedstock through a heated chamber. It relies on mechanical force and direct contact to ensure consistent heat transfer throughout the material.
The Ablative Reactor
An ablative reactor works by pressing the feedstock against the hot interior walls of the reactor, often using centrifugal force. The material essentially "melts" upon contact, leaving a thin film of oil that lubricates the process for subsequent particles. This method is highly effective for large particles like wood chunks.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Once you understand the basic principles, you can select a technology that aligns with your specific goals for waste processing or resource recovery.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and batch processing: The straightforward design of a fixed-bed reactor is a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is continuous operation and uniform output: An auger reactor provides excellent control over processing time and heat exposure for consistent results.
- If your primary focus is handling large or non-uniform feedstock: An ablative reactor's direct-contact heating method is uniquely capable of processing bulky materials efficiently.
Ultimately, pyrolysis technology offers a powerful and flexible method for transforming low-value waste into high-value energy and products.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Bed | Simplicity, Batch Processing | Stationary bed, slow heat diffusion |
| Auger | Continuous Operation, Uniform Output | Rotating screw for consistent movement |
| Ablative | Large/Non-uniform Feedstock | Direct contact heating via centrifugal force |
Ready to transform your waste stream into profit? KINTEK specializes in lab-scale pyrolysis equipment and consumables, helping researchers and pilot plants optimize their processes. Whether you're testing new feedstocks or scaling up production, our reliable systems ensure precise temperature control and efficient product recovery. Contact our experts today to discuss how our pyrolysis solutions can advance your recycling or energy recovery project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















