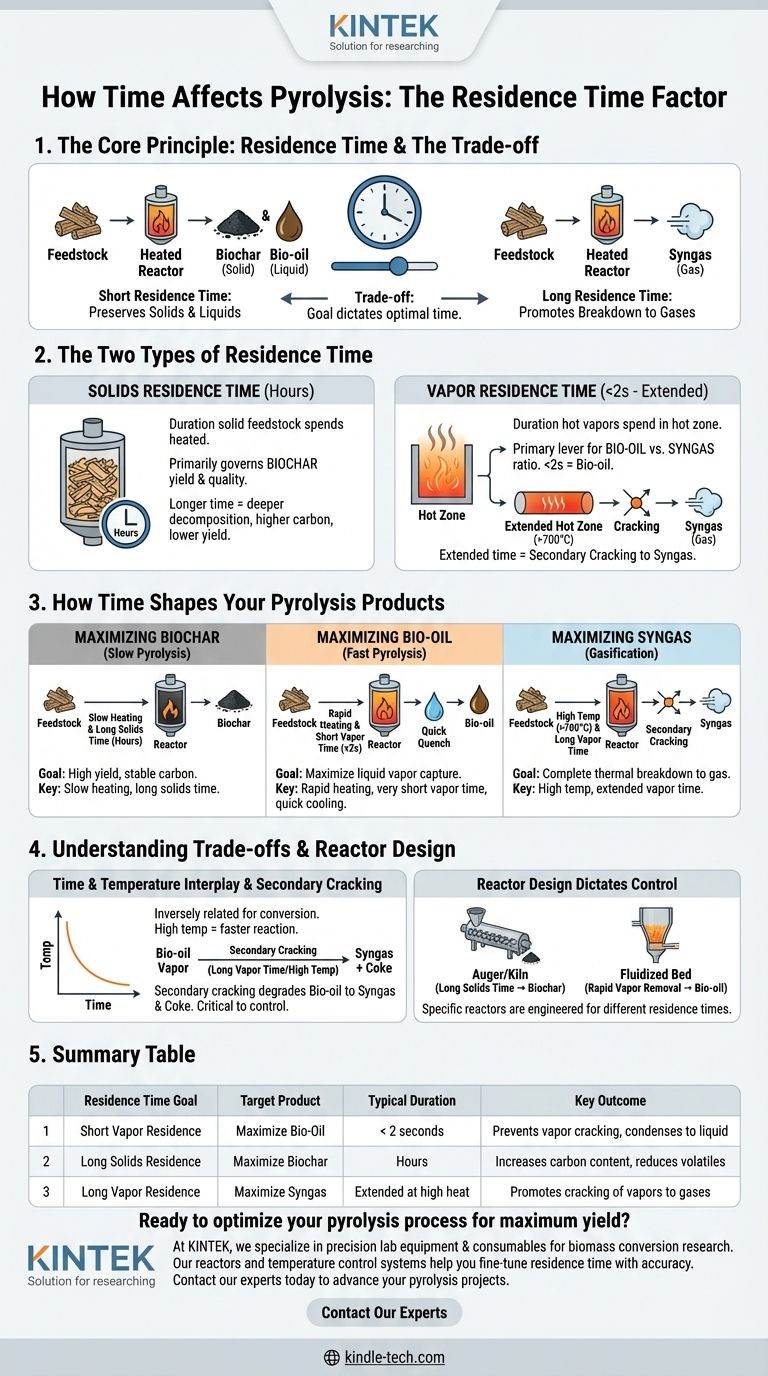
In pyrolysis, time is the controlling factor that dictates the final distribution of products. This duration, known as residence time, determines how completely the initial feedstock breaks down, directly influencing the final yield of solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, and non-condensable syngas. A longer residence time generally leads to more complete thermal conversion, shifting the output away from solids and liquids toward gases.
The core principle is a trade-off: short residence times preserve valuable solids (biochar) and liquids (bio-oil), while long residence times promote the breakdown of these products into gases (syngas). Your goal for the final product dictates the optimal residence time.
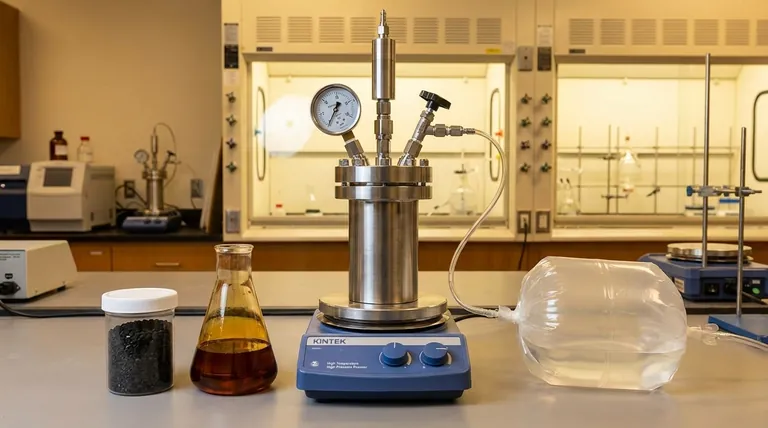

The Two Types of Residence Time
To truly understand the process, it's critical to distinguish between the residence time of the solid material and the residence time of the vapors it produces. They are not the same and have different effects on the outcome.
Solids Residence Time
This is the total duration the solid feedstock (like wood chips or agricultural waste) spends inside the heated reactor. It primarily governs the yield and quality of the biochar.
Longer solid residence times allow for deeper thermal decomposition, reducing the final char yield but increasing its carbon content and stability. Shorter times yield more char, but it will contain more volatile compounds.
Vapor Residence Time
This is the duration the hot gases and vapors, released from the solids, spend in the hot zone of the reactor before they are cooled or exit. This variable is the primary lever for controlling the ratio of bio-oil to syngas.
Vapors that are removed and cooled quickly will condense into a liquid bio-oil. Vapors that remain in the hot zone for longer will undergo further "cracking" reactions, breaking down into simpler, non-condensable gas molecules.
How Time Shapes Your Pyrolysis Products
The specific residence time you target depends entirely on which product you want to maximize. These processes are often categorized as slow, fast, or flash pyrolysis, which are defined by both temperature and residence time.
Maximizing Biochar (Slow Pyrolysis)
To produce the highest yield of biochar, a long solids residence time (hours) at relatively lower temperatures is used. This process, known as slow pyrolysis or carbonization, aims to gently drive off volatile matter while preserving the carbon skeleton of the feedstock.
The key is a slow heating rate, which minimizes the violent breakdown of the solid structure and allows for a controlled conversion to char.
Maximizing Bio-Oil (Fast Pyrolysis)
To maximize bio-oil, the goal is to create vapors and then remove them from the heat almost instantly. This requires a very short vapor residence time, typically less than two seconds.
This process, known as fast pyrolysis, uses a moderate-to-high temperature and extremely rapid heating of the feedstock. The vapors are immediately quenched (cooled rapidly) to condense them into bio-oil before they have time to break down into gases.
Maximizing Syngas (Gasification)
To maximize syngas (a mix of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane), you need a long vapor residence time at high temperatures (often >700°C). This environment promotes the secondary reactions that crack the heavier molecules found in bio-oil vapor.
Essentially, you are intentionally allowing the bio-oil vapors to continue "cooking" until they are thermally broken down into the simplest, most stable gas molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Manipulating time is not a simple, isolated variable. It is intrinsically linked to temperature and reactor design, creating a series of trade-offs you must manage.
The Interplay of Time and Temperature
Time and temperature are inversely related to achieve a certain degree of conversion. A reaction that takes hours at 400°C might be completed in seconds at 600°C.
Therefore, "fast pyrolysis" for bio-oil doesn't just use a short residence time; it must use a high temperature to ensure the feedstock breaks down quickly enough in that short window.
The Problem of Secondary Cracking
The single biggest trade-off is secondary cracking. This is the process that degrades your valuable bio-oil vapors into lower-value syngas and additional char (coke).
What is beneficial for syngas production (long vapor residence time) is detrimental to bio-oil yield. Controlling vapor residence time is therefore the most critical factor in determining whether your output is primarily liquid or gas.
Reactor Design Dictates Control
Different pyrolysis reactors are engineered specifically to control residence time. An auger or rotating kiln reactor allows for long solids residence times, ideal for biochar. In contrast, a fluidized bed reactor provides excellent heat transfer and allows for the rapid removal of vapors, making it ideal for fast pyrolysis and bio-oil production.
Tuning Residence Time for Your Goal
Ultimately, the optimal residence time is not a single number but an operational window defined by your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-quality biochar: Use a long solids residence time (minutes to hours) with slow heating rates to maximize char stability and carbon content.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil yield: Use an extremely short vapor residence time (under 2 seconds) with rapid heating to capture vapors before they undergo secondary cracking.
- If your primary focus is producing syngas: Use a long vapor residence time at high temperatures to ensure the complete thermal cracking of all volatile compounds into non-condensable gases.
By understanding and controlling residence time, you move from simply heating biomass to precisely engineering its transformation into value-added products.
Summary Table:
| Residence Time Goal | Target Product | Typical Duration | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short Vapor Residence | Maximize Bio-Oil | < 2 seconds | Prevents vapor cracking, condenses to liquid |
| Long Solids Residence | Maximize Biochar | Hours | Increases carbon content, reduces volatiles |
| Long Vapor Residence | Maximize Syngas | Extended at high heat | Promotes cracking of vapors to gases |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum yield? At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables tailored for biomass conversion research. Whether you're developing biochar for soil enhancement, bio-oil for renewable fuels, or syngas for energy, our reactors and temperature control systems help you fine-tune residence time with accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can advance your laboratory's pyrolysis projects and deliver the reliable results you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal synthesis autoclave necessary for MnO2 nanowires? Precision Catalyst Growth
- What role does a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave play in the synthesis of BiOBr precursor nanosheets?
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- Why must SCWG reactors maintain a specific heating rate? Protect Your High-Pressure Vessels from Thermal Stress
- Why are high-precision pressure sensors and temperature control systems critical for hydrothermal reaction equilibrium?


















