In an induction melting furnace, the vacuum's primary role is protection. It accomplishes this by physically removing atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen from the melting chamber. This prevents the highly reactive molten metal from coming into contact with these elements, which would otherwise form impurities and fundamentally compromise the final alloy's integrity and performance.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum in induction melting is not to aid the melting process itself, but to create a chemically inert environment. By removing reactive gases, it ensures the final product meets exacting standards for purity, strength, and performance, especially for advanced and reactive materials.
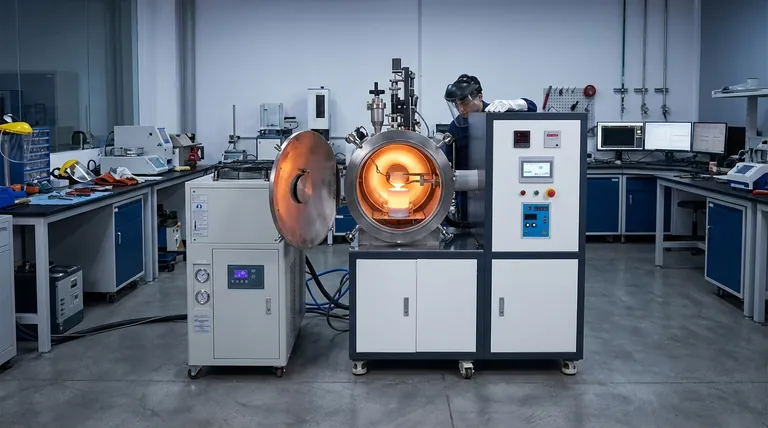

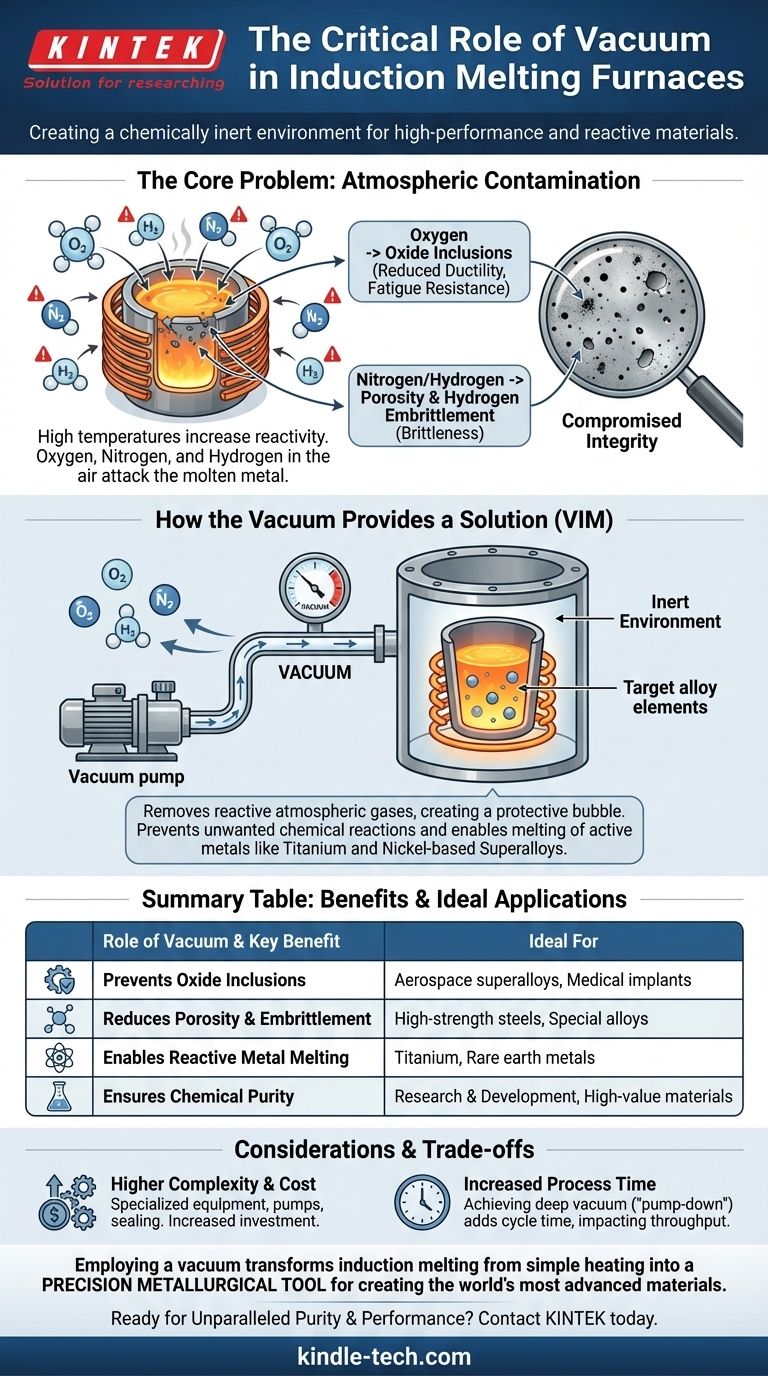
The Core Problem: Atmospheric Contamination at High Temperatures
When metals are heated to their melting point, their atoms become incredibly energetic and are primed to react with any available elements. The air we breathe is a rich source of these reactive elements, posing a significant threat to metallurgical quality.
The Impact of Oxygen
Oxygen is highly reactive with most molten metals. This reaction forms oxides, which are essentially microscopic ceramic particles or films within the metal structure.
These non-metallic inclusions act as stress points, significantly reducing the alloy's ductility, fatigue resistance, and overall strength.
The Threat of Nitrogen and Hydrogen
Gases like nitrogen and hydrogen can dissolve into the molten metal. As the metal cools and solidifies, the solubility of these gases decreases sharply.
This forces the trapped gases out of solution, creating internal porosity (tiny bubbles) or leading to a condition known as hydrogen embrittlement, which can make the finished material dangerously brittle.
How the Vacuum Provides a Complete Solution
A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace directly addresses the problem of atmospheric contamination by creating an environment that is nearly devoid of these harmful gases.
Creating a Controlled Environment
The vacuum system pumps the air out of the sealed furnace chamber before melting begins. This process removes the primary source of oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases.
This protective "bubble" ensures that the only elements present are those intentionally included in the alloy's recipe.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
By eliminating contact with atmospheric gases, the vacuum furnace prevents the formation of the oxide and nitride inclusions that degrade mechanical properties.
This is absolutely critical for materials where purity is paramount, such as in aerospace superalloys or medical implants.
Enabling the Melting of Active Metals
Some of the most advanced materials, such as titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and rare earth metals, have an extremely high affinity for oxygen.
Melting these materials in the open air is impossible, as they would be contaminated instantly. The vacuum environment is the only practical way to melt and cast them successfully.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly effective, VIM technology is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not the default solution for all melting operations.
Higher Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive than their atmospheric counterparts. They require robust vacuum chambers, high-performance pumps, and precise sealing mechanisms, all of which add to the initial investment and maintenance costs.
Increased Process Time
Achieving a deep vacuum (a process known as "pump-down") takes time. This can extend the overall cycle time for each melt compared to a simple air-melt furnace, impacting throughput.
When a Vacuum is Overkill
For many common, less-reactive materials like standard carbon steels or certain aluminum alloys, the benefits of a vacuum do not justify the added cost and complexity. An atmospheric or protective gas furnace is often a more economical and efficient choice for these applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the material's properties and the required quality of the final product.
- If your primary focus is high-performance superalloys for aerospace or power generation: A vacuum is non-negotiable to eliminate oxide inclusions and ensure maximum mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is melting reactive metals like titanium or rare earths: A vacuum is the only method that can prevent immediate and catastrophic contamination from the atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is producing ultra-high purity metals or special steels for research: The vacuum environment is essential for achieving precise chemical compositions and removing dissolved gases.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose casting of non-reactive ferrous and non-ferrous alloys: A standard air-melt or controlled-atmosphere furnace is almost always the more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, employing a vacuum transforms induction melting from a simple heating process into a precision metallurgical tool for creating the world's most advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Role of Vacuum | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Removes Oxygen | Prevents oxide inclusions | Aerospace superalloys, medical implants |
| Eliminates Nitrogen/Hydrogen | Reduces porosity & embrittlement | High-strength steels, special alloys |
| Creates Inert Environment | Enables melting of reactive metals | Titanium, rare earth metals |
| Ensures Chemical Purity | Achieves precise alloy composition | Research & development, high-value materials |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and performance in your metal melting process?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces designed for high-performance alloys and reactive metals. Our solutions help you eliminate contamination, improve material integrity, and meet the most demanding specifications.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our expertise can support your specific metallurgical challenges. Let's transform your melting process into a precision tool for creating superior materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















