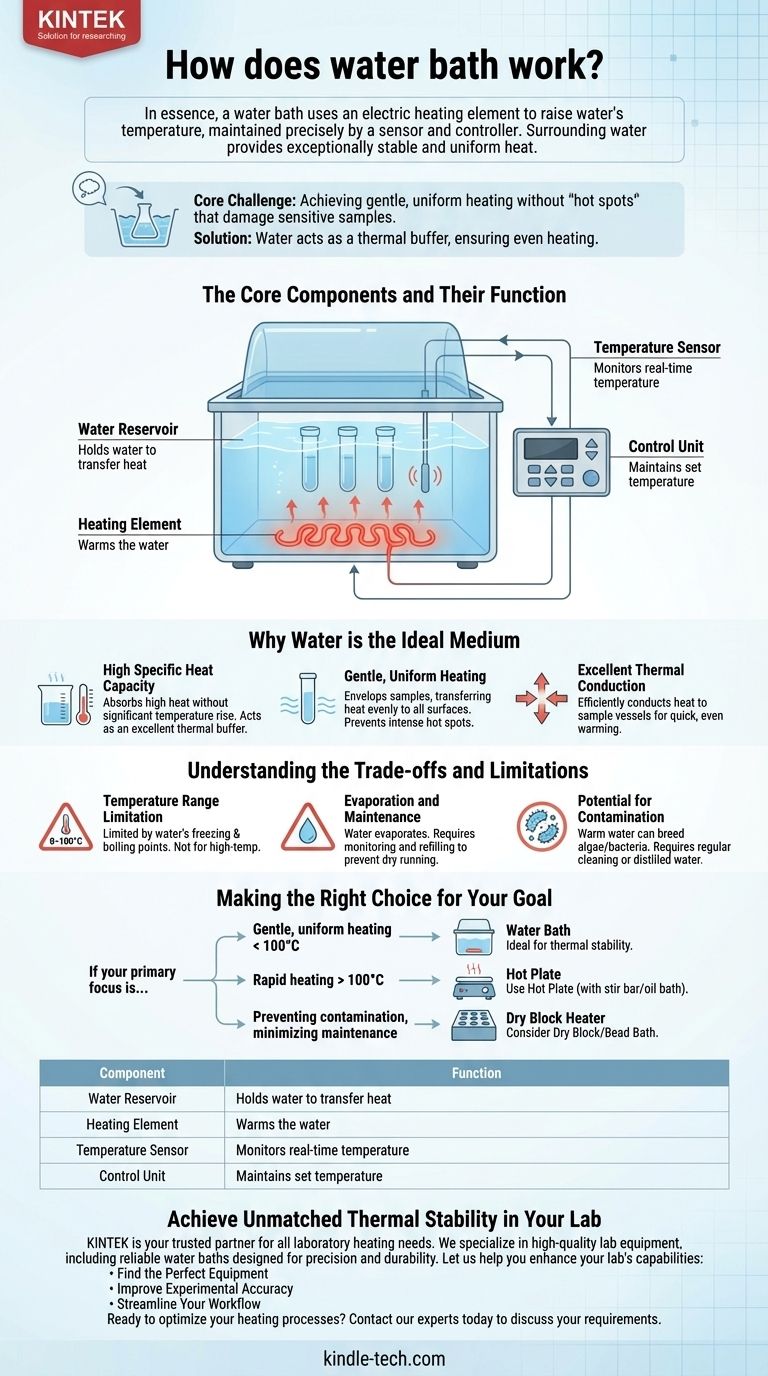
In essence, a water bath works by using an electric heating element to raise the temperature of a water-filled reservoir to a user-defined setpoint. A temperature sensor and controller then work together to maintain this temperature with high precision. The surrounding water provides exceptionally stable and uniform heat to any samples immersed within it, making it a cornerstone tool in scientific labs.
The core challenge in many lab procedures is achieving gentle, uniform heating without creating "hot spots" that can damage sensitive samples. A water bath masterfully solves this by using water as a thermal buffer, ensuring that samples are heated evenly from all sides at a precisely controlled temperature.

The Core Components and Their Function
A water bath's design is simple yet highly effective. It combines a few key parts to create a stable thermal environment.
The Water Reservoir
The main body is a stainless steel or plastic basin designed to hold water. This water serves as the medium for transferring heat from the heating element to the samples.
The Heating Element
Typically located at the bottom of the reservoir, an immersion heater converts electrical energy into heat. This element is responsible for initially warming the water to the desired temperature.
The Temperature Sensor
A sensor, such as a thermistor or thermocouple, is submerged in the water. It continuously measures the real-time temperature of the water and feeds this information back to the control unit.
The Control Unit
This is the brain of the device. The user sets a target temperature on a digital or analog interface. The control unit constantly compares the sensor's reading to this setpoint and cycles the heating element on and off to maintain the target temperature with minimal fluctuation.
Why Water is the Ideal Medium
The choice of water is not accidental; its physical properties make it uniquely suited for this application.
High Specific Heat Capacity
Water has a very high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb a large amount of heat energy without a significant increase in its own temperature. This property makes it an excellent thermal buffer, smoothing out temperature fluctuations from the heating element and providing superior stability.
Gentle, Uniform Heating
Unlike a hot plate that creates an intense hot spot at the point of contact, a water bath envelops the sample container. This ensures that heat is transferred gently and uniformly to all surfaces, which is critical for temperature-sensitive enzymes, cell cultures, or chemical reactions.
Excellent Thermal Conduction
Water efficiently conducts heat to the immersed sample vessels (e.g., test tubes, flasks, or beakers), ensuring the contents quickly and evenly reach the target temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly useful, a water bath is not the perfect solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Temperature Range Limitation
A standard water bath is fundamentally limited by the freezing and boiling points of water. Its effective operating range is typically from a few degrees above ambient temperature to just below 100°C (212°F). It cannot be used for high-temperature applications.
Evaporation and Maintenance
The water in the bath will evaporate over time, especially at higher temperatures. This requires users to regularly monitor the water level and refill it to prevent the heating element from running dry. Using a lid can reduce but not eliminate evaporation.
Potential for Contamination
Standing, warm water is an ideal breeding ground for algae, fungi, and bacteria. Without regular cleaning and changing of the water, this can become a source of contamination for your experiments. Some labs use distilled water or add algaecides to mitigate this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating device depends entirely on your experimental needs.
- If your primary focus is gentle, uniform heating of samples below 100°C: A water bath is the ideal choice due to its unparalleled thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating a solution or you require temperatures above 100°C: A hot plate, often paired with a stir bar or an oil bath for better distribution, is the more appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination and minimizing maintenance: Consider alternatives like a dry block heater or a bead bath, which provide a similar function without using water.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the precise tool for achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Water Reservoir | Holds water to transfer heat to samples. |
| Heating Element | Warms the water to the desired temperature. |
| Temperature Sensor | Monitors the water temperature in real-time. |
| Control Unit | Maintains the set temperature with high precision. |
Achieve Unmatched Thermal Stability in Your Lab
Does your research require precise, uniform heating for sensitive samples like enzymes or cell cultures? The gentle, consistent heat of a water bath is essential for reliable, repeatable results.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory heating needs. We specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable water baths designed for precision and durability.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities:
- Find the Perfect Equipment: Get expert guidance on selecting the right water bath for your specific applications.
- Improve Experimental Accuracy: Ensure your samples are heated uniformly without hot spots.
- Streamline Your Workflow: With the right tools, achieve consistent results batch after batch.
Ready to optimize your heating processes? Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- Why are constant temperature water baths used in refractory testing? Accelerate MgO Hydration & Binder Evaluation
- What is the primary role of a constant temperature water bath in biomass washing? Optimize Poplar Pretreatment.
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath? Ensure Reliable Dental Resin Conversion Rates
- Why is a constant temperature water bath necessary for evaluating corrosion inhibitors? Ensure Precise Thermal Control
- What is the importance of an automatic temperature control circulation device? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data



















