In short, a high-quality black PVD coating is exceptionally durable. It provides a hard, wear-resistant surface that significantly enhances a product's resistance to scratches, abrasion, and corrosion. However, its ultimate lifespan is not a fixed value; it depends heavily on the specific type of PVD coating applied, the quality of the application process, and the hardness of the base material it is protecting.
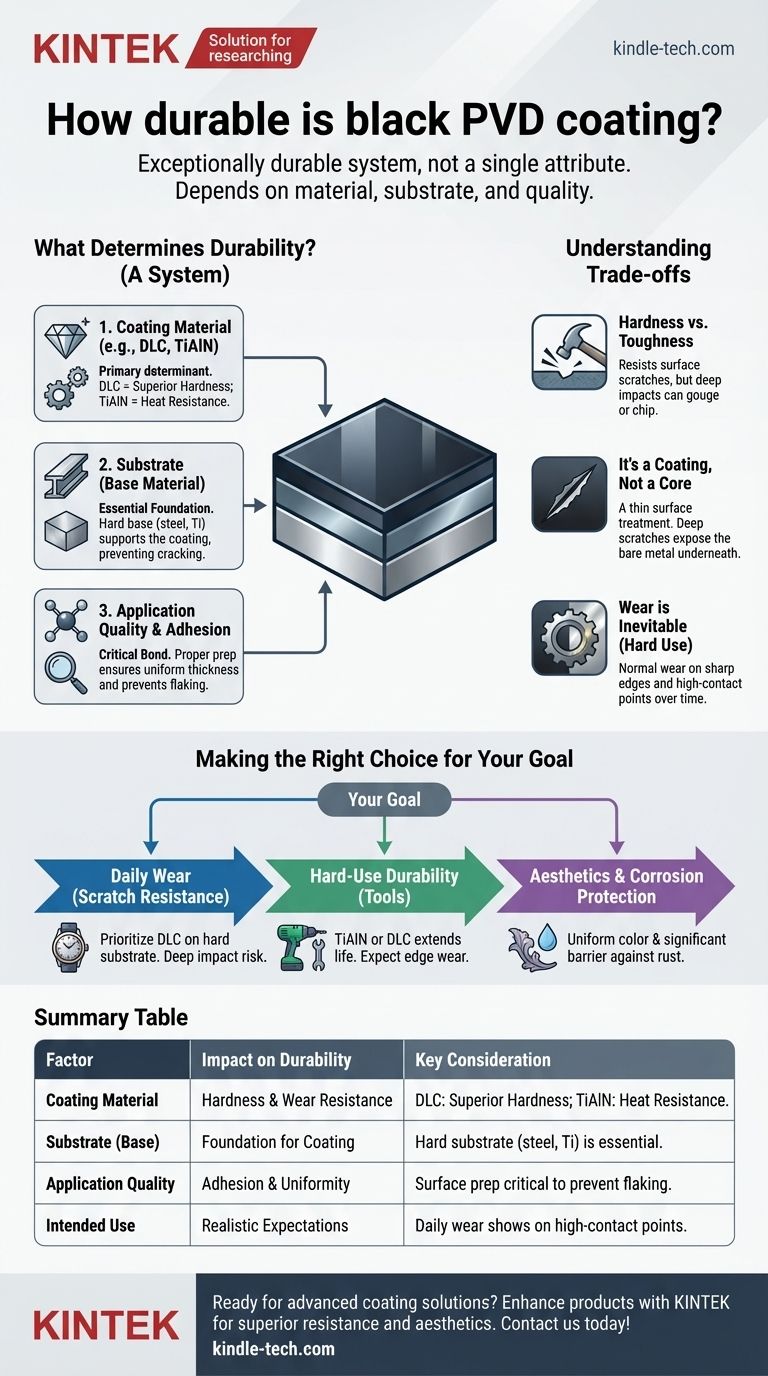
The durability of a black PVD coating is not a single attribute but the result of a system. Its real-world performance depends less on the "PVD" label and more on the specific coating material used (like DLC or TiAlN), the quality of its application, and the hardness of the underlying substrate.

What Determines PVD Durability?
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a process, not a single material. The "durability" you experience comes from a combination of factors that work together. Understanding these factors is key to judging the quality of a PVD finish.
The Specific Coating Material
Not all black PVD coatings are created equal. The material deposited onto the surface is the primary determinant of its properties.
For black finishes, two common high-performance materials are:
- Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN): This creates a slick, very hard surface with excellent heat resistance, often appearing as a matte black or dark graphite gray. It is a workhorse coating for industrial tools.
- Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC): This is one of the hardest and most wear-resistant coatings available. DLC provides superior hardness and a low coefficient of friction (making it very slick), which is ideal for high-end watches, firearm components, and medical implants.
The Substrate (Base Material)
The material underneath the coating is just as important as the coating itself. A hard PVD coating on a soft base material offers limited protection.
Think of it like a thin layer of hard ice over soft mud. The ice can resist a light scratch, but any significant pressure will push the ice down into the mud, causing it to crack and fail. A hard coating on a hard substrate (like stainless steel or titanium) provides a stable foundation, making the entire component far more resistant to damage.
Coating Thickness and Adhesion
The bond between the PVD coating and the substrate is critical. A perfectly hard coating is useless if it flakes off. Proper surface preparation before the PVD process is essential to ensure maximum adhesion.
While a thicker coating can offer more wear life, there is a point of diminishing returns. An excessively thick coating can become brittle and more prone to chipping. Quality application focuses on an optimal, uniform thickness with an unbreakable bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Even the best PVD coatings have limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging where they might fall short.
Hardness vs. Toughness
PVD coatings are extremely hard, which means they excel at resisting surface-level scratches and abrasion. However, they are not infinitely tough.
A sharp, deep impact from a hard object can still create a gouge that penetrates the coating. The PVD layer itself may even chip at the point of impact if the force is great enough.
It's a Coating, Not a Core Material
This is the most important concept to grasp. A PVD coating is a surface treatment, typically only a few microns thick.
If a scratch is deep enough to go through the PVD layer, it will expose the bare metal underneath. The coating will not "heal," and the damage will be visible. Its purpose is to prevent the thousands of micro-scratches that cause a finish to look dull and worn over time.
Wear is Inevitable with Hard Use
On items subject to constant metal-on-metal contact or extreme abrasion (like industrial tools or the bracelet clasp of a daily-worn watch), the PVD coating will eventually show wear on sharp edges and corners. This is a normal part of its lifecycle, not a sign of a defective coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your evaluation of a PVD-coated product should align with its intended use and your expectations for its appearance over time.
- If your primary focus is maximum scratch resistance for daily wear (e.g., a luxury watch): Prioritize a DLC coating on a hard substrate like stainless steel or titanium, and be aware that deep impacts can still cause damage.
- If your primary focus is hard-use durability (e.g., tools, certain components): A well-applied TiAlN or DLC coating will drastically extend the usable life and performance, but you should expect signs of wear to appear on high-contact points over time.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and corrosion protection: Nearly any professionally applied PVD coating will provide a durable, uniform color and a significant barrier against rust and chemical damage.
Ultimately, a well-executed PVD coating is a significant functional upgrade, not merely a cosmetic finish.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Durability | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Material | Primary determinant of hardness and wear resistance. | DLC offers superior hardness; TiAlN provides excellent heat resistance. |
| Base Material (Substrate) | Provides the foundation for the coating. | A hard substrate (e.g., steel, titanium) is essential for optimal performance. |
| Application Quality | Ensures strong adhesion and uniform thickness. | Proper surface preparation is critical to prevent flaking or chipping. |
| Intended Use | Defines realistic expectations for wear over time. | Daily-worn items will show wear on high-contact points; this is normal. |
Ready to enhance your products with a durable, high-performance finish?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced coating solutions for laboratory equipment, tools, and precision components. Our expertise ensures your products benefit from superior scratch resistance, corrosion protection, and a long-lasting aesthetic appeal.
Let our experts help you select the ideal PVD coating for your specific needs. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project and request a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















