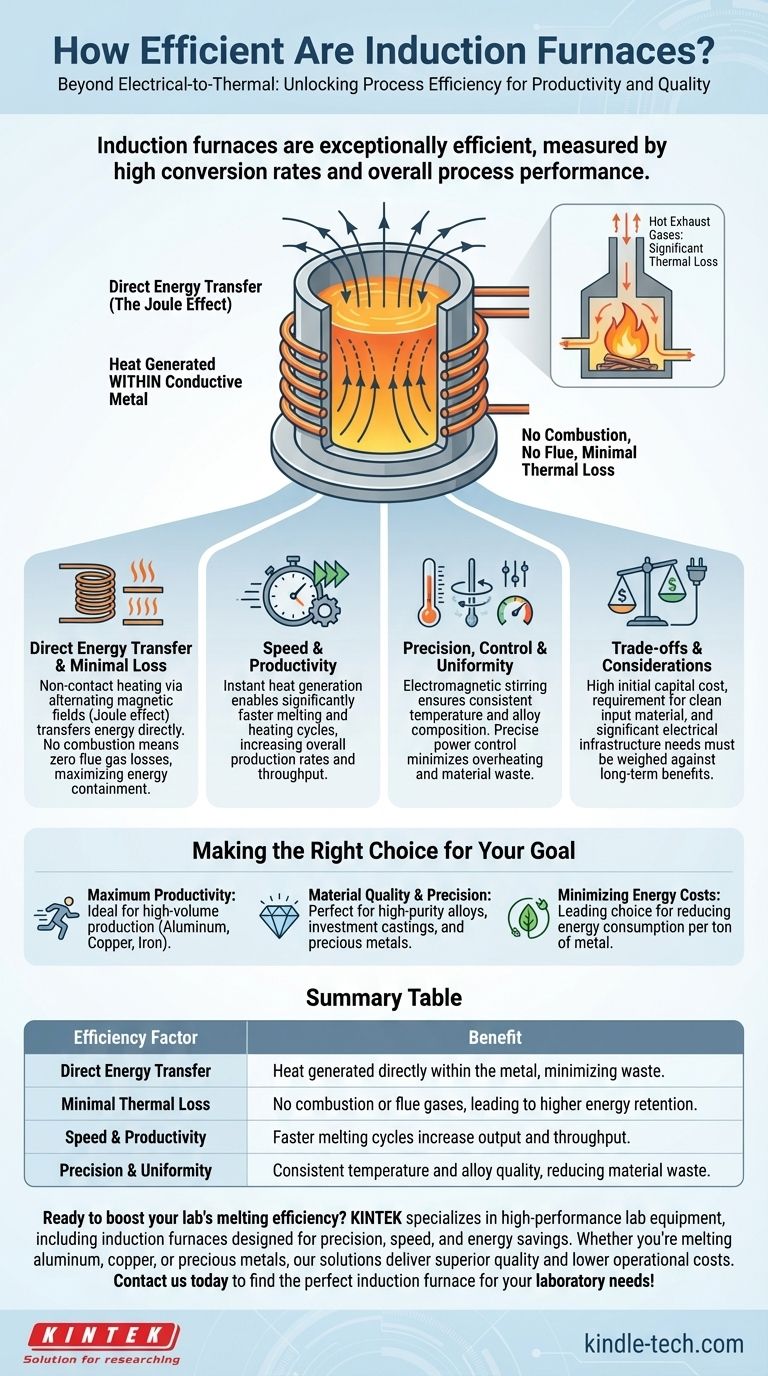
Induction furnaces are exceptionally efficient, but their true value is measured in two distinct ways. First is their high electrical-to-thermal conversion rate, and second is their overall process efficiency, which dramatically boosts productivity, speed, and material quality in a way traditional furnaces cannot match.
The true efficiency of an induction furnace is not just about its high electrical-to-thermal energy conversion. It's about the combination of speed, precise control, and minimal energy loss, which translates directly into higher productivity, better material quality, and lower operational costs per unit produced.
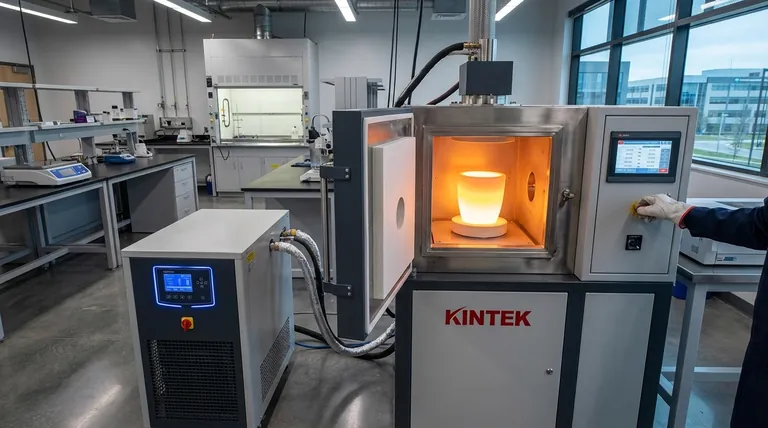

The Pillars of Induction Furnace Efficiency
To understand why induction furnaces are a superior choice for many applications, you must look beyond a single efficiency number and analyze the principles that drive their performance.
Direct Energy Transfer (The Joule Effect)
Unlike fuel-fired furnaces that heat a chamber and rely on radiant heat and convection, an induction furnace generates heat directly within the conductive metal itself.
This process, known as the Joule effect, is triggered by a powerful, alternating magnetic field. It is a form of non-contact heating, meaning energy is transferred directly to the workpiece with minimal waste. Think of it as the industrial equivalent of a microwave, which heats the food directly, rather than a conventional oven, which must first heat all the air inside it.
Minimal Thermal Loss
Traditional combustion furnaces lose a significant amount of energy as hot exhaust gases vented through a flue. This is a fundamental inefficiency of burning fuel for heat.
Induction furnaces have no combustion and no flue, so this primary source of heat loss is eliminated entirely. The main avenues for energy loss are through thermal radiation from the molten metal's surface and minor electrical losses in the coil, making it a much more contained and efficient system.
Speed and Productivity
The ability to generate heat instantly and directly within the metal leads to significantly faster melting and heating cycles.
For businesses with high production demands, this speed is a direct component of efficiency. Faster cycles mean more batches can be processed in the same amount of time, increasing overall production rates and allowing companies to fulfill orders more quickly.
Precision, Control, and Uniformity
The electromagnetic field that heats the metal also creates a natural stirring effect. This ensures the molten bath has a consistent temperature and chemical composition, leading to higher-quality, uniform alloys.
Furthermore, the power to the induction coil can be controlled with extreme precision. This allows for exact temperature management, preventing overheating, reducing the loss of valuable alloy elements through oxidation, and minimizing rejected parts. This level of control reduces material waste, which is a critical form of process efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, induction furnaces are not the universal solution for every metal heating application. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging their limitations.
High Initial Capital Cost
The technology behind induction furnaces, including the power supply and copper coils, typically results in a higher upfront investment compared to simpler cupola or reverb furnaces. The long-term savings in energy, material, and productivity must be weighed against this initial cost.
Reliance on Input Material Quality
Induction furnaces are primarily melters, not refiners. They are less tolerant of dirt, oil, and excessive slag on the charge material. Using unclean scrap can lead to inconsistent melt quality and damage to the furnace lining, requiring more rigorous material sorting and cleaning processes.
Electrical Infrastructure Requirements
These are powerful machines that place a significant demand on a facility's electrical grid. Installing an induction furnace may require a substantial upgrade to the site's power supply, which must be factored into the total project cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an induction furnace should be based on your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum productivity and speed: The rapid heating cycles of induction furnaces offer a decisive advantage for high-volume production of materials like aluminum, copper, and iron.
- If your primary focus is material quality and precision: The uniform heating and precise temperature control are ideal for creating high-purity alloys, investment castings, and working with precious metals.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term energy costs: The high electrical-to-thermal conversion efficiency makes induction a leading choice for reducing energy consumption per ton of metal melted.
Ultimately, choosing an induction furnace is an investment in a faster, more controlled, and more energy-conscious manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Efficiency Factor | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Direct Energy Transfer | Heat generated directly within the metal, minimizing waste |
| Minimal Thermal Loss | No combustion or flue gases, leading to higher energy retention |
| Speed & Productivity | Faster melting cycles increase output and throughput |
| Precision & Uniformity | Consistent temperature and alloy quality, reducing material waste |
Ready to boost your lab's melting efficiency? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for precision, speed, and energy savings. Whether you're melting aluminum, copper, or precious metals, our solutions deliver superior quality and lower operational costs. Contact us today to find the perfect induction furnace for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















