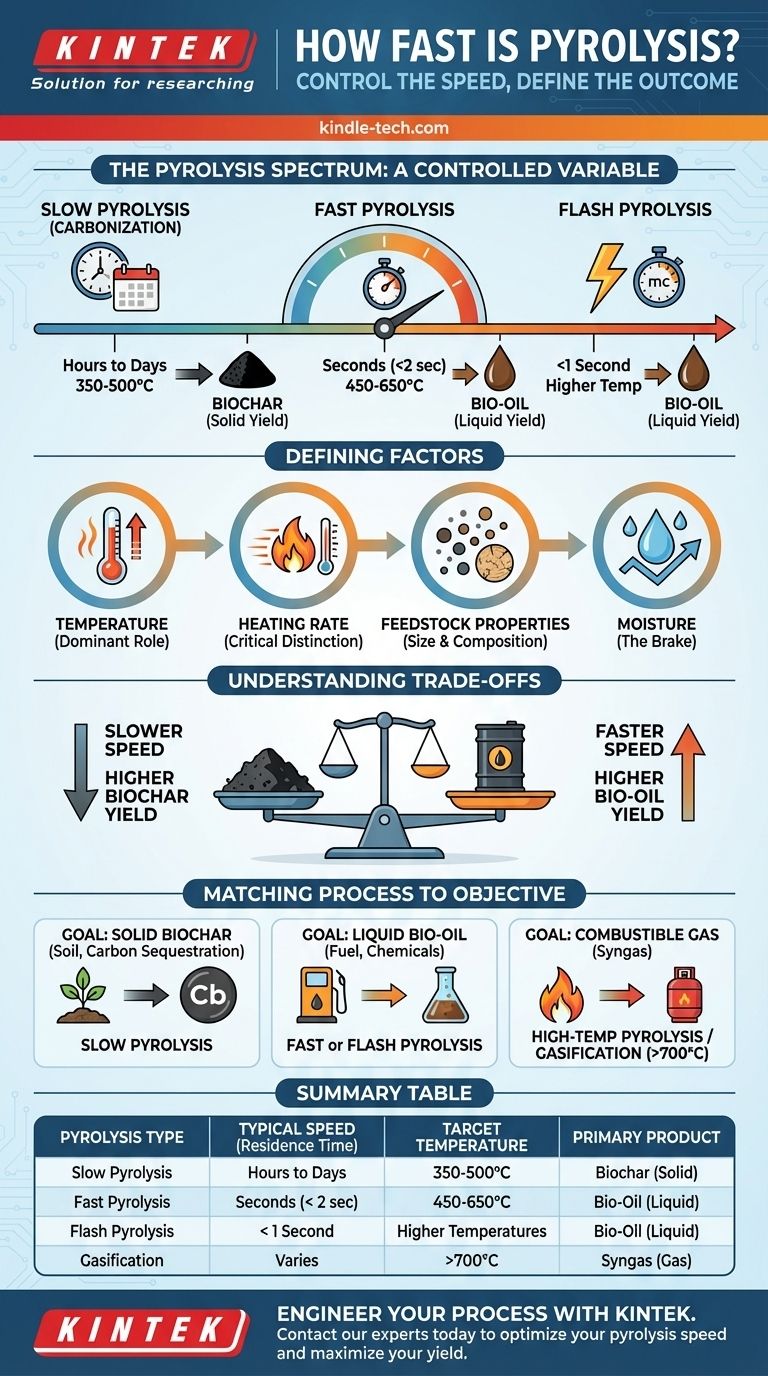
The speed of pyrolysis is not a single value but a highly controlled process variable, with reaction times ranging from less than a second to several days. The rate is deliberately engineered based on the feedstock being used and, most importantly, the desired end product—whether it be solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible gas.
The question isn't "how fast is pyrolysis?" but rather "how fast should my pyrolysis process be to achieve a specific goal?" The speed is dictated by temperature and heating rate, which are adjusted to optimize the yield of either solid, liquid, or gas products.

The Defining Factors of Pyrolysis Speed
To understand the rate of pyrolysis, you must first understand the variables that control it. The "speed" is a result of chemical kinetics, heat transfer, and mass transfer working in concert.
The Dominant Role of Temperature
At its core, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material in the absence of oxygen. Like most chemical reactions, its rate is exponentially dependent on temperature.
Higher temperatures provide more energy to break chemical bonds, dramatically accelerating the decomposition reactions.
Heating Rate: The Critical Distinction
The heating rate—how quickly the feedstock is brought to the target pyrolysis temperature—is the most important factor distinguishing different pyrolysis modes.
A high heating rate ensures the material passes quickly through lower temperature ranges where char-forming reactions dominate. This is crucial for maximizing liquid yields.
Feedstock Properties: Size and Composition
The physical and chemical nature of the input material, or feedstock, directly impacts the overall process time.
Particle size is a primary bottleneck. Heat must travel from the particle's surface to its core. Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, enabling significantly faster and more uniform heating.
Composition also matters. Organic materials like biomass are composed of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin, each of which decomposes at different temperatures and rates.
The Impact of Moisture
Any water present in the feedstock must be evaporated before the material's temperature can rise to the point of pyrolysis.
This drying phase consumes significant energy and time, acting as a major brake on the overall process speed. Pre-drying the feedstock is a common and critical step in many operations.
Three Speeds for Three Different Goals
Engineers have developed distinct pyrolysis regimes, each defined by its speed and temperature, to target the production of a specific product.
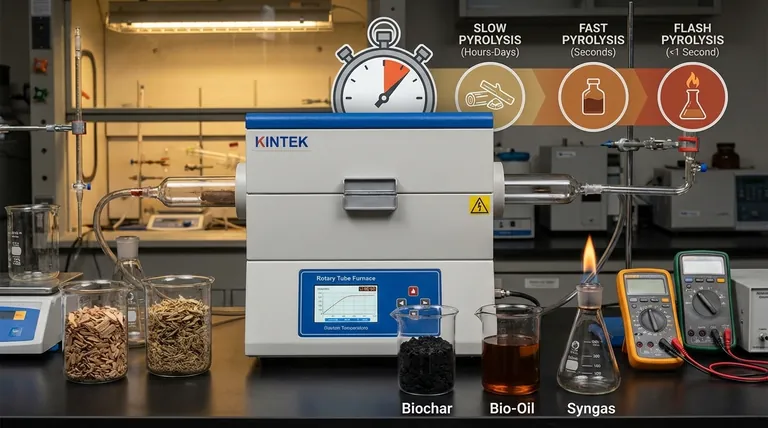
Slow Pyrolysis (Carbonization): Hours to Days
This process uses low temperatures (around 350-500°C) and very slow heating rates. The residence time of the solid material in the reactor can be many hours or even days.
The goal here is to maximize the yield of the solid product, biochar. The slow process favors secondary char-forming reactions.
Fast Pyrolysis: A Matter of Seconds
Fast pyrolysis uses moderate temperatures (around 450-650°C) but demands extremely high heating rates.
The feedstock is heated to the target temperature in a fraction of a second. The resulting vapors are then rapidly cooled (quenched) to prevent further reactions. The total vapor residence time is typically less than 2 seconds. This entire process is engineered to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
Flash Pyrolysis: Less Than a Second
This is an even more extreme version of fast pyrolysis, often using higher temperatures and even faster heating rates.
The goal is the same—to maximize liquid bio-oil—by minimizing the time the vapors spend in the hot reaction zone. The vapor residence time is often less than one second.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis speed is an engineering decision with direct consequences for product distribution, operational complexity, and cost.
Speed vs. Product Yield
There is an inverse relationship between process speed and biochar yield.
Slower processes allow for char-forming reactions to occur, maximizing the solid output. Faster processes with rapid quenching are designed to "freeze" the reaction at the liquid intermediate stage, maximizing bio-oil.
The Heat Transfer Bottleneck
Achieving the high heating rates required for fast pyrolysis is a significant engineering challenge. It is the primary limiting factor.
This is why fast pyrolysis reactors often use very fine feedstock particles (e.g., <1-2 mm) and sophisticated designs like fluidized beds or ablative reactors to ensure heat gets into the material almost instantaneously.
Process Complexity and Cost
Generally, faster processes require more complex and expensive equipment. A simple batch kiln for slow pyrolysis (charcoal production) is far less complex than a continuously operating circulating fluidized bed reactor for fast pyrolysis.
Matching the Process to Your Objective
The optimal pyrolysis speed is determined entirely by your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating solid biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: You need a slow pyrolysis process with a residence time of hours to days.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid bio-oil as a renewable fuel or chemical precursor: You must use a fast or flash pyrolysis process with a residence time of seconds.
- If your primary focus is generating a combustible gas (syngas): You should look toward high-temperature pyrolysis or gasification, where temperatures exceed 700°C to favor the cracking of all tars into permanent gases.
Ultimately, controlling the speed of pyrolysis is the key to controlling the outcome of the process.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Typical Speed (Residence Time) | Target Temperature | Primary Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Hours to Days | 350-500°C | Biochar (Solid) |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Seconds (< 2 sec) | 450-650°C | Bio-Oil (Liquid) |
| Flash Pyrolysis | < 1 Second | Higher Temperatures | Bio-Oil (Liquid) |
| Gasification | Varies | >700°C | Syngas (Gas) |
Ready to Engineer Your Pyrolysis Process?
Choosing the right speed and temperature is critical to achieving your product goals, whether it's high-yield biochar for carbon sequestration or liquid bio-oil for renewable fuel. The right laboratory equipment is essential for R&D and process optimization.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. From precise temperature-controlled furnaces to reactor systems, we provide the reliable tools you need to scale your process from the lab to production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application. Let us help you select the ideal equipment to optimize your pyrolysis speed and maximize your product yield.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the factors affecting the yield of bio-oil from the pyrolysis of coconut shell? Control 4 Key Parameters
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies



















