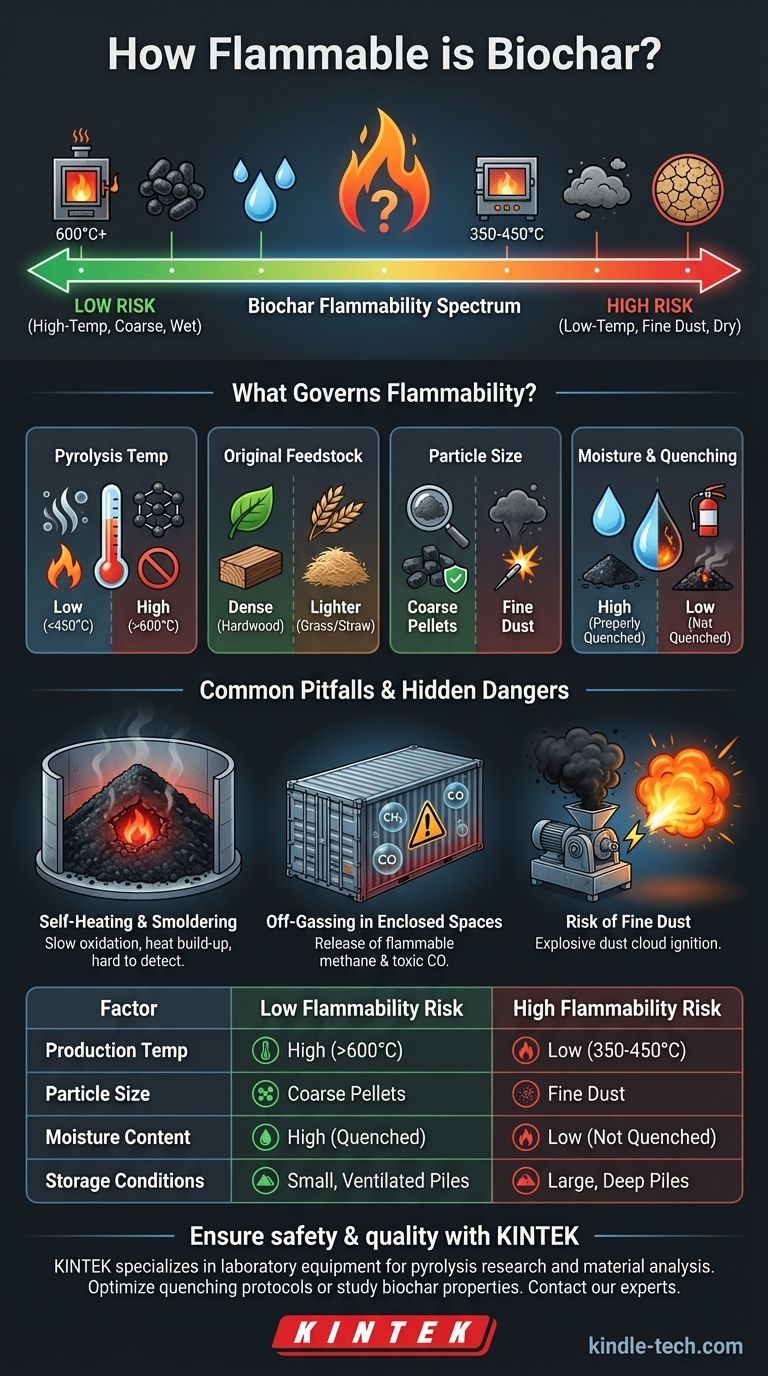
Contrary to what its appearance suggests, biochar’s flammability is not straightforward and varies dramatically based on how it was produced and is currently handled. While it is generally less flammable than the raw biomass it came from (like wood chips), it can still pose a significant fire risk through both open flame ignition and, more insidiously, slow, smoldering combustion. The primary danger often lies in retained volatile gases and the potential for self-heating in large piles.
Biochar's fire risk is not a fixed property but a spectrum. The key to safety is understanding that its flammability is dictated by its production temperature and particle size, with the most significant hidden danger being smoldering combustion in storage, not just open flames.

What Governs Biochar's Flammability?
The fire risk associated with a specific batch of biochar is a direct result of its chemical and physical properties. Four key factors determine its propensity to ignite and burn.
The Role of Pyrolysis Temperature
The temperature at which biochar is created is the single most important factor.
Low-temperature biochars (produced around 350-450°C) do not fully drive off all volatile organic compounds. These residual gases make the char easier to ignite and capable of sustaining a flame.
High-temperature biochars (produced above 600°C) have very little volatile matter remaining. They are more structurally similar to pure carbon or graphite, making them much more difficult to ignite.
Impact of Original Feedstock
The type of biomass used influences the final product's structure.
Biochars made from dense materials like hardwoods tend to be less reactive. Those made from lighter materials like grasses or straw can be fluffier and have more surface area, potentially increasing their reactivity.
Particle Size and Surface Area
This is a critical factor, especially concerning dust.
A pile of coarse biochar pellets has limited oxygen exposure. However, fine biochar dust has an enormous surface area-to-volume ratio, allowing it to react with oxygen in the air very rapidly. A cloud of biochar dust can be explosive if it encounters an ignition source.
Moisture Content and Quenching
Properly "quenched" or cooled biochar is essential for safety.
If biochar is not fully cooled with water or by restricting oxygen after production, it can retain embers deep within its pores. These hidden hot spots can lead to re-ignition hours or even days later. A high moisture content, however, will make the biochar very difficult to ignite.
Common Pitfalls and Hidden Dangers
Understanding the obvious risk of a flame is easy. The more complex dangers of biochar require a deeper understanding of its behavior, especially in storage.
The Danger of Self-Heating and Smoldering
This is the most significant risk in bulk storage. Large, deep piles of biochar can self-insulate.
Slow oxidation at the center of the pile generates heat. If this heat cannot escape, the temperature builds in a runaway process, eventually leading to a smoldering fire that is extremely difficult to detect and extinguish.
Off-Gassing in Enclosed Spaces
Freshly produced biochar, particularly low-temperature varieties, can continue to release gases for some time after production.
These gases can include flammable methane (CH₄) and toxic carbon monoxide (CO). In a poorly ventilated, enclosed space like a silo or a sealed shipping container, these gases can accumulate to dangerous or even explosive levels.
The Risk of Fine Dust
Never underestimate the danger of dust. Many industrial accidents are caused by dust explosions.
Activities that generate dust, such as transport, grinding, or bagging, create the highest risk. All it takes is a static discharge or a spark from machinery to ignite a suspended dust cloud with devastating force.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Managing biochar's flammability is about aligning your safety protocols with your specific use case.
- If you are a producer: Your primary focus is ensuring complete and thorough quenching to eliminate all internal embers before storage or transport.
- If you are storing biochar in bulk: Your primary focus must be preventing self-heating by keeping piles small, allowing for ventilation, and monitoring for temperature increases.
- If you are a home user or gardener: Your primary focus is simple fire safety—store it away from ignition sources in a dry, contained environment and handle it in a way that minimizes dust.
By understanding the factors that influence its behavior, you can confidently manage the risks and unlock the full benefits of biochar.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Low Flammability Risk | High Flammability Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Production Temperature | High (>600°C) | Low (350-450°C) |
| Particle Size | Coarse Pellets | Fine Dust |
| Moisture Content | High (Properly Quenched) | Low (Not Quenched) |
| Storage Conditions | Small, Ventilated Piles | Large, Deep Piles |
Ensure the safety and quality of your biochar processes. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and material analysis. Whether you are a producer needing to optimize quenching protocols or a researcher studying biochar properties, our solutions can help. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how we can support your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the carbon footprint of diamond mining? Uncovering the True Environmental and Ethical Cost
- What causes sputtering when accelerating? Fix Engine Hesitation and Misfires
- What is the importance of sintering? Unlock Strength, Density, and Complex Part Production
- What is the number 1 rule of soldering? Master the Heat for Strong, Reliable Connections
- How is argon ionized in sputtering? The Key to Igniting a Stable Plasma
- What is the target substrate distance for sputtering? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is magnetron plasma? A Guide to High-Efficiency Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of XRF? Understanding Its Limits for Accurate Elemental Analysis



















