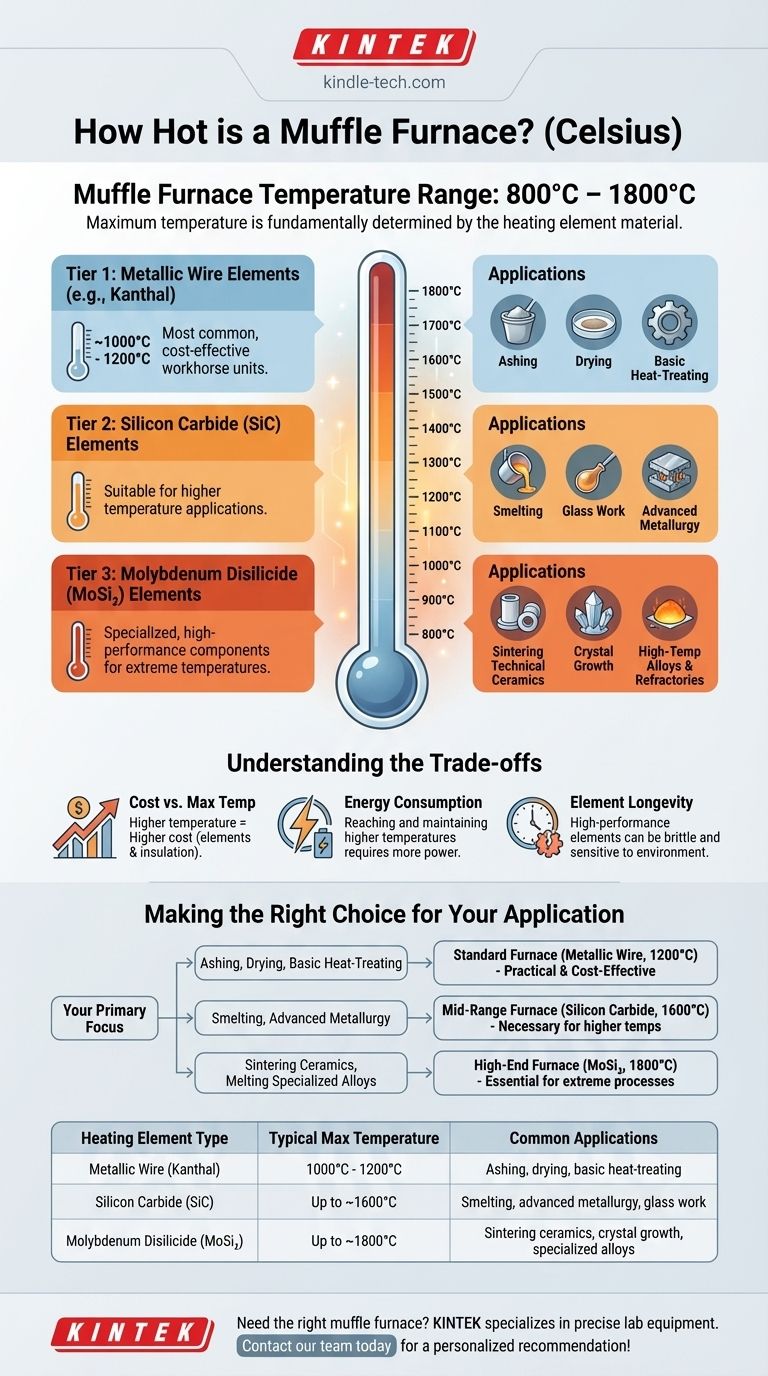
A typical muffle furnace operates within a broad temperature range, generally from 800°C to as high as 1800°C. However, the maximum temperature a specific furnace can achieve is not a single standard value. It is fundamentally determined by the materials used in its heating elements.
The critical takeaway is that a muffle furnace's temperature capability is defined by its construction. Common models reach 1100-1200°C, while specialized units with advanced heating elements are required to reach 1600°C or 1800°C.

Why Muffle Furnace Temperatures Vary So Widely
Understanding the temperature range of muffle furnaces means looking at their core components. The material used for the heating element is the single most important factor dictating the unit's maximum safe operating temperature.
The Role of the Heating Element
The heating element is the component that converts electrical energy into heat. Different materials have different physical limits for how hot they can get before degrading or failing, which creates distinct tiers of furnace performance.
Tier 1: Metallic Wire Elements (~1000°C - 1200°C)
The most common and cost-effective muffle furnaces use heating elements made from metallic wire, such as Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminium alloy).
These are workhorse units ideal for many standard laboratory applications like ashing, drying, and basic heat-treating of metals. Most general-purpose lab furnaces fall into this category.
Tier 2: Silicon Carbide Elements (~1600°C)
For applications requiring higher temperatures, furnaces are equipped with silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements.
These elements can operate at much higher temperatures than metallic wire, making them suitable for some smelting operations, glass work, and more demanding metallurgical processes.
Tier 3: Molybdenum Disilicide Elements (~1800°C)
The highest temperature range is achieved with molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements.
These are specialized, high-performance components designed for extreme temperature applications. This includes sintering technical ceramics, growing crystals, and working with high-temperature alloys and refractory materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a muffle furnace isn't just about picking the highest temperature. Higher performance capabilities come with significant trade-offs in cost, complexity, and operational requirements.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its price. The advanced materials in high-temperature elements and the required supporting insulation are significantly more expensive.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining 1800°C requires substantially more electrical power than holding 1100°C. The energy cost of operating a high-temperature furnace is a critical factor for any facility.
Element Longevity and Atmosphere
High-performance elements like silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide can be more brittle and sensitive to their operating environment than standard metallic wire. Their lifespan can be affected by rapid heating/cooling cycles or specific atmospheric conditions within the chamber.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific thermal processing goal.
- If your primary focus is ashing, sample drying, or basic metal heat-treating: A standard furnace with metallic wire elements capable of 1100°C to 1200°C is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is smelting common metals or advanced metallurgy: A mid-range furnace with silicon carbide elements reaching up to 1600°C is necessary.
- If your primary focus is sintering high-performance ceramics or melting specialized alloys: You must invest in a high-end furnace with molybdenum disilicide elements that can safely achieve 1800°C.
Ultimately, selecting the right muffle furnace is about choosing the precise tool required for your specific high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Typical Max Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (e.g., Kanthal) | 1000°C - 1200°C | Ashing, drying, basic heat-treating |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to ~1600°C | Smelting, advanced metallurgy, glass work |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to ~1800°C | Sintering ceramics, crystal growth, specialized alloys |
Need the right muffle furnace for your specific temperature requirements?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need. Whether your application requires a standard 1200°C furnace for ashing or a high-temperature 1800°C unit for advanced ceramics, our experts can help you select the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
Contact our team today to discuss your thermal processing needs and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the muffle furnace method? A Guide to Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- How do you adjust the temperature on a muffle furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab
- What is the principle of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Precise High-Temperature Heating
- How do you maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- What is the range of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Temperature for Your Lab



















