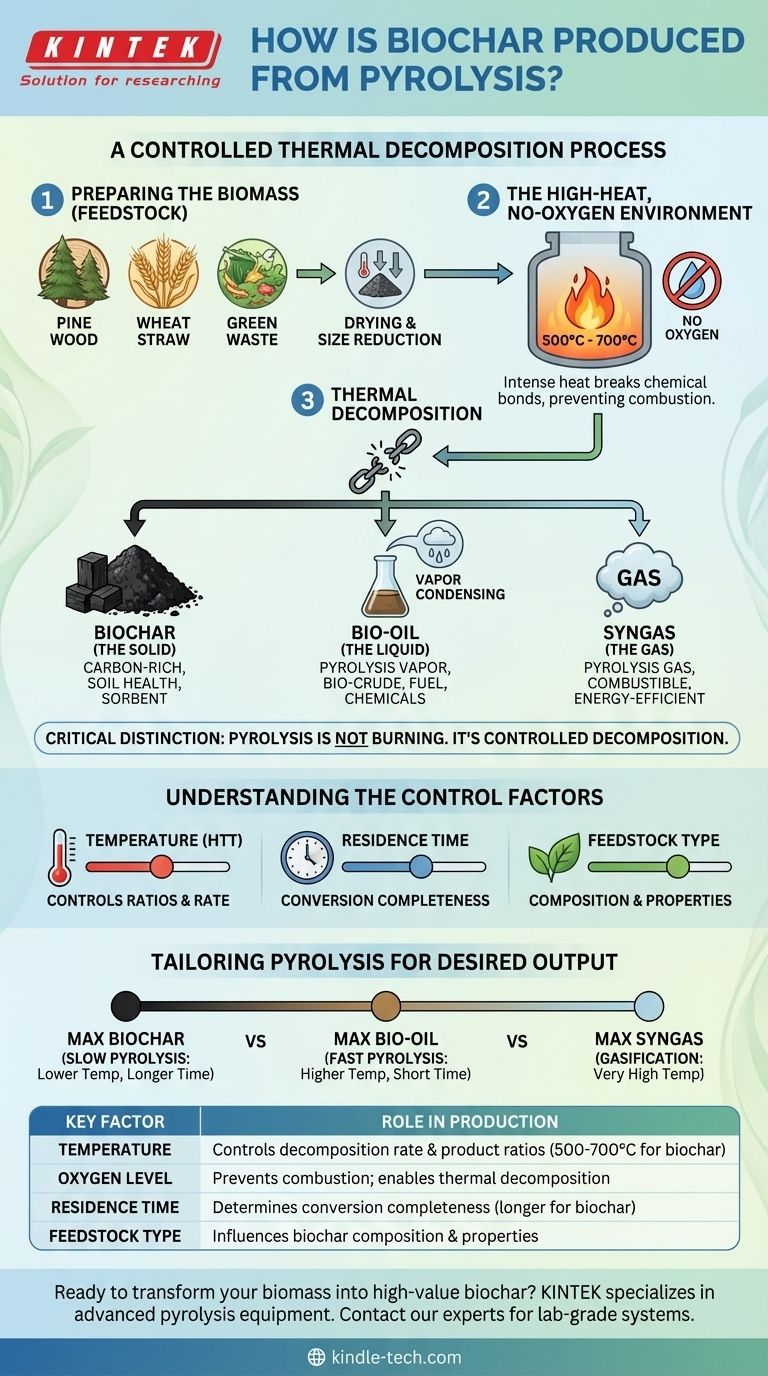
To produce biochar, pyrolysis involves heating organic material, known as biomass, to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen. This lack of oxygen prevents the material from combusting (burning) and instead causes it to thermally decompose into a solid, carbon-rich material (biochar), along with a liquid (bio-oil) and a gas (syngas).
The critical distinction to understand is that pyrolysis is not burning. It is a controlled thermal decomposition process that deconstructs biomass into its core components by intentionally starving it of oxygen, which fundamentally changes the chemical outcome.

The Core Mechanism of Pyrolysis
To understand how biochar is made, it's essential to visualize the process as a series of controlled steps designed to break down organic matter into stable, valuable products.
Step 1: Preparing the Biomass (Feedstock)
The process begins with organic material, or feedstock. This can be a wide range of materials.
Common feedstocks include pine wood, wheat straw, agricultural green waste, and even dried algae. The type of feedstock significantly influences the final composition of the biochar.
Step 2: The High-Heat, No-Oxygen Environment
The prepared biomass is fed into a reactor which is then sealed to create an oxygen-free environment.
Inside the reactor, the material is heated rapidly to high temperatures, typically between 500°C and 700°C. This combination of high heat and no oxygen is the defining condition of pyrolysis.
Step 3: Thermal Decomposition
The intense heat breaks the chemical bonds within the biomass, causing it to break down into three distinct outputs.
These products are a solid char, vapors, and non-condensable gases. Because combustion is prevented, the carbon in the biomass remains as a stable, solid structure.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis doesn't just produce biochar; it creates a trio of useful substances. The precise ratio of these products depends on the process conditions.
Biochar (The Solid)
This is the solid, black, carbon-rich material left behind in the reactor. It is also referred to as char or coke.
Biochar is highly valued in agriculture for its ability to improve soil health and as a sorbent for environmental remediation.
Bio-oil (The Liquid)
During decomposition, a significant portion of the biomass turns into hot pyrolysis vapor.
When these vapors are captured, cooled, and condensed, they form a liquid known as bio-crude or pyrolysis oil. This liquid can be used as an alternative fuel or refined into other valuable chemicals.
Syngas (The Gas)
The remaining output is a mix of non-condensable gases, often called pyrolysis gas or syngas.
This gas is combustible and is typically captured and used to provide the heat energy for the pyrolysis plant itself, making the entire process more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Control Factors
The final output of the pyrolysis process is not accidental. Operators can precisely control the conditions to favor the production of one product over another.
The Role of Temperature
The highest treatment temperature (HTT) is a primary control lever. Different temperatures will break down the biomass in different ways, altering the ratio of char, oil, and gas produced.
The Impact of Residence Time
Residence time—how long the biomass is held at the target temperature—is another critical variable. Longer residence times can lead to a more complete conversion and affect the final properties of the biochar.
The Feedstock Determines the Outcome
The starting material matters. A woody biomass like pine will yield a different set of products compared to a lighter material like wheat straw or nutrient-dense algae under the exact same process conditions.
Tailoring Pyrolysis for Your Desired Output
By adjusting these key variables, the pyrolysis process can be optimized to meet specific goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar yield: You would typically use a "slow pyrolysis" process, which involves lower temperatures and longer residence times to preserve the solid carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil production: A "fast pyrolysis" process is preferred, using higher temperatures and very short residence times to rapidly vaporize the biomass before it converts fully to char.
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas production: You would use extremely high temperatures in a process known as gasification, which is designed to convert as much of the biomass as possible into gaseous fuel.
Understanding these principles allows you to transform diverse organic materials into specifically engineered and highly valuable products.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Biochar Production |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Controls decomposition rate and product ratios (typically 500-700°C for biochar) |
| Oxygen Level | Prevents combustion; enables thermal decomposition (oxygen-free environment) |
| Residence Time | Determines conversion completeness (longer times favor biochar yield) |
| Feedstock Type | Influences biochar composition and properties (e.g., wood vs. agricultural waste) |
Ready to transform your biomass into high-value biochar? KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis equipment tailored for laboratory and research needs. Whether you're optimizing for biochar yield, bio-oil, or syngas production, our solutions ensure precise temperature control, efficiency, and reliable performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab-grade pyrolysis systems can accelerate your sustainable material research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















