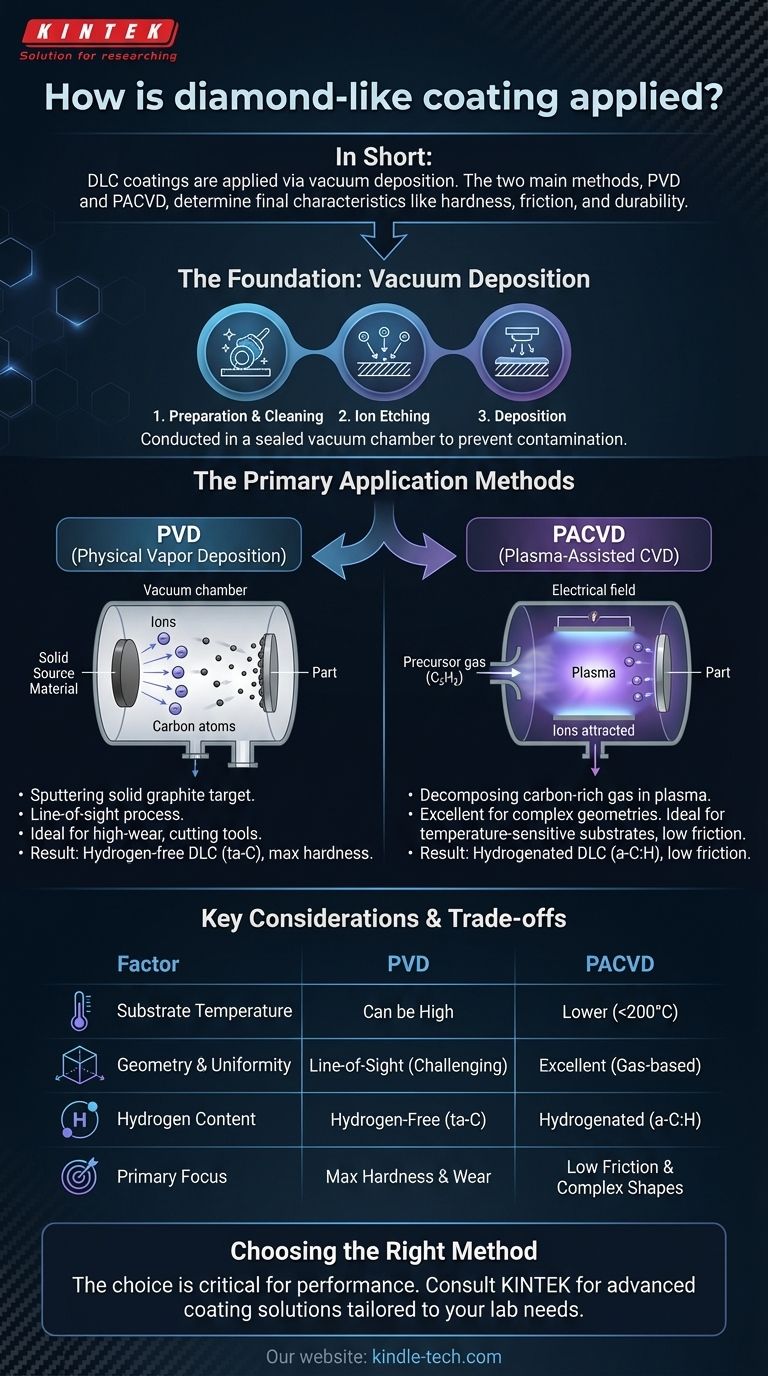
In short, Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings are applied using highly controlled vacuum deposition technologies. The two principal methods are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), where a solid carbon source is vaporized, and Plasma-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (PACVD), where a carbon-containing gas is decomposed in a plasma to build the film. The choice of method is critical as it directly determines the coating's final characteristics.
Understanding the application process is not just a technical curiosity; it is the key to specifying a coating with the right hardness, friction, and durability for your specific goal. The method chosen dictates the properties you get.
The Foundation of DLC Application: Vacuum Deposition
All professional DLC application methods take place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is non-negotiable and serves as the foundation for creating a high-quality, durable coating.
Why a Vacuum is Essential
A vacuum environment removes atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. These molecules would otherwise contaminate the coating, creating weak points and preventing proper adhesion to the part's surface (the substrate).
Creating a vacuum allows for a pure, high-energy process where individual atoms and ions can be precisely controlled and directed onto the substrate to form a dense, uniform film.
The Three Core Stages of Deposition
Regardless of the specific technology used, the process follows three fundamental steps:
- Preparation & Cleaning: The parts are meticulously cleaned to remove all oils, debris, and oxides. This is often the most critical step for ensuring the coating will adhere properly.
- Ion Etching: Inside the vacuum chamber, the part is bombarded with ions (typically Argon). This microscopic "sandblasting" removes any remaining surface contaminants at an atomic level and slightly roughens the surface to promote strong mechanical bonding.
- Deposition: This is the coating stage itself, where the specific PVD or PACVD process is used to grow the DLC film atom by atom onto the substrate.
The Primary Application Methods Explained
The "deposition" stage is where the methods diverge. The choice between PVD and PACVD depends entirely on the desired coating properties and the nature of the part being coated.
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
In PVD processes, a solid source material (a target, usually made of graphite) is converted into a vapor that physically travels to and condenses on the substrate.
The most common PVD method for DLC is sputtering. Here, the graphite target is bombarded by high-energy ions, which knock carbon atoms loose. These "sputtered" atoms then travel across the chamber and deposit onto the parts, forming the coating.
PACVD (Plasma-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition)
In PACVD, there is no solid target. Instead, a carbon-rich precursor gas (like acetylene, C₂H₂) is introduced into the vacuum chamber.
An electrical field is used to ignite a plasma, which is an energized state of gas. This plasma breaks the precursor gas molecules apart, creating reactive carbon and hydrogen ions. A negative voltage applied to the part accelerates these ions toward it, where they combine on the surface to build the DLC film.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
The decision to use PVD or PACVD is a technical one based on crucial trade-offs.
Substrate Temperature: The Critical Limiter
PACVD is generally a lower-temperature process, often performed below 200°C (392°F). This makes it ideal for temperature-sensitive materials like aluminum, certain tool steels, and even some polymers that would soften or distort at higher temperatures.
Some PVD processes can require significantly higher temperatures, limiting their use on materials that cannot withstand the heat without losing their engineered properties.
Component Geometry and Uniformity
Because PACVD uses a gas that fills the entire chamber, it is exceptionally good at coating complex shapes, internal bores, and intricate features with a uniform layer.
PVD is more of a line-of-sight process. While chamber fixtures rotate the parts to improve coverage, it can be challenging to uniformly coat deep pockets or hidden surfaces.
Hydrogen Content and Final Properties
The application method directly controls the coating's atomic structure. PACVD processes inherently incorporate hydrogen into the film, creating hydrogenated DLC (a-C:H). These films are known for having extremely low coefficients of friction, making them ideal for sliding components.
PVD methods like sputtering can produce hydrogen-free DLC (ta-C). These films are generally harder, denser, and more wear-resistant, making them better suited for cutting tools and high-impact applications.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
Selecting the correct application process is a matter of aligning the method's strengths with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A hydrogen-free PVD process is often the superior choice, provided the substrate can handle the processing temperature.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: The low-temperature nature of PACVD makes it the safest and most effective option.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lowest possible friction or coating a complex geometry: The gas-based approach and hydrogenated films of PACVD will deliver the best results.
By understanding how the application process dictates the final outcome, you can move beyond a generic request for "DLC" and specify the exact coating your project requires to succeed.
Summary Table:
| Application Method | Key Process | Ideal For | Key Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | Sputtering a solid graphite target | High-wear applications, cutting tools | Maximum hardness, wear resistance (Hydrogen-free DLC) |
| PACVD (Plasma-Assisted CVD) | Decomposing a carbon-rich gas (e.g., acetylene) in a plasma | Complex geometries, temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., aluminum), low friction needs | Excellent uniformity, low friction (Hydrogenated DLC), low-temperature process |
Specify the perfect DLC coating for your project's unique requirements. The choice between PVD and PACVD is critical for achieving the desired hardness, friction, and durability for your lab equipment or components. KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions for laboratory needs. Our experts will help you select the ideal process to enhance performance and longevity. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance








