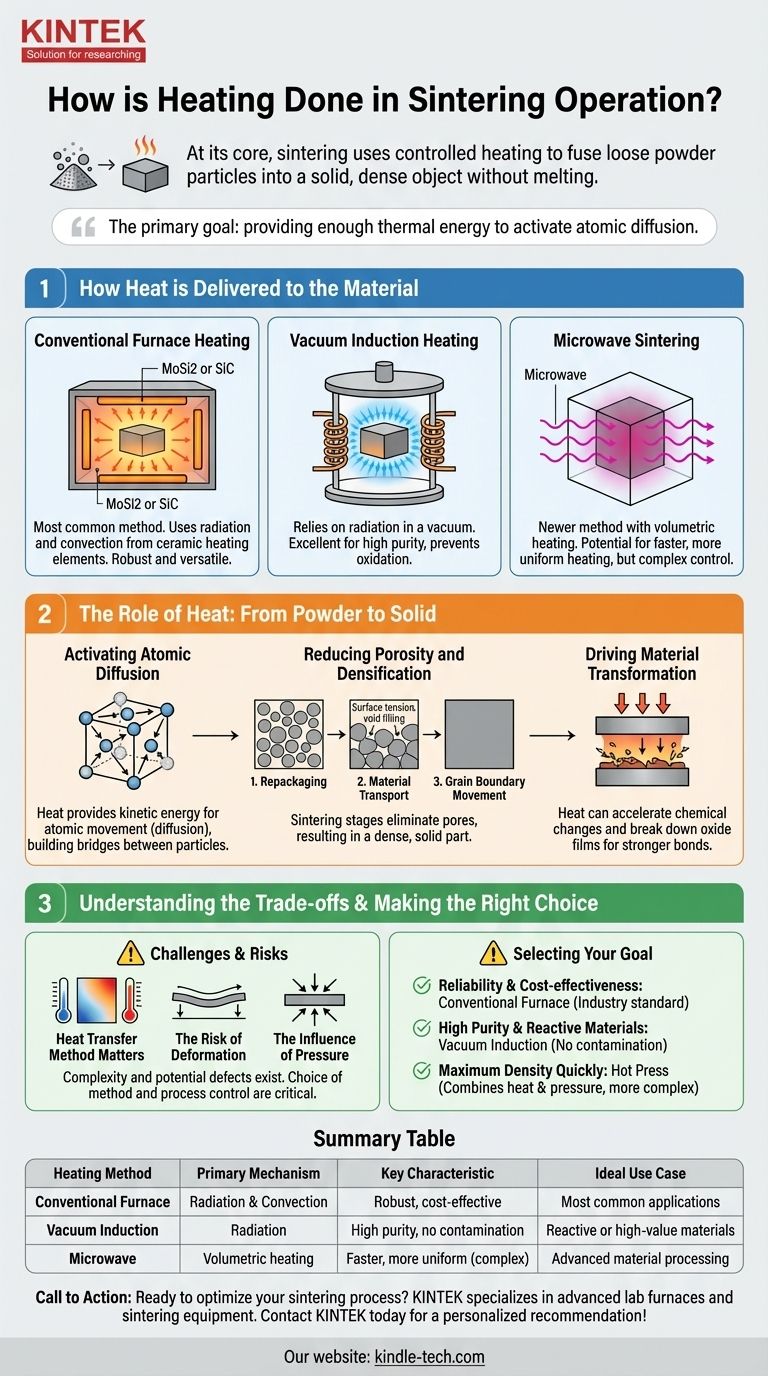
At its core, sintering uses controlled heating to fuse loose powder particles into a solid, dense object without melting the material. The most common heating methods rely on radiation and convection from ceramic heating elements, while more specialized processes use vacuum induction or microwaves to deliver the necessary thermal energy.
The specific heating method is secondary to the primary goal: providing enough thermal energy to activate atomic diffusion. This process allows atoms from individual particles to move and bond together, systematically eliminating the empty spaces between them and creating a solid mass.

How Heat is Delivered to the Material
Heating is the engine of the sintering process. The way this thermal energy is transferred to the powdered material is critical for achieving a uniform and dense final part.
Conventional Furnace Heating
The most widely used method involves placing the material inside a furnace equipped with high-temperature ceramic heating elements.
These elements, often made from materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or silicon carbide (SiC), become extremely hot and transfer heat to the part primarily through radiation and convection. This is a robust and well-understood method suitable for a vast range of materials.
Vacuum Induction Heating
In a vacuum environment, conventional heat transfer through air (convection) is not possible. Instead, vacuum induction sintering relies almost exclusively on radiation.
A heating module or coil surrounds the material without touching it. It radiates thermal energy directly onto the material's surface. This method is excellent for preventing oxidation or contamination, as the vacuum removes reactive gases.
Microwave Sintering
A newer and less common method is microwave sintering. Unlike conventional methods that heat from the outside-in, microwaves can penetrate the material and heat it more volumetrically. This has the potential for faster and more uniform heating, but it is a more complex technology to control.
The Role of Heat: From Powder to Solid
Applying heat does more than just make the material hot. It initiates a series of physical transformations at the atomic level that are responsible for turning a loose powder into a strong, solid component.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Heat provides the kinetic energy that allows atoms within the crystal structure to move. This atomic diffusion is the fundamental mechanism behind sintering. As atoms migrate, they move from particle to particle, effectively building bridges across the gaps.
Reducing Porosity and Densification
The initial powder compact is full of pores or empty spaces. The sintering process occurs in stages to eliminate this porosity.
First, particles repackage into a more tightly packed arrangement. Then, driven by surface tension, material transport occurs as atoms diffuse to fill the remaining voids. In the final stage, atoms move along grain boundaries to smooth and eliminate the last internal pores, resulting in a dense, solid part.
Driving Material Transformation
Heat can also enable or accelerate chemical and physical changes. For instance, in hot pressing, the combination of heat and pressure can break down stubborn oxide films on powder surfaces. This exposes pure metal, allowing for stronger bonds and greater final density.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While heating is essential, it also introduces complexities and potential for defects. The choice of method and control over the process are critical for success.
Heat Transfer Method Matters
The way heat enters the part is crucial. Surface heating from conventional furnaces can sometimes lead to temperature gradients, where the outside of the part is hotter than the inside. The selection of the heating module must be carefully matched to the material and part geometry to ensure even densification.
The Risk of Deformation
At sintering temperatures, the material is soft and malleable before it becomes fully dense. During this vulnerable stage, forces like gravity or friction can cause the part to warp, sag, or distort. Proper support within the furnace is essential to maintain the desired shape.
The Influence of Pressure
Processes like hot pressing introduce continuous pressure alongside heat. This is not traditional sintering. The external pressure actively forces particles together, which can accelerate densification but also creates different internal stresses and microstructures compared to pressureless sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heating method is not just about reaching a target temperature; it's about controlling the material's transformation to achieve a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is reliability and cost-effectiveness: A conventional furnace with ceramic heating elements is the industry standard and workhorse for most applications.
- If your primary focus is high purity or processing reactive materials: Vacuum induction sintering is superior, as it eliminates atmospheric contamination that could compromise the material.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density quickly: Combining heat with pressure in a hot press is an effective, though more complex, path to densification.
Ultimately, the heating method you choose is the tool you use to control the atomic-level journey from a loose powder to a finished, functional component.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Primary Mechanism | Key Characteristic | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Furnace | Radiation & Convection | Robust, cost-effective | Most common applications |
| Vacuum Induction | Radiation | High purity, no contamination | Reactive or high-value materials |
| Microwave | Volumetric heating | Faster, more uniform (complex) | Advanced material processing |
Ready to optimize your sintering process? The right heating method is critical for achieving the density, strength, and purity your materials require. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and sintering equipment, including vacuum and high-temperature solutions. Our experts can help you select the perfect system for your specific materials and goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength
- What is the sintering process of powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Durable Metal Parts
- What are the methods of brazing heating? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Needs



















