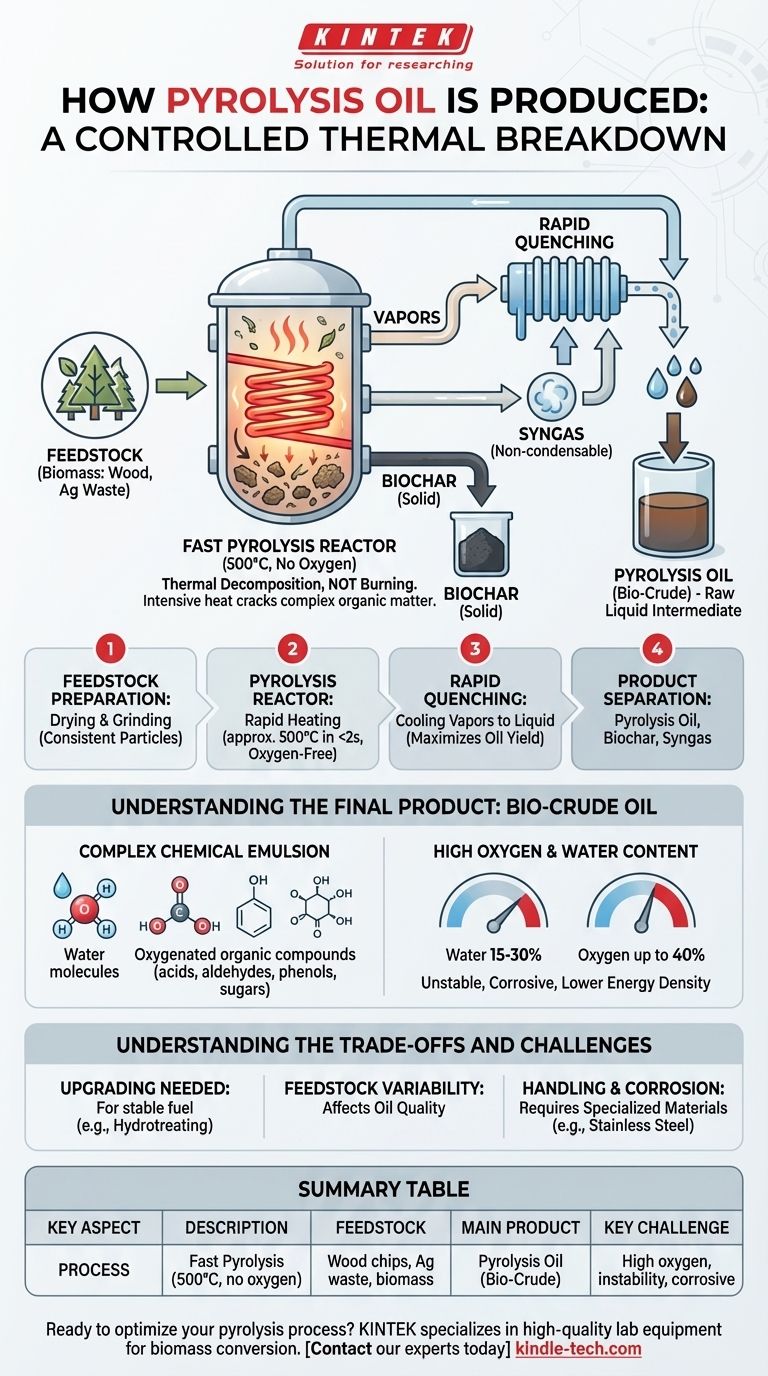
Pyrolysis oil is produced by rapidly heating organic materials, such as wood or agricultural waste, to around 500°C in the complete absence of oxygen. This process, known as fast pyrolysis, avoids combustion and instead thermally decomposes the biomass into vapors. These vapors are then rapidly cooled, or "quenched," to condense them into a liquid, which is the raw pyrolysis oil.
The core principle is thermal decomposition, not burning. By removing oxygen, intense heat cracks the complex organic matter into smaller, volatile compounds that are captured as a liquid, rather than being destroyed as smoke and ash.

The Core Principle: A Controlled Thermal Breakdown
The production of pyrolysis oil hinges on creating a very specific chemical environment: high heat with no oxygen. This forces the organic feedstock to break down in a way that is fundamentally different from combustion.
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of a material in an inert atmosphere. Without oxygen, the material cannot burn.
Instead, the intense heat breaks the long, complex chemical bonds within the biomass (like cellulose and lignin) into a mix of smaller, volatile molecules. This process yields three distinct products: the liquid pyrolysis oil (also called bio-oil or bio-crude), a solid char known as biochar, and non-condensable syngas.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
The process begins with biomass. This can be virtually any organic material, including wood chips, sawdust, corn stover, straw, or other agricultural residues.
The type and condition of the feedstock, particularly its moisture content, directly influence the efficiency of the process and the final composition of the oil.
The Key Stages of Production
Production is a multi-step engineering process that requires precise control.
- Feedstock Preparation: The biomass is first dried to reduce its moisture content and then ground into small, consistent particles to ensure rapid and uniform heating.
- The Pyrolysis Reactor: The prepared feedstock is fed into a reactor where it is heated to approximately 500°C (932°F) in under two seconds, all while in an oxygen-free environment.
- Rapid Quenching: The resulting hot vapor and aerosol mix is immediately and rapidly cooled. This "quenches" the chemical reactions, forcing the components to condense into a liquid before they can break down further. This step is critical for maximizing oil yield.
- Product Separation: Once condensed, the liquid pyrolysis oil is separated from the solid biochar and the syngas. The syngas is often recycled to provide the energy needed to heat the reactor, making the process more self-sustaining.
Understanding the Final Product: Bio-Crude Oil
It is crucial to understand that pyrolysis oil is not chemically equivalent to petroleum crude oil. It is a complex, raw intermediate with very different properties.
A Complex Chemical Emulsion
As the references note, pyrolysis oil is an emulsion of water and hundreds of different oxygenated organic compounds.
This mixture includes acids (like acetic acid), aldehydes, phenols, and sugars. This complex composition is a direct result of the incomplete breakdown of the original biomass.
High Oxygen and Water Content
Raw pyrolysis oil can contain a significant amount of water (15-30%) and a high concentration of oxygen (up to 40% by weight).
This high oxygen content makes the oil unstable, more corrosive, and gives it a lower energy density compared to conventional hydrocarbon fuels.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While pyrolysis is a powerful technology for converting waste to energy, the resulting oil presents several technical challenges that must be managed.
The Need for Upgrading
Due to its instability, acidity, and high oxygen content, raw pyrolysis oil cannot typically be used as a "drop-in" fuel in standard engines or refineries.
It often requires a secondary processing step called "upgrading," such as hydrotreating, to remove oxygen, reduce acidity, and improve its stability. This adds significant cost and complexity to the overall fuel production chain.
Feedstock Variability
The chemical makeup and quality of the final oil are highly dependent on the biomass used. An oil produced from hardwood will have a different composition and set of properties than one produced from straw.
This variability can be a challenge for applications that require a consistent fuel specification.
Handling and Corrosion Issues
The acidic nature of the oil (often with a pH between 2 and 3) means that it is corrosive to common construction materials like carbon steel.
Specialized stainless steel or plastic-lined pipes, pumps, and storage tanks are required for safe, long-term handling, which increases infrastructure costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The utility of pyrolysis oil depends entirely on how you intend to use it and whether you are prepared to handle its unique properties.
- If your primary focus is direct heat generation: Raw pyrolysis oil can serve as a substitute for fuel oil in specially designed industrial boilers and furnaces, but requires equipment built to resist its corrosive nature.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced biofuels: You must treat pyrolysis oil as an intermediate bio-crude that requires significant downstream upgrading to become a stable, high-grade fuel.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is a highly effective method for converting low-value, bulky biomass waste into a dense, transportable energy carrier and a valuable biochar co-product.
Ultimately, understanding the production process reveals that pyrolysis oil is a unique chemical intermediate, whose immense potential is unlocked by actively managing its challenging properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Fast Pyrolysis (500°C, no oxygen) |
| Feedstock | Wood chips, agricultural waste, biomass |
| Key Stages | Drying, grinding, rapid heating, quenching, separation |
| Main Product | Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-Crude) |
| Co-Products | Biochar and Syngas |
| Key Challenge | High oxygen content, instability, corrosive nature |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process or explore lab-scale pyrolysis systems? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research. Whether you're developing new pyrolysis reactors, analyzing bio-oil composition, or scaling up your process, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve precise and efficient results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















